Abstract
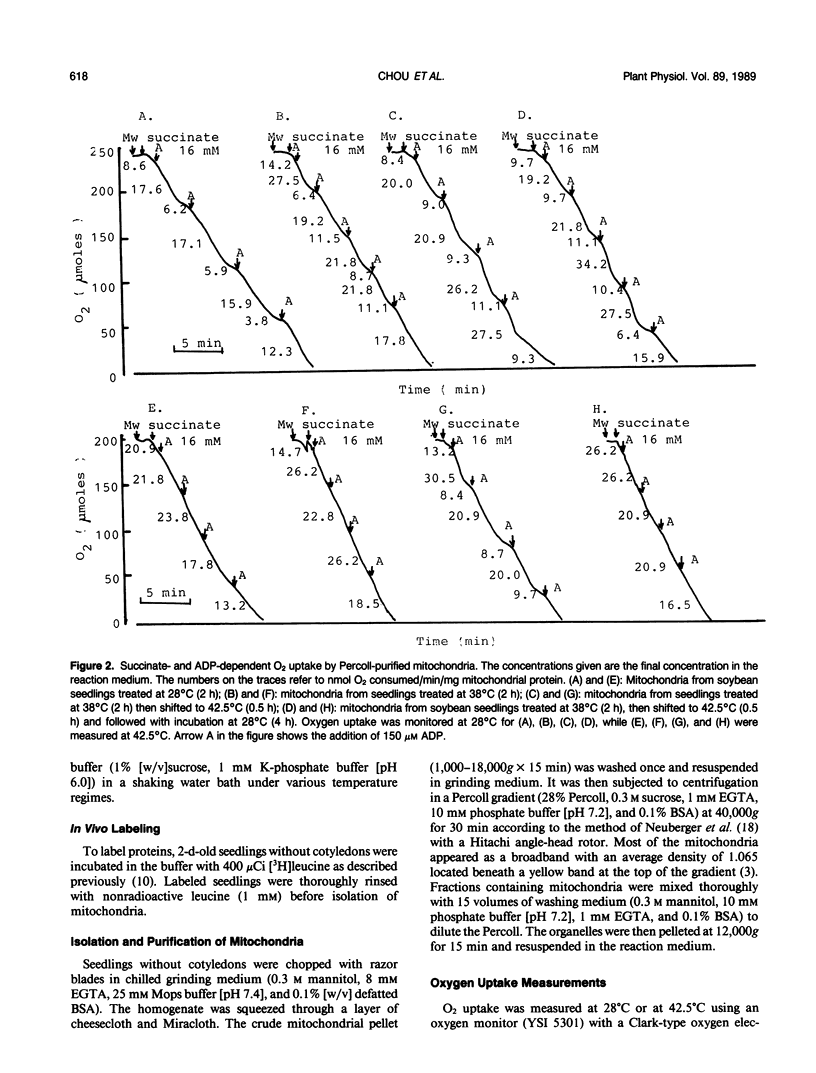
Mitochondria isolated from 2-day-old etiolated soybean (Glycine max) seedlings which had been subjected to various heat shock treatments, i.e. (A) 28°C (2 h), (B) 38°C (2 h), (C) 38°C (2 h)-42.5°C (0.5 h), and (D) 38°C (2 h)-42.5°C (0.5 h)-28°C (4 h), were monitored for O2 uptake using an oxygen electrode. Mitochondria isolated after all four heat shock treatments were active in O2 consumption at 28°C in response to succinate and ADP (derived P/O ratios were 1.6, 1.7, 1.3, and 1.3, respectively.) The mitochondria from all four treatments were also active in O2 uptake at 42.5°C. However, only mitochondria isolated after treatment (C) were tightly coupling at 42.5°C (derived ADP/O ratio was about 1.4). Combined with our earlier findings on the subcellular localization of heat shock proteins, our present data demonstrate that association of heat shock proteins with mitochondria by treatment (C) enables them to phosphorylate at 42.5°C (i.e. they become thermotolerant). Isolated mitochondria from treatment (C) and treatment (A) were compared by electron microscopy. They appeared to be very similar and no significant ultrastructural differences were noted.
Full text
PDF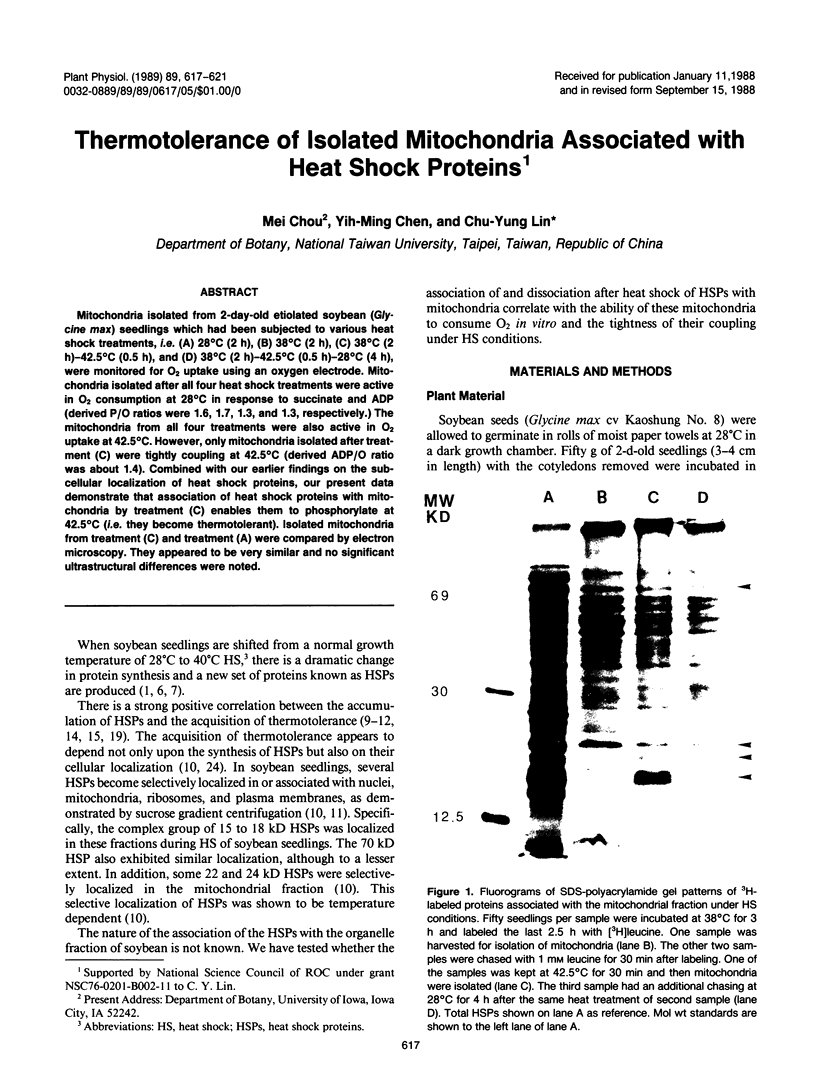


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bond U., Schlesinger M. J. Ubiquitin is a heat shock protein in chicken embryo fibroblasts. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 May;5(5):949–956. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.5.949. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Key J. L., Lin C. Y., Chen Y. M. Heat shock proteins of higher plants. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jun;78(6):3526–3530. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.6.3526. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li G. C., Werb Z. Correlation between synthesis of heat shock proteins and development of thermotolerance in Chinese hamster fibroblasts. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 May;79(10):3218–3222. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.10.3218. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin C. Y., Roberts J. K., Key J. L. Acquisition of Thermotolerance in Soybean Seedlings : Synthesis and Accumulation of Heat Shock Proteins and their Cellular Localization. Plant Physiol. 1984 Jan;74(1):152–160. doi: 10.1104/pp.74.1.152. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindquist S. The heat-shock response. Annu Rev Biochem. 1986;55:1151–1191. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.55.070186.005443. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McAlister L., Finkelstein D. B. Heat shock proteins and thermal resistance in yeast. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1980 Apr 14;93(3):819–824. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(80)91150-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moreau F., Romani R. Preparation of Avocado Mitochondria Using Self-Generated Percoll Density Gradients and Changes in Buoyant Density during Ripening. Plant Physiol. 1982 Nov;70(5):1380–1384. doi: 10.1104/pp.70.5.1380. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagao R. T., Czarnecka E., Gurley W. B., Schöffl F., Key J. L. Genes for low-molecular-weight heat shock proteins of soybeans: sequence analysis of a multigene family. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Dec;5(12):3417–3428. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.12.3417. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neuburger M., Journet E. P., Bligny R., Carde J. P., Douce R. Purification of plant mitochondria by isopycnic centrifugation in density gradients of Percoll. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1982 Aug;217(1):312–323. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(82)90507-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petersen N. S., Mitchell H. K. Recovery of protein synthesis after heat shock: prior heat treatment affects the ability of cells to translate mRNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Mar;78(3):1708–1711. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.3.1708. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phillips T. A., VanBogelen R. A., Neidhardt F. C. lon gene product of Escherichia coli is a heat-shock protein. J Bacteriol. 1984 Jul;159(1):283–287. doi: 10.1128/jb.159.1.283-287.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanders M. M. Identification of histone H2b as a heat-shock protein in Drosophila. J Cell Biol. 1981 Nov;91(2 Pt 1):579–583. doi: 10.1083/jcb.91.2.579. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schönfelder M., Horsch A., Schmid H. P. Heat shock increases the synthesis of the poly(A)-binding protein in HeLa cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Oct;82(20):6884–6888. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.20.6884. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor M. W., Long T., Martinez-Valdez H., Downing J., Zeige G. Induction of gamma-interferon activity by elevated temperatures in human B-lymphoblastoid cell lines. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jul;81(13):4033–4036. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.13.4033. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Velazquez J. M., Lindquist S. hsp70: nuclear concentration during environmental stress and cytoplasmic storage during recovery. Cell. 1984 Mar;36(3):655–662. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90345-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]