Abstract
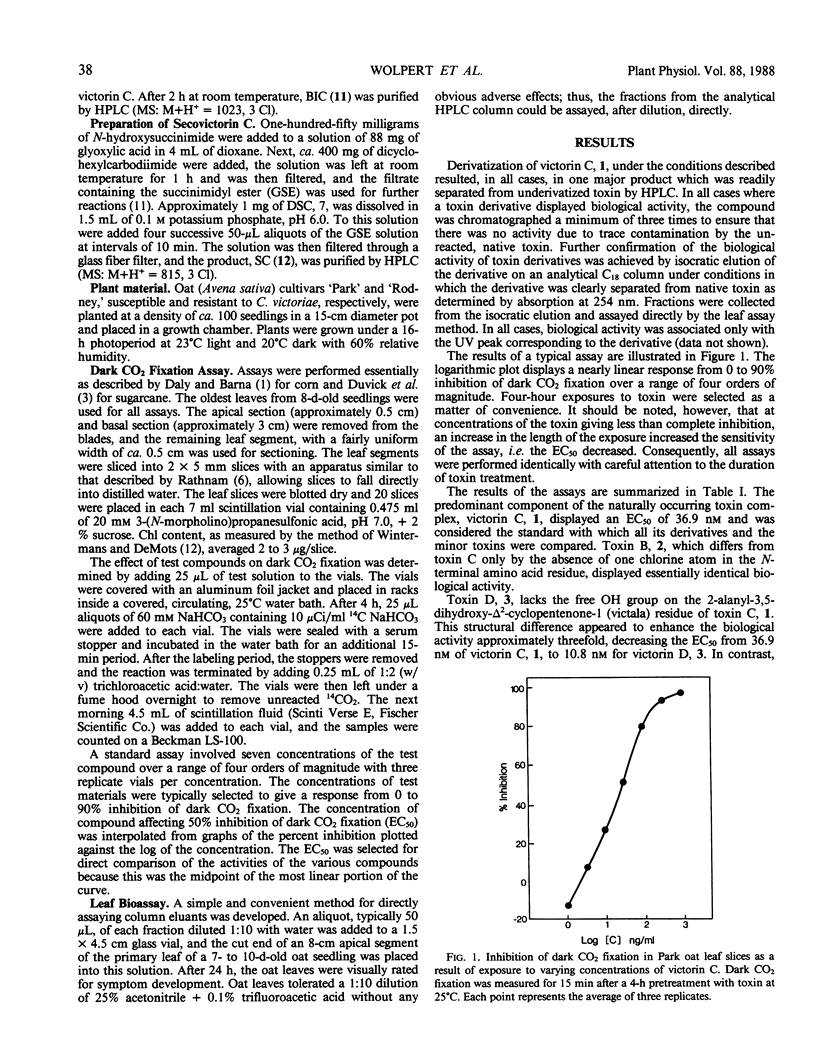
The structures of the toxins produced by Cochliobolus victoriae, victorin B, C, D, E, and victoricine, have recently been established. These toxins and modified forms of victorin C were tested for their effect on dark CO2 fixation in susceptible oat (Avena sativa) leaf slices. Half-maximal inhibition of dark CO2 fixation occurred with the native toxins in the range of 0.004 to 0.546 micromolar. An essential component for the inhibitory activity of victorin is the glyoxylic acid residue, particularly its hydrated aldehyde group. Removal of glyoxylic acid completely abolished the inhibitory activity of victorin, and the reduction of the aldehydo group transformed the toxin into a protectant. Conversion of victorin to its methyl ester resulted in diminution of inhibitory activity to 10% of the original activity of the toxin, whereas derivatization of the ε-amino group of the β-hydroxylysine moiety resulted in a decrease of inhibitory activity to 1% of that of victorin C. However, the derivatized toxin retained its host selectivity. In addition, the opening of the macrocyclic ring of the toxin drastically reduced the inhibitory activity.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Daly J. M., Barna B. A Differential Effect of Race T Toxin on Dark and Photosynthetic CO(2) Fixation by Thin Leaf Slices from Susceptible Corn. Plant Physiol. 1980 Oct;66(4):580–583. doi: 10.1104/pp.66.4.580. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duvick J. P., Daly J. M., Kratky Z., Macko V., Acklin W., Arigoni D. Biological Activity of the Isomeric Forms of Helminthosporium sacchari Toxin and of Homologs Produced in Culture. Plant Physiol. 1984 Jan;74(1):117–122. doi: 10.1104/pp.74.1.117. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macko K. A., Hodos W. Near point of accommodation in pigeons. Vision Res. 1985;25(10):1529–1530. doi: 10.1016/0042-6989(85)90232-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swack J. A., Zander G. L., Utter M. F. Use of avidin-sepharose to isolate and idenify biotin polypeptides from crude extracts. Anal Biochem. 1978 Jun 15;87(1):114–126. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(78)90575-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilchek M., Givol D. Haloacetyl derivatives. Methods Enzymol. 1977;46:153–157. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(77)46015-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wintermans J. F., de Mots A. Spectrophotometric characteristics of chlorophylls a and b and their pheophytins in ethanol. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1965 Nov 29;109(2):448–453. doi: 10.1016/0926-6585(65)90170-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


