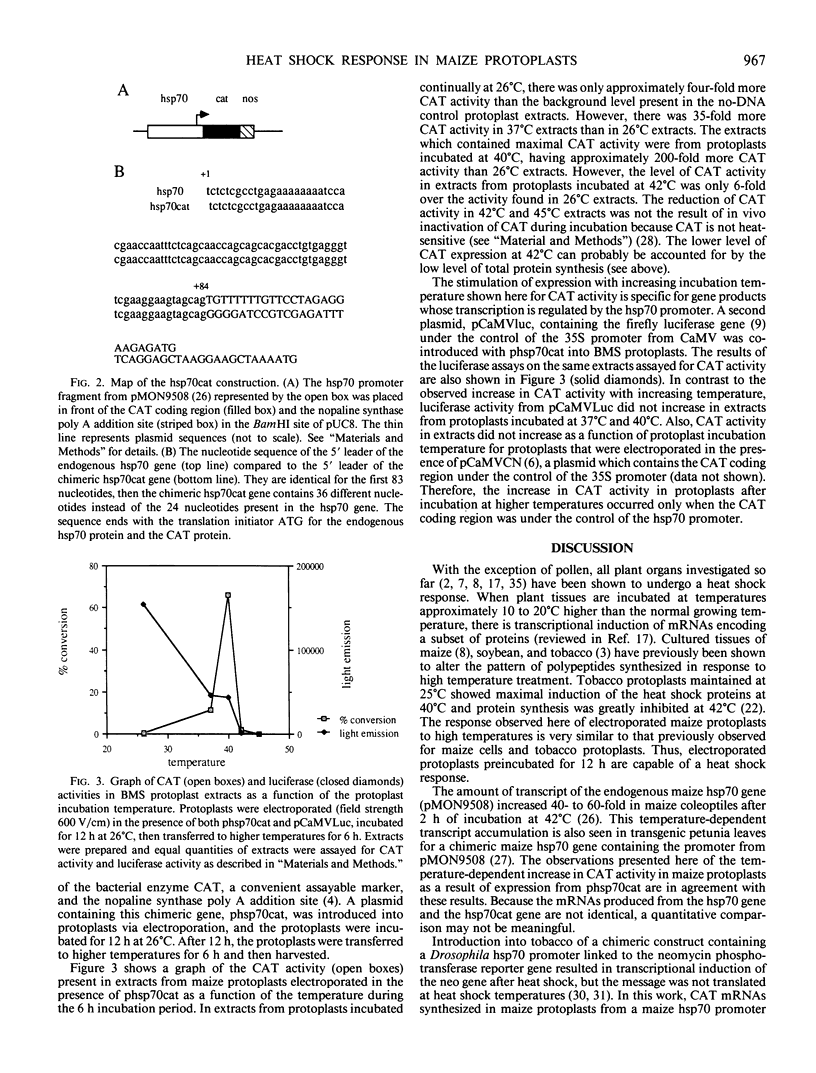
Abstract
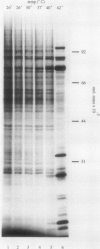
The response of maize (Zea mays L.) protoplasts to high temperature stress was investigated. After isolation and electroporation, protoplasts were preincubated for 12 hours at 26°C then incubated for 6 hours at elevated temperatures. The pattern of polypeptides synthesized by these protoplasts during the last hour was monitored by in vivo labeling with 35S-methionine. Incubation at 40° and 42°C resulted in the synthesis of polypeptides not detectable at 26°C. Introduction of a chimeric maize heat shock protein 70 promoter-chloramphenicol acetyltransferase coding region gene into protoplasts via electroporation resulted in the temperature-dependent induction of chloramphenicol acetyltransferase activity with maximal activity at 40°C. In the same protoplasts, a second chimeric gene, in which the firefly luciferase coding region was under the control of the 35S promoter from cauliflower mosaic virus, did not show an increase in expression after incubation at higher temperatures. Maize protoplasts provide a system to study molecular responses to high temperature stress.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alton N. K., Vapnek D. Nucleotide sequence analysis of the chloramphenicol resistance transposon Tn9. Nature. 1979 Dec 20;282(5741):864–869. doi: 10.1038/282864a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bevan M., Barnes W. M., Chilton M. D. Structure and transcription of the nopaline synthase gene region of T-DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Jan 25;11(2):369–385. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.2.369. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biggin M. D., Gibson T. J., Hong G. F. Buffer gradient gels and 35S label as an aid to rapid DNA sequence determination. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jul;80(13):3963–3965. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.13.3963. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Callis J., Fromm M., Walbot V. Introns increase gene expression in cultured maize cells. Genes Dev. 1987 Dec;1(10):1183–1200. doi: 10.1101/gad.1.10.1183. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper P., Ho T. H., Hauptmann R. M. Tissue specificity of the heat-shock response in maize. Plant Physiol. 1984 Jun;75(2):431–441. doi: 10.1104/pp.75.2.431. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper P., Ho T. H. Heat shock proteins in maize. Plant Physiol. 1983 Feb;71(2):215–222. doi: 10.1104/pp.71.2.215. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fromm M. E., Taylor L. P., Walbot V. Stable transformation of maize after gene transfer by electroporation. 1986 Feb 27-Mar 5Nature. 319(6056):791–793. doi: 10.1038/319791a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fromm M., Taylor L. P., Walbot V. Expression of genes transferred into monocot and dicot plant cells by electroporation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Sep;82(17):5824–5828. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.17.5824. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindquist S. The heat-shock response. Annu Rev Biochem. 1986;55:1151–1191. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.55.070186.005443. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MANS R. J., NOVELLI G. D. A convenient, rapid and sensitive method for measuring the incorporation of radioactive amino acids into protein. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1960 Nov;3:540–543. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(60)90171-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyer Y., Chartier Y. Long-lived and short-lived heat-shock proteins in tobacco mesophyll protoplasts. Plant Physiol. 1983 May;72(1):26–32. doi: 10.1104/pp.72.1.26. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moran N., Ehrenstein G., Iwasa K., Bare C., Mischke C. Ion channels in plasmalemma of wheat protoplasts. Science. 1984 Nov 16;226(4676):835–838. doi: 10.1126/science.6093255. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paszkowski J., Shillito R. D., Saul M., Mandák V., Hohn T., Hohn B., Potrykus I. Direct gene transfer to plants. EMBO J. 1984 Dec 1;3(12):2717–2722. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb02201.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pomeroy M. K., Mudd J. B. Chilling sensitivity of cucumber cotyledon protoplasts and seedlings. Plant Physiol. 1987 Jul;84(3):677–681. doi: 10.1104/pp.84.3.677. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rochester D. E., Winer J. A., Shah D. M. The structure and expression of maize genes encoding the major heat shock protein, hsp70. EMBO J. 1986 Mar;5(3):451–458. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04233.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaw W. V. Chloramphenicol acetyltransferase from chloramphenicol-resistant bacteria. Methods Enzymol. 1975;43:737–755. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(75)43141-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spena A., Hain R., Ziervogel U., Saedler H., Schell J. Construction of a heat-inducible gene for plants. Demonstration of heat-inducible activity of the Drosophila hsp70 promoter in plants. EMBO J. 1985 Nov;4(11):2739–2743. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03997.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vernet T., Fleck J., Durr A., Fritsch C., Pinck M., Hirth L. Expression of the gene coding for the small subunit of ribulosebisphosphate carboxylase during differentiation of tobacco plant protoplasts. Eur J Biochem. 1982 Sep 1;126(3):489–494. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1982.tb06806.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker J. C., Howard E. A., Dennis E. S., Peacock W. J. DNA sequences required for anaerobic expression of the maize alcohol dehydrogenase 1 gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Oct;84(19):6624–6628. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.19.6624. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xiao C. M., Mascarenhas J. P. High temperature-induced thermotolerance in pollen tubes of tradescantia and heat-shock proteins. Plant Physiol. 1985 Aug;78(4):887–890. doi: 10.1104/pp.78.4.887. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Wet J. R., Wood K. V., DeLuca M., Helinski D. R., Subramani S. Firefly luciferase gene: structure and expression in mammalian cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Feb;7(2):725–737. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.2.725. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]