Abstract
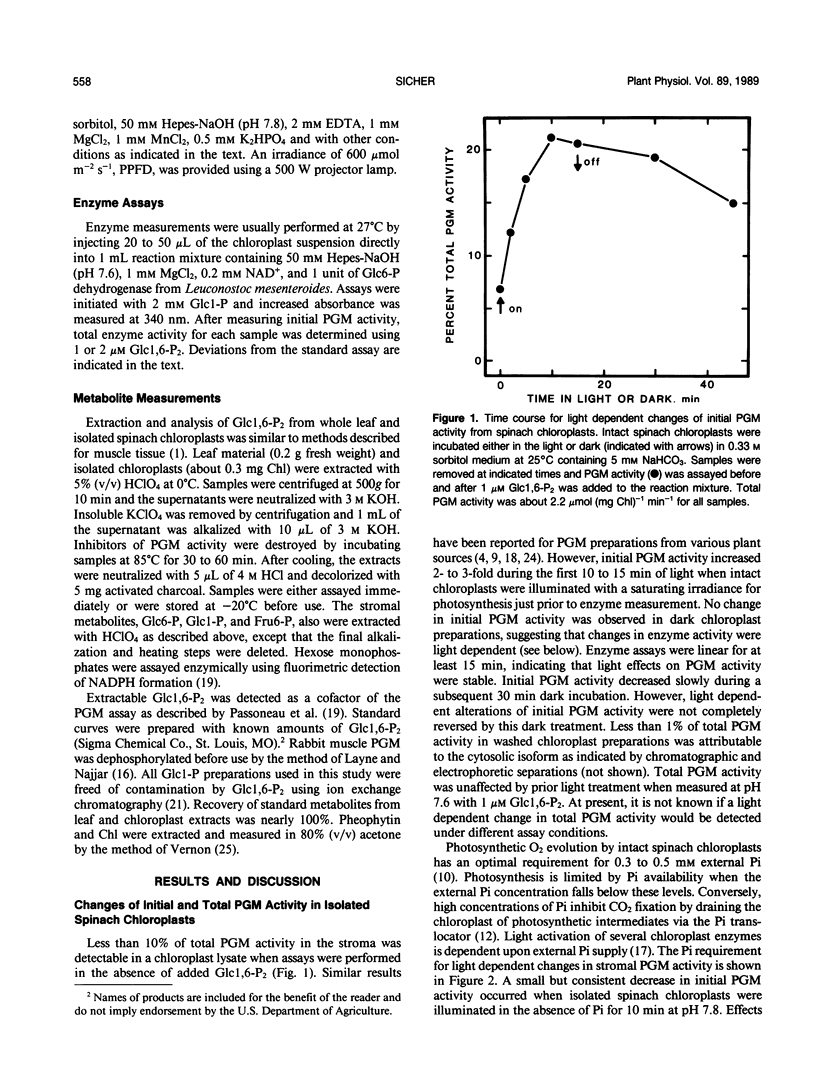
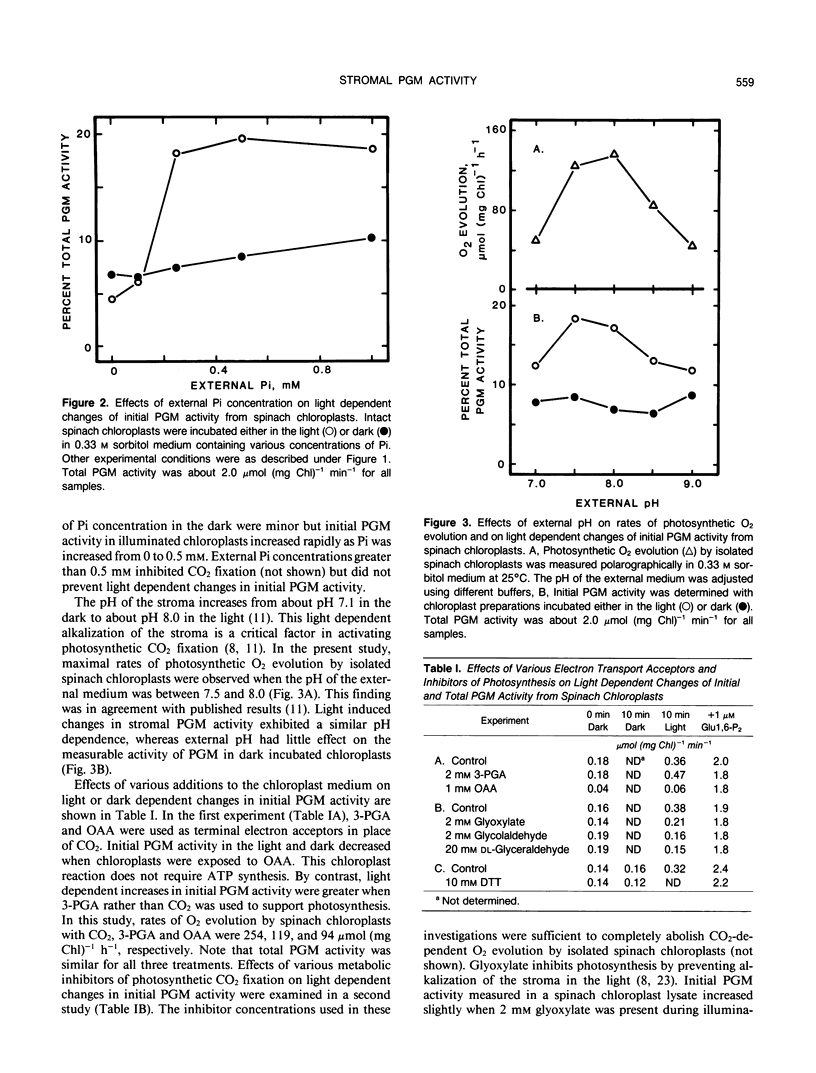
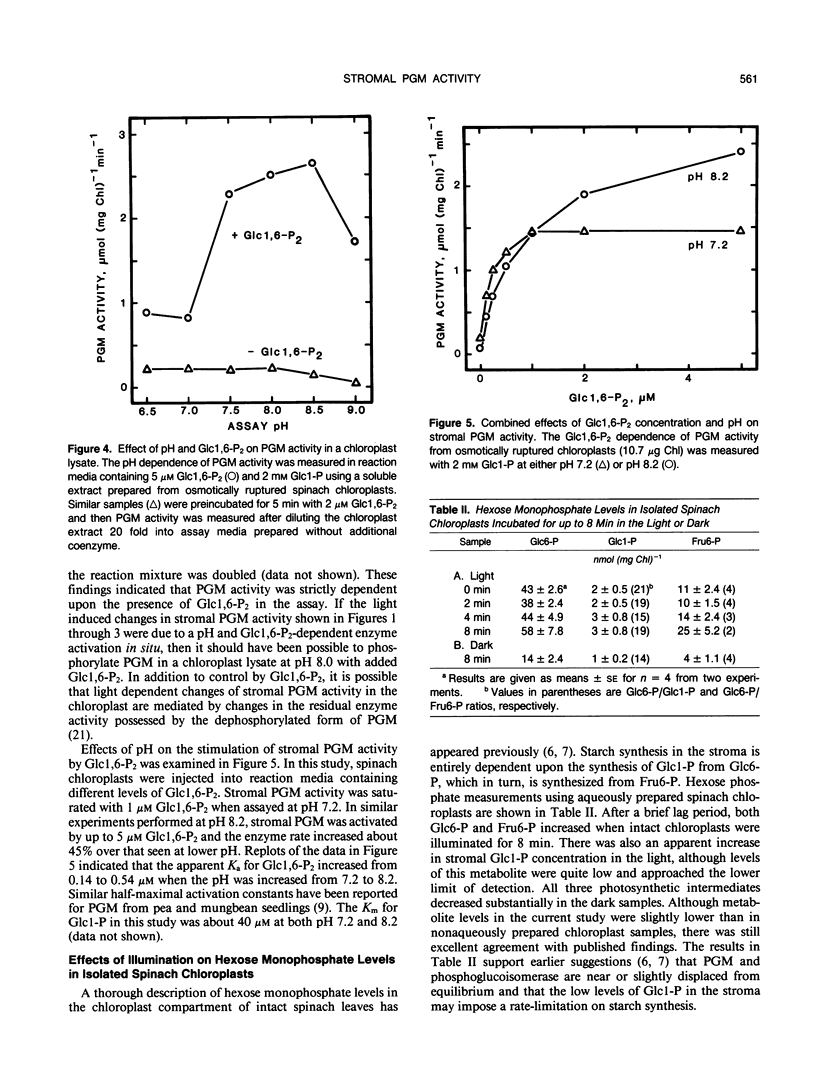
Phosphoglucomutase (PGM) activity was measured in spinach (Spinacia oleracea L.) chloroplasts. Initial enzyme activity in a chloroplast lysate was 5 to 10% of total activity measured with 1 micromolar glucose 1,6-bisphosphate (Glc 1,6-P2) in the assay. Initial PGM activity increased 2- to 3-fold when chloroplasts were illuminated for 10 minutes prior to enzyme measurement and then decreased slowly in the dark. Measurements of total enzyme activity were unchanged by prior light treatment. Initial PGM activity from light treated chloroplasts was sufficient to account for in vivo rates of starch synthesis. Changes in PGM activity were affected by stromal pH and orthophosphate concentration. Photosynthetic inhibitors, dl-glyceraldehyde, glycolaldehyde, and glyoxylate, decreased and 3-phosphoglyceric acid increased light induced changes of PGM activity. Dark preincubation of chloroplasts with 10 millimolar dithiothreitol had no effect upon initial PGM activity, suggesting that light effects did not involve a sulfhydryl mechanism. Hexose monophosphate levels increased in illuminated chloroplasts. Activation of PGM in a chloroplast lysate by Glc 1,6-P2 was maximal between pH 7.5 and 8.5. Stromal concentrations of Glc 1,6-P2 were between 20 and 30 micromolar for both light and dark incubated chloroplasts and these levels should saturate PGM activity. Light dependent alterations of enzyme activity may be due to changes of phosphorylated PGM levels in the stroma or are the result of changes in residual activity by the dephosphorylated form of the enzyme. The above results indicate that PGM activity in spinach chloroplasts may be regulated by light, stromal pH, and Glc 1,6-P2 concentration.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bassols A. M., Carreras J., Cussó R. Changes in glucose 1,6-bisphosphate content in rat skeletal muscle during contraction. Biochem J. 1986 Dec 15;240(3):747–751. doi: 10.1042/bj2400747. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carreras M., Bartrons R., Climent F., Carreras J. Effects of fructose 2,6-bisphosphate on phosphoglucomutase from plants. Plant Physiol. 1986 Oct;82(2):619–621. doi: 10.1104/pp.82.2.619. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galloway C. M., Dugger W. M., Black C. C. In vitro activation of phosphoglucomutase by fructose 2,6-bisphosphate. Plant Physiol. 1985 Nov;79(3):920–922. doi: 10.1104/pp.79.3.920. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heldt H. W., Chon C. J., Maronde D. Role of orthophosphate and other factors in the regulation of starch formation in leaves and isolated chloroplasts. Plant Physiol. 1977 Jun;59(6):1146–1155. doi: 10.1104/pp.59.6.1146. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heldt H. W., Rapley L. Specific transport of inorganic phosphate, 3-phosphoglycerate and dihydroxyacetonephosphate, and of dicarboxylates across the inner membrane of spinach chloroplasts. FEBS Lett. 1970 Oct 5;10(3):143–148. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(70)80438-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heldt W. H., Werdan K., Milovancev M., Geller G. Alkalization of the chloroplast stroma caused by light-dependent proton flux into the thylakoid space. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 Aug 31;314(2):224–241. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(73)90137-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirose M., Sugimoto E., Sasaki R., Chiaa H. Crystallization and reaction mechanism of yeast phosphoglucomutase. J Biochem. 1970 Oct;68(4):449–457. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a129375. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jamil H., Clarke J. B. Mechanism of action of rabbit liver phosphoglucomutase. Biochem J. 1985 Sep 15;230(3):791–795. doi: 10.1042/bj2300791. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jensen R. G., Bassham J. A. Photosynthesis by isolated chloroplasts. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1966 Oct;56(4):1095–1101. doi: 10.1073/pnas.56.4.1095. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Layne P. P., Najjar V. A. The dephosphorylation of phosphoglucomutase by nucleophilic reagents. J Biol Chem. 1975 Feb 10;250(3):966–972. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Passonneau J. V., Lowry O. H., Schulz D. W., Brown J. G. Glucose 1,6-diphosphate formation by phosphoglucomutase in mammalian tissues. J Biol Chem. 1969 Feb 10;244(3):902–909. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RAY W. J., Jr, ROSCELLI G. A. A KINETIC STUDY OF THE PHOSPHOGLUCOMUTASE PATHWAY. J Biol Chem. 1964 Apr;239:1228–1236. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sicher R. C. Characteristics of light-dependent inorganic carbon uptake by isolated spinach chloroplasts. Plant Physiol. 1984 Apr;74(4):962–966. doi: 10.1104/pp.74.4.962. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wirtz W., Stitt M., Heldt H. W. Enzymic determination of metabolites in the subcellular compartments of spinach protoplasts. Plant Physiol. 1980 Jul;66(1):187–193. doi: 10.1104/pp.66.1.187. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


