Abstract
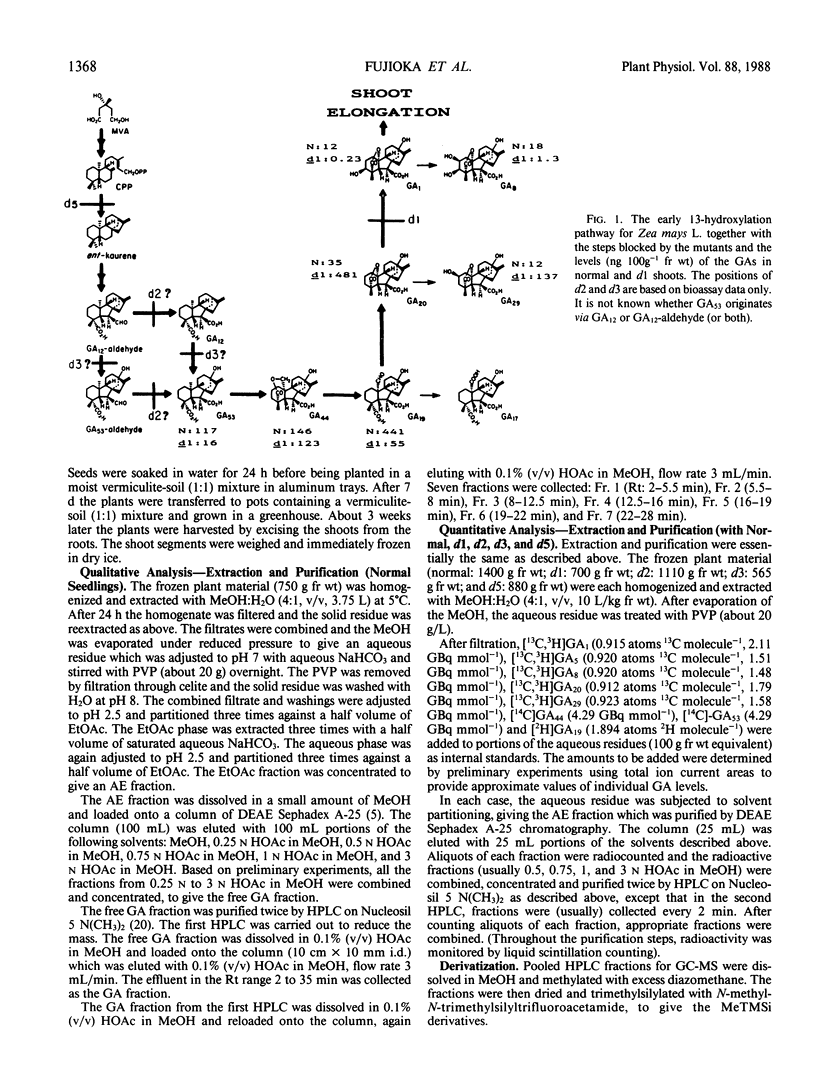
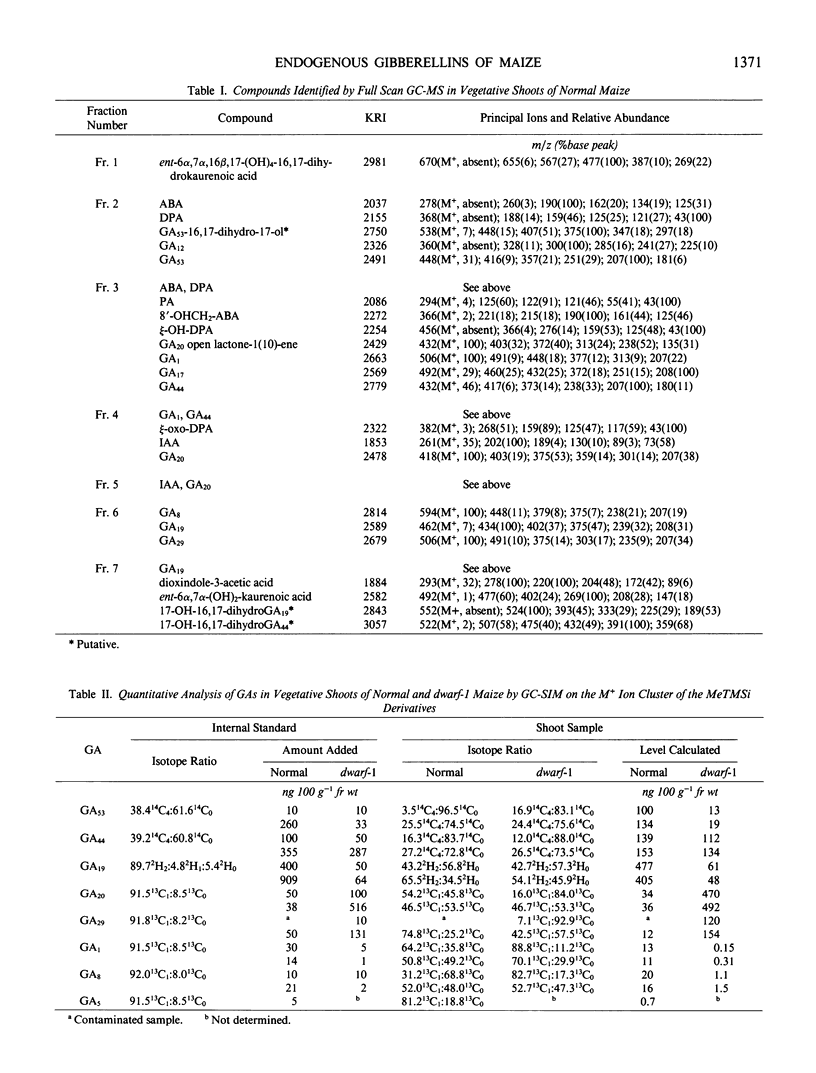
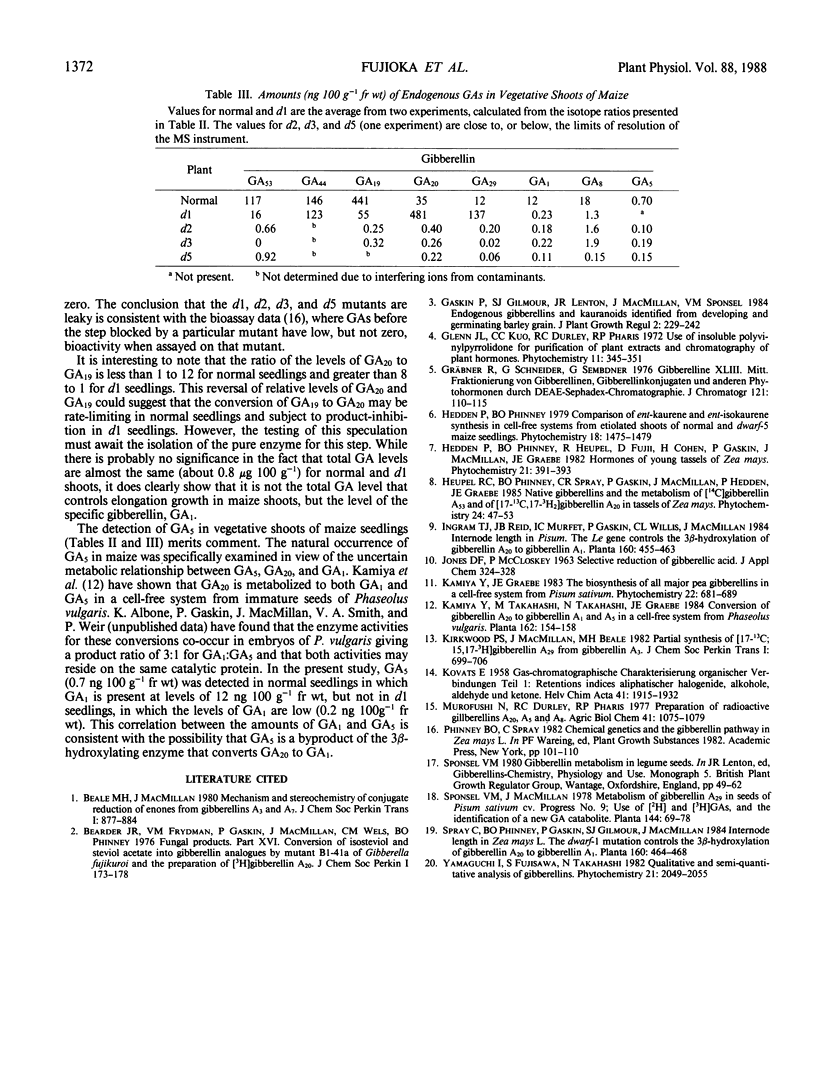
Gibberellins A12 (GA12), GA53, GA44, GA19, GA17, GA20, GA29, GA1, and GA8 have been identified from extracts of vegetative shoots of normal (wild type) maize using full scan capillary gas chromatography-mass spectrometry and Kovats retention indices. Seven of these gibberellins (GAs) have been quantified by capillary gas chromatography-selected ion monitoring using internal standards of [14C4]GA53, [14C4]GA44, [2H2] GA19, [13C1]GA20, [13C1]GA29, [13C1]GA1, and [13C1]GA8. Quantitative data from extracts of normal, dwarf-1, dwarf-2, dwarf-3, and dwarf-5 seedlings support the operation of the early 13-hydroxylation pathway in vegetative shoots of Zea mays. These data support the positions in the pathway blocked by the mutants, previously assigned by bioassay data and metabolic studies. The GA levels in dwarf-2, dwarf-3, and dwarf-5 were equal to, or less than, 2.0 nanograms per 100 grams fresh weight, showing that these mutants are blocked for steps early in the pathway. In dwarf-1, the level of GA1 was very low (0.23 nanograms per 100 grams fresh weight) and less than 2% of that in normal shoots, while GA20 and GA29 accumulated to levels over 10 times those in normals; these results confirm that the dwarf-1 mutant blocks the conversion of GA20 to GA1. Since the level of GAs beyond the blocked step for each mutant is greater than zero, each mutated gene probably codes for an altered gene product, thus leading to impaired enzyme activities.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bearder J. R., Frydman V. M., Gaskin P., MacMillan J., Wels C. M., Phinney B. O. Fungal products. Part XVI. Conversion of isosteviol and steviol acetate into gibberellin analogues by mutant b1-41a of Gibberella fujikuroi and the preparation of (3H)gibberellin A20. J Chem Soc Perkin 1. 1976;(2):173–178. doi: 10.1039/p19760000173. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gräbner R., Schneider G., Sembdner G. Gibberelline. XLIII. Mitt. Fraktionierung von Gibberellinen, Gibberellinkonjugaten und anderen Phytohormonen durch DEAE-Sephadex-Chromatographie. J Chromatogr. 1976 Jun 9;121(1):110–115. doi: 10.1016/s0021-9673(00)82310-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


