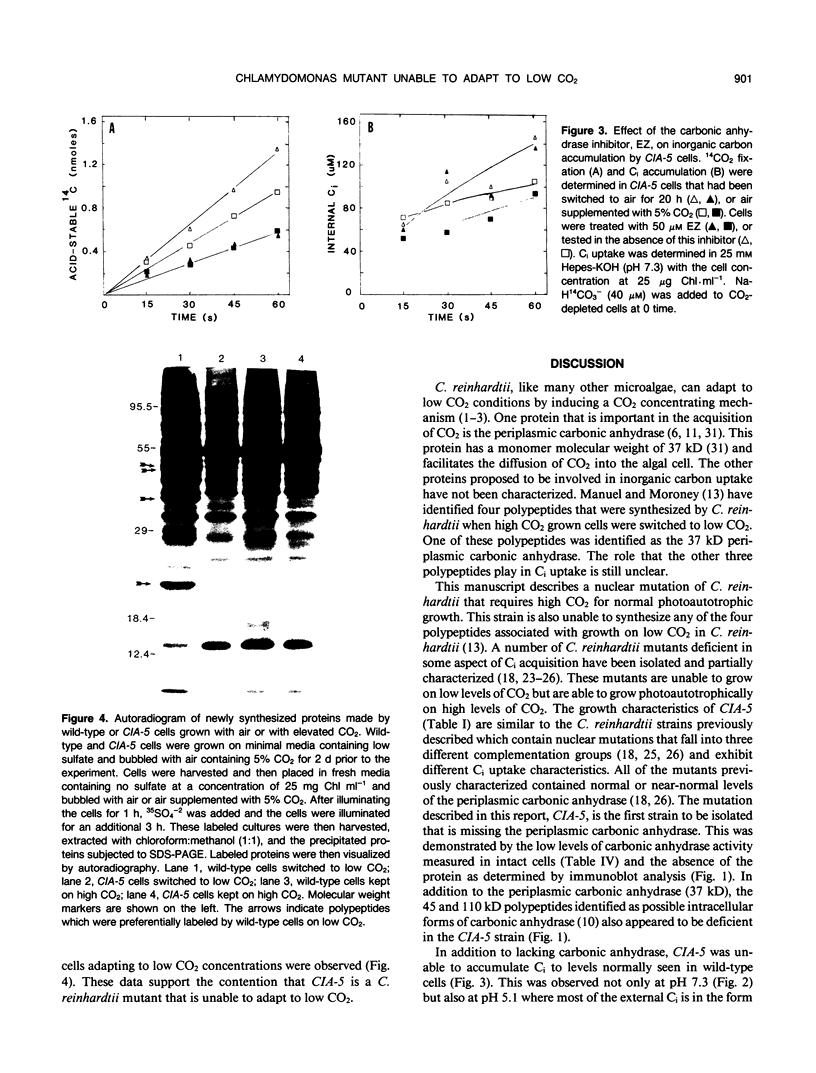
Abstract
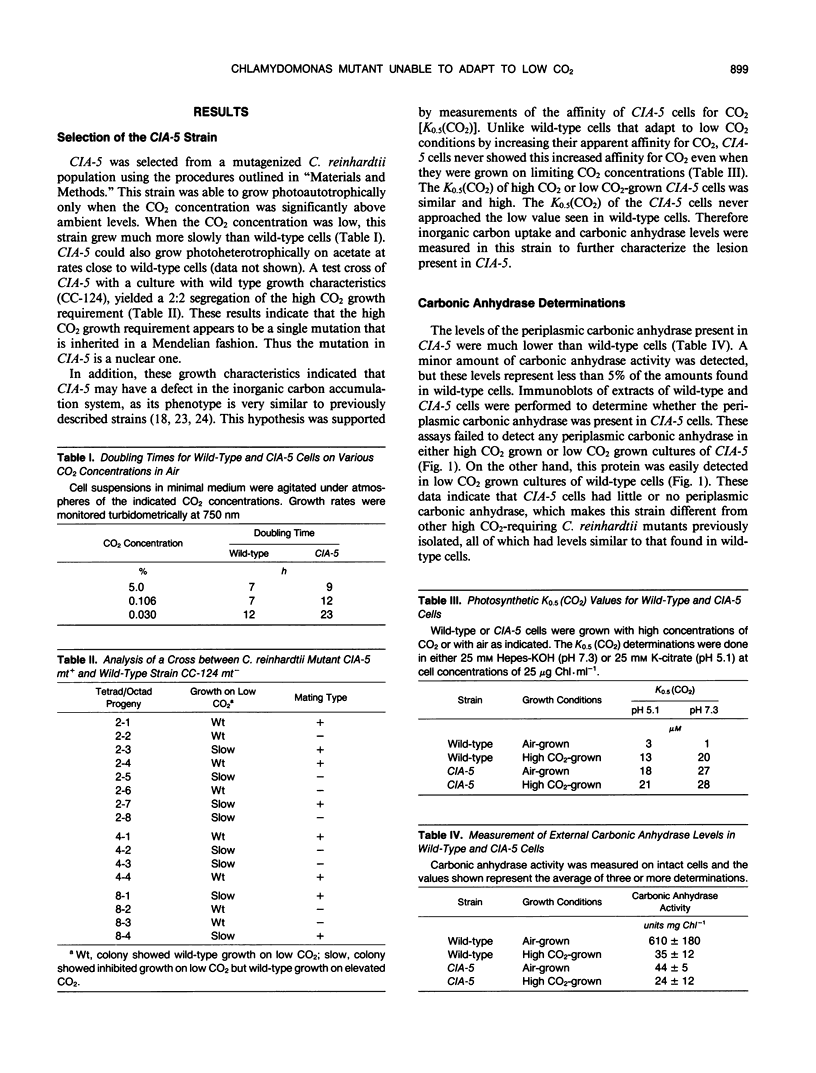
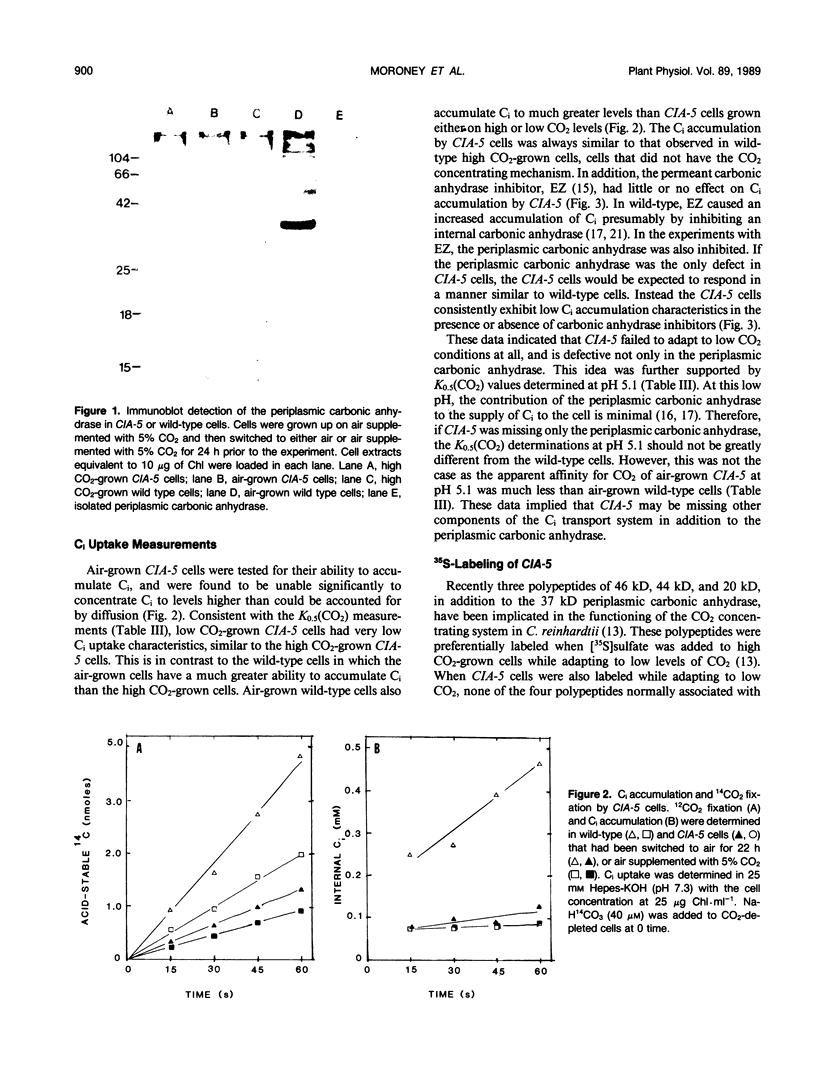
A Chlamydomonas reinhardtii mutant has been isolated that cannot grow photoautotrophically on low CO2 concentrations but can grow on elevated CO2. In a test cross, the high CO2-requirement for growth showed a 2:2 segregation. This mutant, designated CIA-5, had a phenotype similar to previously identified mutants that were defective in some aspect of CO2 accumulation. Unlike previously isolated mutants, CIA-5 did not have detectable levels of the periplasmic carbonic anhydrase, an inducible protein that participates in the acquisition of CO2 by C. reinhardtii. CIA-5 also did not accumulate inorganic carbon to levels higher than could be accounted for by diffusion. This mutant strain did not synthesize any of the four polypeptides preferentially made by wild type C. reinhardtii when switched from an environment containing elevated CO2 levels to an environment low in CO2. It is concluded that this mutant fails to induce the CO2 concentrating system and is incapable of adapting to low CO2 conditions.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baba S., Mishima H., Miyachi Y. Levels of cyclic-AMP, cyclic-GMP and betamethasone in the aqueous humor following topical administration of betamethasone in rabbit eyes. Hiroshima J Med Sci. 1983 Sep;32(3):301–304. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Badger M. R., Kaplan A., Berry J. A. Internal Inorganic Carbon Pool of Chlamydomonas reinhardtii: EVIDENCE FOR A CARBON DIOXIDE-CONCENTRATING MECHANISM. Plant Physiol. 1980 Sep;66(3):407–413. doi: 10.1104/pp.66.3.407. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coleman J. R., Berry J. A., Togasaki R. K., Grossman A. R. Identification of Extracellular Carbonic Anhydrase of Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. Plant Physiol. 1984 Oct;76(2):472–477. doi: 10.1104/pp.76.2.472. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coleman J. R., Grossman A. R. Biosynthesis of carbonic anhydrase in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii during adaptation to low CO(2). Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Oct;81(19):6049–6053. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.19.6049. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorman D. S., Levine R. P. Cytochrome f and plastocyanin: their sequence in the photosynthetic electron transport chain of Chlamydomonas reinhardi. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1965 Dec;54(6):1665–1669. doi: 10.1073/pnas.54.6.1665. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Husic H. D., Kitayama M., Togasaki R. K., Moroney J. V., Morris K. L., Tolbert N. E. Identification of Intracellular Carbonic Anhydrase in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii which Is Distinct from the Periplasmic Form of the Enzyme. Plant Physiol. 1989 Mar;89(3):904–909. doi: 10.1104/pp.89.3.904. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manuel L. J., Moroney J. V. Inorganic Carbon Accumulation by Chlamydomonas reinhardtii: New Proteins are made During Adaptation to Low CO(2). Plant Physiol. 1988 Oct;88(2):491–496. doi: 10.1104/pp.88.2.491. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maren T. H. The general physiology of reactions catalyzed by carbonic anhydrase and their inhibition by sulfonamides. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1984;429:568–579. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1984.tb12389.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moroney J. V., Husic H. D., Tolbert N. E. Effect of Carbonic Anhydrase Inhibitors on Inorganic Carbon Accumulation by Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. Plant Physiol. 1985 Sep;79(1):177–183. doi: 10.1104/pp.79.1.177. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moroney J. V., Kitayama M., Togasaki R. K., Tolbert N. E. Evidence for Inorganic Carbon Transport by Intact Chloroplasts of Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. Plant Physiol. 1987 Mar;83(3):460–463. doi: 10.1104/pp.83.3.460. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moroney J. V., Togasaki R. K., Husic H. D., Tolbert N. E. Evidence That an Internal Carbonic Anhydrase Is Present in 5% CO(2)-Grown and Air-Grown Chlamydomonas. Plant Physiol. 1987 Jul;84(3):757–761. doi: 10.1104/pp.84.3.757. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moroney J. V., Tolbert N. E. Inorganic Carbon Uptake by Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. Plant Physiol. 1985 Feb;77(2):253–258. doi: 10.1104/pp.77.2.253. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moroney J. V., Wilson B. J., Tolbert N. E. Glycolate Metabolism and Excretion by Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. Plant Physiol. 1986 Nov;82(3):821–826. doi: 10.1104/pp.82.3.821. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sears B. B., Boynton J. E., Gillham N. W. The Effect of Gametogenesis Regimes on the Chloroplast Genetic System of CHLAMYDOMONAS REINHARDTII. Genetics. 1980 Sep;96(1):95–114. doi: 10.1093/genetics/96.1.95. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spalding M. H., Spreitzer R. J., Ogren W. L. Carbonic Anhydrase-Deficient Mutant of Chlamydomonas reinhardii Requires Elevated Carbon Dioxide Concentration for Photoautotrophic Growth. Plant Physiol. 1983 Oct;73(2):268–272. doi: 10.1104/pp.73.2.268. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spalding M. H., Spreitzer R. J., Ogren W. L. Reduced Inorganic Carbon Transport in a CO(2)-Requiring Mutant of Chlamydomonas reinhardii. Plant Physiol. 1983 Oct;73(2):273–276. doi: 10.1104/pp.73.2.273. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sueoka N. MITOTIC REPLICATION OF DEOXYRIBONUCLEIC ACID IN CHLAMYDOMONAS REINHARDI. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1960 Jan;46(1):83–91. doi: 10.1073/pnas.46.1.83. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toguri T., Muto S., Miyachi S. Biosynthesis and intracellular processing of carbonic anhydrase in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. Eur J Biochem. 1986 Aug 1;158(3):443–450. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1986.tb09773.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]