Abstract
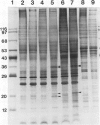
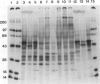
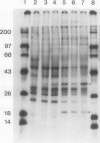
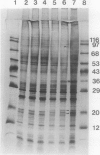
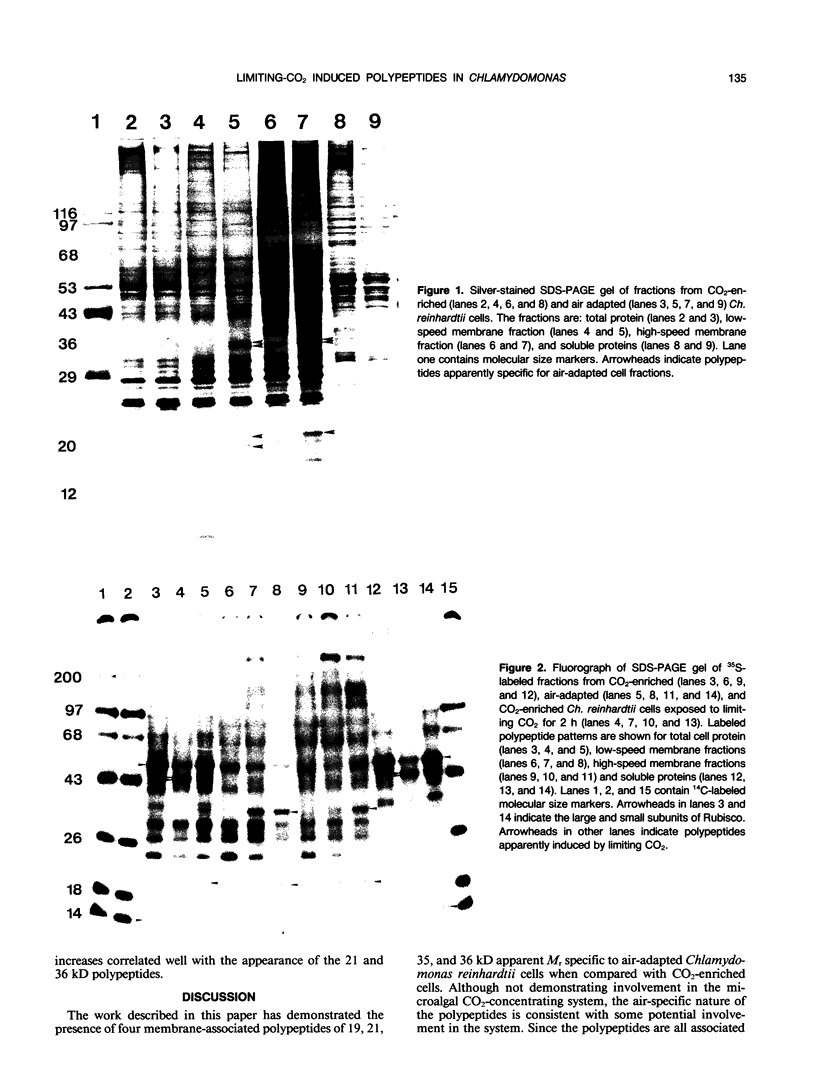
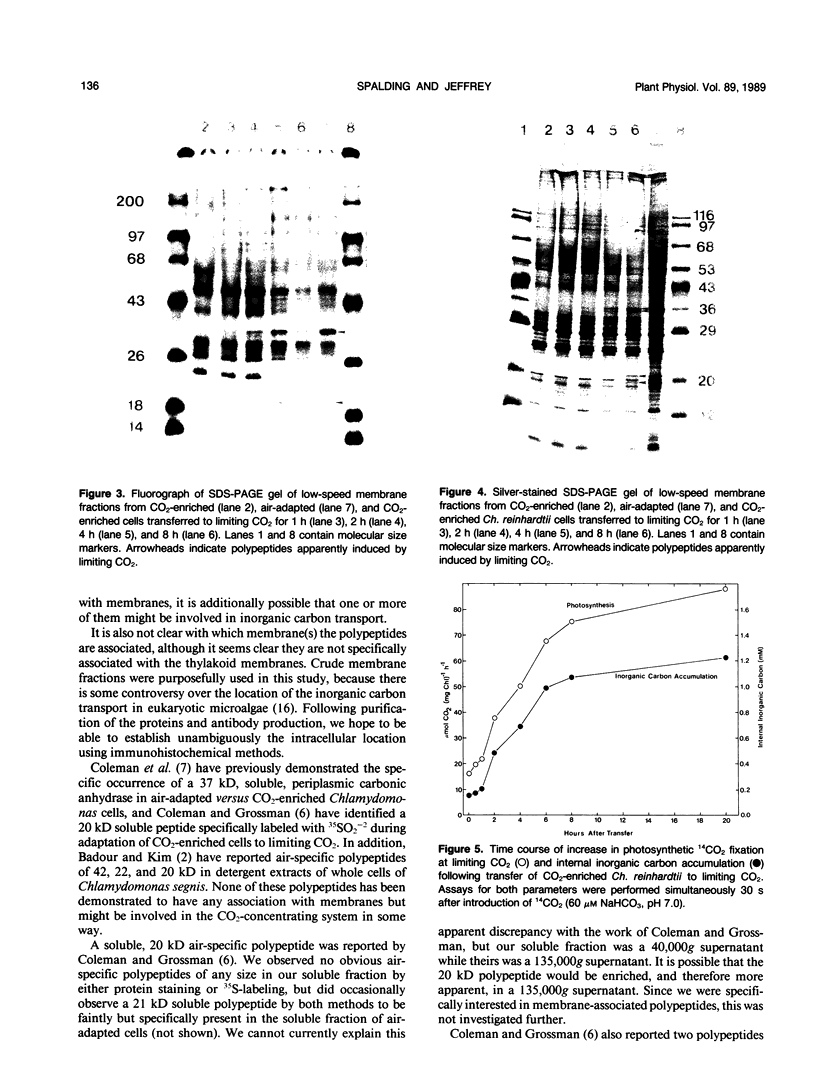
Chlamydomonas reinhardtii and other unicellular green algae have a high apparent affinity for CO2, little O2 inhibition of photosynthesis, and reduced photorespiration. These characteristics result from operation of a CO2-concentrating system. The CO2-concentrating system involves active inorganic carbon transport and is under environmental control. Cells grown at limiting CO2 concentrations have inorganic carbon transport activity, but cells grown at 5% CO2 do not. Four membrane-associated polypeptides (Mr 19, 21, 35, and 36 kilodaltons) have been identified which either appear or increase in abundance during adaptation to limiting CO2 concentrations. The appearance of two of the polypeptides occurs over roughly the same time course as the appearance of the CO2-concentrating system activity in response to CO2 limitation.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Badger M. R., Kaplan A., Berry J. A. Internal Inorganic Carbon Pool of Chlamydomonas reinhardtii: EVIDENCE FOR A CARBON DIOXIDE-CONCENTRATING MECHANISM. Plant Physiol. 1980 Sep;66(3):407–413. doi: 10.1104/pp.66.3.407. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coleman J. R., Berry J. A., Togasaki R. K., Grossman A. R. Identification of Extracellular Carbonic Anhydrase of Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. Plant Physiol. 1984 Oct;76(2):472–477. doi: 10.1104/pp.76.2.472. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greer K. L., Plumley F. G., Schmidt G. W. The Water Oxidation Complex of Chlamydomonas: Accumulation and Maturation of the Largest Subunit in Photosystem II Mutants. Plant Physiol. 1986 Sep;82(1):114–120. doi: 10.1104/pp.82.1.114. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moroney J. V., Husic H. D., Tolbert N. E. Effect of Carbonic Anhydrase Inhibitors on Inorganic Carbon Accumulation by Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. Plant Physiol. 1985 Sep;79(1):177–183. doi: 10.1104/pp.79.1.177. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moroney J. V., Kitayama M., Togasaki R. K., Tolbert N. E. Evidence for Inorganic Carbon Transport by Intact Chloroplasts of Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. Plant Physiol. 1987 Mar;83(3):460–463. doi: 10.1104/pp.83.3.460. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skinner M. K., Griswold M. D. Fluorographic detection of radioactivity in polyacrylamide gels with 2,5-diphenyloxazole in acetic acid and its comparison with existing procedures. Biochem J. 1983 Jan 1;209(1):281–284. doi: 10.1042/bj2090281. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spalding M. H., Spreitzer R. J., Ogren W. L. Carbonic Anhydrase-Deficient Mutant of Chlamydomonas reinhardii Requires Elevated Carbon Dioxide Concentration for Photoautotrophic Growth. Plant Physiol. 1983 Oct;73(2):268–272. doi: 10.1104/pp.73.2.268. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spalding M. H., Spreitzer R. J., Ogren W. L. Reduced Inorganic Carbon Transport in a CO(2)-Requiring Mutant of Chlamydomonas reinhardii. Plant Physiol. 1983 Oct;73(2):273–276. doi: 10.1104/pp.73.2.273. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsuzuki M., Miyachi S. Effects of CO2 concentration during growth and of ethoxyzolamide on CO2 compensation point in Chlorella. FEBS Lett. 1979 Jul 15;103(2):221–223. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(79)81331-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winder T., Spalding M. H. Imazaquin and chlorsulfuron resistance and cross resistance in mutants of Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. Mol Gen Genet. 1988 Aug;213(2-3):394–399. doi: 10.1007/BF00339608. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]