Abstract
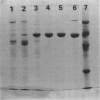
NAD malic enzyme (EC 1.1.1.39), which is involved in C4 photosynthesis, was purified to electrophoretic homogeneity from leaves of Eleusine coracana and to near homogeneity from leaves of Panicum dichotomiflorum. The enzyme from each C4 species was found to have only one type of subunit by SDS polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. The Mr of subunits of the enzme from E. coracana and P. dichotommiflorum was 63 and 61 kilodaltons, respectively. The native Mr of the enzyme from each species was determined by gel filtration to be about 500 kilodaltons, indicating that the NAD malic enzyme from C4 species is an octamer of identical subunits. The purified NAD malic enzyme from each C4 species showed similar kinetic properties with respect to concentrations of malate and NAD; each had a requirement for Mn2+ and activation by fructose- 1,6-bisphosphate (FBP) or CoA. A cooperativity with respect to Mn2+ was apparent with both enzymes. The activator (FBP) did not change the Hill value but greatly decreased K0.5 (the concentration giving half-maximal activity) for Mn2+. The enzyme from E. coracana showed a very low level of activity when NADP was used as substrate, but this activity was also stimulated by FBP. Significant differences between the enzymes from E. coracana and P. dichotomiflorum were observed in their responses to the activators and their immunochemical properties. The enzyme from E. coracana was largely dependent on the activators FBP or CoA, regardless of concentration of Mn2+. In contrast, the enzyme from P. dichotomiflorum showed significant activity in the absence of the activator, especially at high concentrations of Mn2+. Both immunodiffusion and immunoprecipitation, using antiserum raised against the purified NAD malic enzyme from E. coracana, revealed partial antigenic differences between the enzymes from E. coracana and P. dichotomiflorum. The activity of the NAD malic enzyme from Amaranthus edulis, a typical NAD malic enzyme type C4 dicot, was not inhibited by the antiserum raised against the NAD malic enzyme from E. coracana.
Full text
PDF








Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Campbell W. H., Remmler J. L. Regulation of Corn Leaf Nitrate Reductase : I. Immunochemical Methods for Analysis of the Enzyme's Protein Component. Plant Physiol. 1986 Feb;80(2):435–441. doi: 10.1104/pp.80.2.435. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chapman K. S., Hatch M. D. Regulation of mitochondrial NAD-malic enzyme involved in C4 pathway photosynthesis. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1977 Nov;184(1):298–306. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(77)90354-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grissom C. B., Canellas P. F., Wedding R. T. Allosteric regulation of the NAD malic enzyme from cauliflower: activation by fumarate and coenzyme A. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1983 Jan;220(1):133–144. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(83)90394-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grover S. D., Canellas P. F., Wedding R. T. Purification of NAD malic enzyme from potato and investigation of some physical and kinetic properties. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1981 Jul;209(2):396–407. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(81)90297-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grover S. D., Wedding R. T. Kinetic Ramifications of the Association-Dissociation Behavior of NAD Malic Enzyme : A Possible Regulatory Mechanism. Plant Physiol. 1982 Oct;70(4):1169–1172. doi: 10.1104/pp.70.4.1169. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grover S. D., Wedding R. T. Modulation of the activity of NAD malic enzyme from solanum tuberosum by changes in oligomeric state. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1984 Nov 1;234(2):418–425. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(84)90288-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hatch M. D., Kagawa T. NAD malic enzyme in leaves with C-pathway photosynthesis and its role in C4 acid decarboxylation. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1974 Jan;160(1):346–349. doi: 10.1016/s0003-9861(74)80043-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hatch M. D., Mau S. L., Kagawa T. Properties of leaf NAD malic enzyme from plants with C4 pathway photosynthesis. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1974 Nov;165(1):188–200. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(74)90155-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hatch M. D., Tsuzuki M., Edwards G. E. Determination of NAD Malic Enzyme in Leaves of C(4) Plants : EFFECTS OF MALATE DEHYDROGENASE AND OTHER FACTORS. Plant Physiol. 1982 Feb;69(2):483–491. doi: 10.1104/pp.69.2.483. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kagawa T., Hatch M. D. Mitochondria as a site of C4 acid decarboxylation in C4-pathway photosynthesis. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1975 Apr;167(2):687–696. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(75)90513-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsuoka M., Hata S. Comparative studies of phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase from c(3) and c(4) plants. Plant Physiol. 1987 Dec;85(4):947–951. doi: 10.1104/pp.85.4.947. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Valenti V., Pupillo P. Activation Kinetics of NAD-Dependent Malic Enzyme of Cauliflower Bud Mitochondria. Plant Physiol. 1981 Nov;68(5):1191–1196. doi: 10.1104/pp.68.5.1191. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wedding R. T., Black M. K. Physical and Kinetic Properties and Regulation of the NAD Malic Enzyme Purified from Leaves of Crassula argentea. Plant Physiol. 1983 Aug;72(4):1021–1028. doi: 10.1104/pp.72.4.1021. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wedding R. T., Canellas P. F., Black M. K. Slow Transients in the Activity of the NAD Malic Enzyme from Crassula. Plant Physiol. 1981 Dec;68(6):1416–1423. doi: 10.1104/pp.68.6.1416. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Willeford K. O., Wedding R. T. Evidence for a multiple subunit composition of plant NAD malic enzyme. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jun 15;262(17):8423–8429. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Willeford K. O., Wedding R. T. Regulation of the NAD Malic Enzyme from Crassula. Plant Physiol. 1986 Mar;80(3):792–795. doi: 10.1104/pp.80.3.792. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Willeford K. O., Wedding R. T. pH Effects on the Activity and Regulation of the NAD Malic Enzyme. Plant Physiol. 1987 Aug;84(4):1084–1087. doi: 10.1104/pp.84.4.1084. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]