Abstract
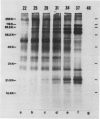
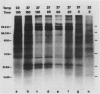
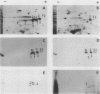
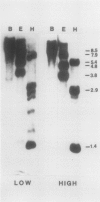
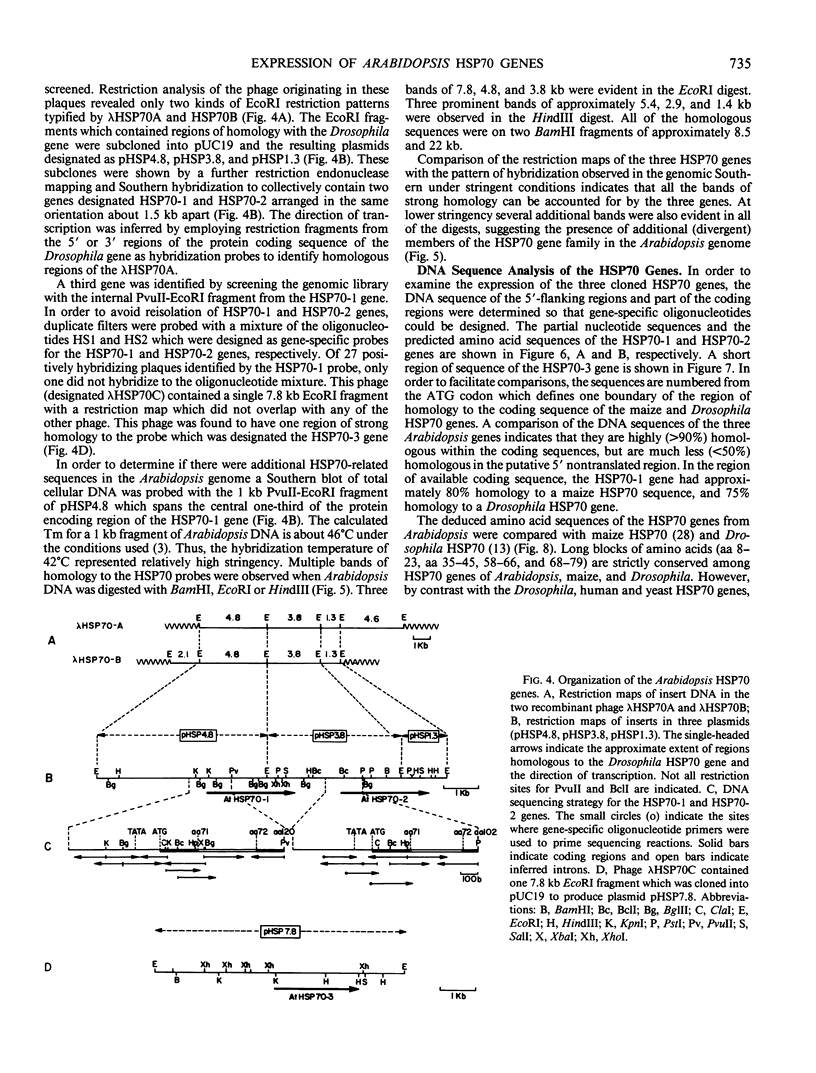
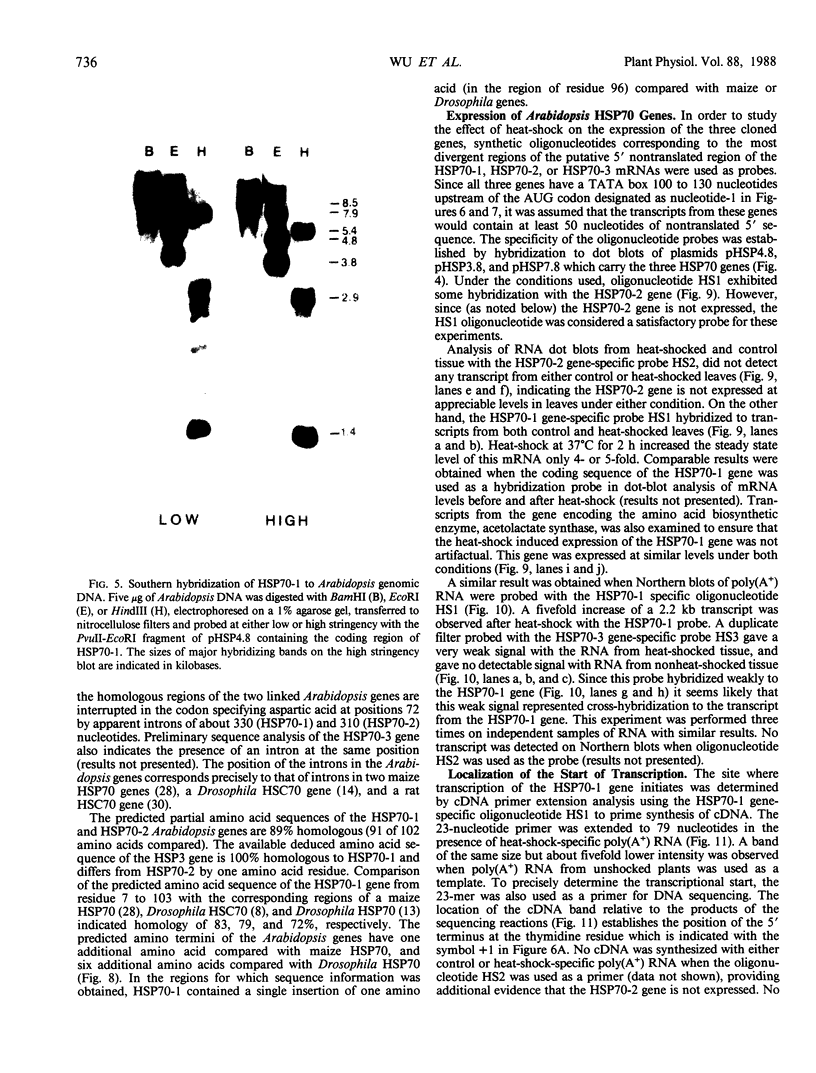
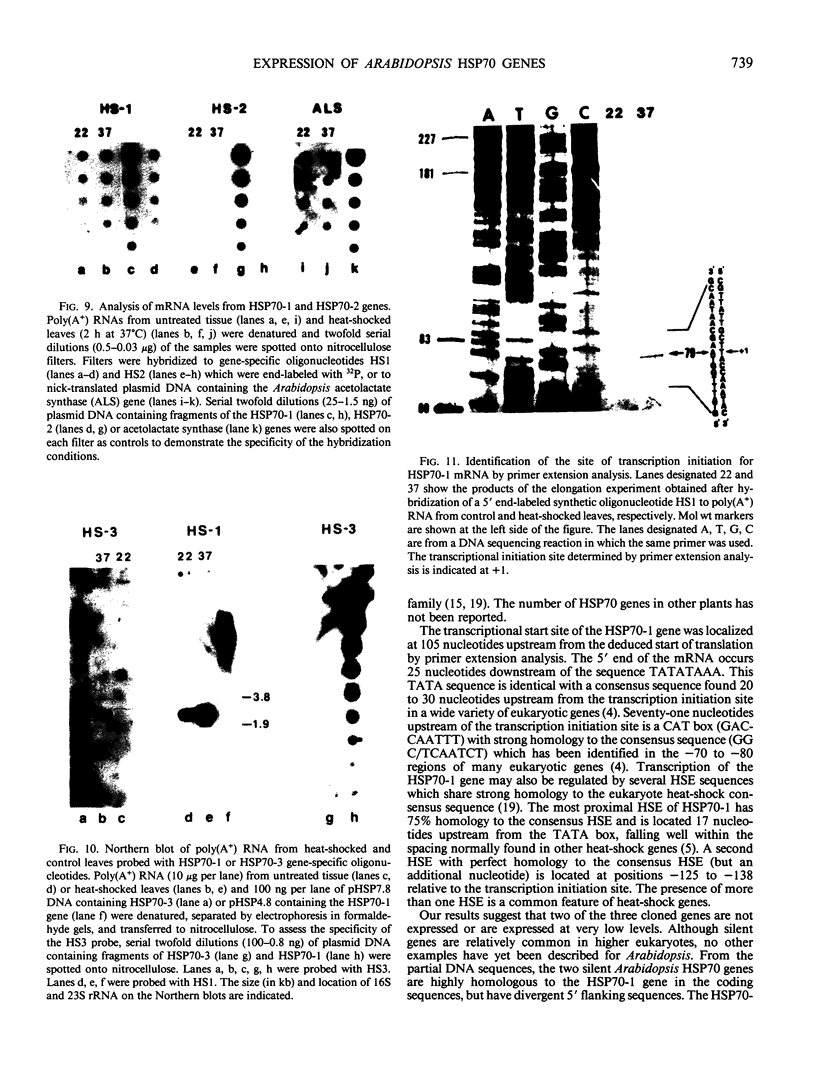
Analysis of the polypeptide composition of extracts from heat-shocked leaves of Arabidopsis indicated the presence of at least 12 HSP70-related polypeptides, most of which were constitutively expressed. In vitro translation of mRNA from heat-shocked and control leaves indicated that the amount of mRNA encoding four HSP70 polypeptides was increased strongly by heat-shock. Three Arabidopsis genes which exhibit homology to a Drosophila HSP70 gene were cloned. Two of the three genes are arranged in direct orientation approximately 1.5 kilobases apart. The third gene is not closely linked to the other two. Nucleotide sequence analysis of the 5′ regions of the two linked genes revealed that both contain a TATA box, the CAAT motif, and several short sequences which are homologous to the Drosophila heat-shock consensus sequence. The deduced partial amino acid sequence of the open reading frames were 79 and 72% homologous to the corresponding regions of the Drosophila HSP70-cognate and HSP70 sequences, respectively. As with the two maize HSP70 genes which have been characterized, and the Drosophila HSP70-cognate genes, the Arabidopsis genes contained a putative intron in the codon specifying amino acid 72. Analysis of mRNA levels with gene-specific oligonucleotide probes indicated that two of the genes were not expressed or were expressed at very low levels in leaves during normal growth or after heat-shock, whereas the other gene was constitutively expressed. By analogy with the results of similar studies of other organisms, it appears that the three cloned genes are members of a small family which are most closely related to the HSP70-cognate genes found in other species.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Beltz G. A., Jacobs K. A., Eickbush T. H., Cherbas P. T., Kafatos F. C. Isolation of multigene families and determination of homologies by filter hybridization methods. Methods Enzymol. 1983;100:266–285. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)00061-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benoist C., O'Hare K., Breathnach R., Chambon P. The ovalbumin gene-sequence of putative control regions. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 Jan 11;8(1):127–142. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.1.127. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biggin M. D., Gibson T. J., Hong G. F. Buffer gradient gels and 35S label as an aid to rapid DNA sequence determination. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jul;80(13):3963–3965. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.13.3963. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper P., Ho T. H. Heat shock proteins in maize. Plant Physiol. 1983 Feb;71(2):215–222. doi: 10.1104/pp.71.2.215. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Craig E. A., Ingolia T. D., Manseau L. J. Expression of Drosophila heat-shock cognate genes during heat shock and development. Dev Biol. 1983 Oct;99(2):418–426. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(83)90291-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guy C. L., Niemi K. J., Brambl R. Altered gene expression during cold acclimation of spinach. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jun;82(11):3673–3677. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.11.3673. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heikkila J. J., Papp J. E., Schultz G. A., Bewley J. D. Induction of heat shock protein messenger RNA in maize mesocotyls by water stress, abscisic Acid, and wounding. Plant Physiol. 1984 Sep;76(1):270–274. doi: 10.1104/pp.76.1.270. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmgren R., Corces V., Morimoto R., Blackman R., Meselson M. Sequence homologies in the 5' regions of four Drosophila heat-shock genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jun;78(6):3775–3778. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.6.3775. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hurkman W. J., Tanaka C. K. Solubilization of plant membrane proteins for analysis by two-dimensional gel electrophoresis. Plant Physiol. 1986 Jul;81(3):802–806. doi: 10.1104/pp.81.3.802. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ingolia T. D., Craig E. A. Drosophila gene related to the major heat shock-induced gene is transcribed at normal temperatures and not induced by heat shock. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Jan;79(2):525–529. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.2.525. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ingolia T. D., Craig E. A., McCarthy B. J. Sequence of three copies of the gene for the major Drosophila heat shock induced protein and their flanking regions. Cell. 1980 Oct;21(3):669–679. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90430-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ingolia T. D., Slater M. R., Craig E. A. Saccharomyces cerevisiae contains a complex multigene family related to the major heat shock-inducible gene of Drosophila. Mol Cell Biol. 1982 Nov;2(11):1388–1398. doi: 10.1128/mcb.2.11.1388. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurtz S., Rossi J., Petko L., Lindquist S. An ancient developmental induction: heat-shock proteins induced in sporulation and oogenesis. Science. 1986 Mar 7;231(4742):1154–1157. doi: 10.1126/science.3511530. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin C. Y., Roberts J. K., Key J. L. Acquisition of Thermotolerance in Soybean Seedlings : Synthesis and Accumulation of Heat Shock Proteins and their Cellular Localization. Plant Physiol. 1984 Jan;74(1):152–160. doi: 10.1104/pp.74.1.152. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindquist S. The heat-shock response. Annu Rev Biochem. 1986;55:1151–1191. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.55.070186.005443. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGarry T. J., Lindquist S. Inhibition of heat shock protein synthesis by heat-inducible antisense RNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jan;83(2):399–403. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.2.399. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGarry T. J., Lindquist S. The preferential translation of Drosophila hsp70 mRNA requires sequences in the untranslated leader. Cell. 1985 Oct;42(3):903–911. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90286-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palter K. B., Watanabe M., Stinson L., Mahowald A. P., Craig E. A. Expression and localization of Drosophila melanogaster hsp70 cognate proteins. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Apr;6(4):1187–1203. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.4.1187. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pruitt R. E., Meyerowitz E. M. Characterization of the genome of Arabidopsis thaliana. J Mol Biol. 1986 Jan 20;187(2):169–183. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(86)90226-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rochester D. E., Winer J. A., Shah D. M. The structure and expression of maize genes encoding the major heat shock protein, hsp70. EMBO J. 1986 Mar;5(3):451–458. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04233.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sorger P. K., Pelham H. R. Cloning and expression of a gene encoding hsc73, the major hsp70-like protein in unstressed rat cells. EMBO J. 1987 Apr;6(4):993–998. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb04850.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wood W. I., Gitschier J., Lasky L. A., Lawn R. M. Base composition-independent hybridization in tetramethylammonium chloride: a method for oligonucleotide screening of highly complex gene libraries. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Mar;82(6):1585–1588. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.6.1585. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]