Abstract
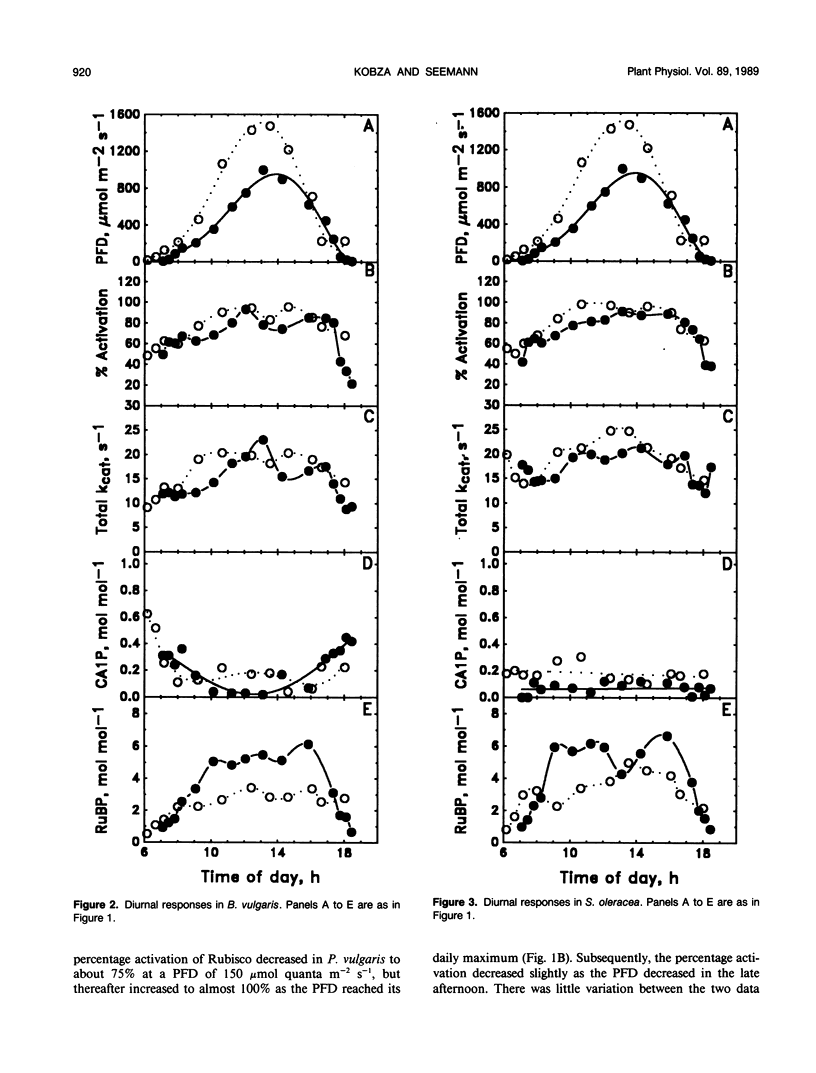
The regulation of ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate (RuBP) carboxylase (Rubisco) activity and metabolite pool sizes in response to natural diurnal changes in photon flux density (PFD) was examined in three species (Phaseolus vulgaris, Beta vulgaris, and Spinacia oleracea) known to differ in the mechanisms used for this regulation. Diurnal regulation of Rubisco activity in P. vulgaris was primarily the result of metabolism of the naturally occurring tight-binding inhibitor of Rubisco, 2-carboxyarabinitol 1-phosphate (CA1P). In B. vulgaris, the regulation of Rubisco activity was the result of both changes in activation state and CA1P metabolism. In S. oleracea, Rubisco activity was regulated by a combination of changes in activation state and the binding/release of another tight binding inhibitor, probably RuBP. Despite these different mechanisms for the light regulation of Rubisco activity, the relationship between the in vivo activity of Rubisco and the PFD was the same for all three species. Rates of CA1P metabolism were thus sufficient to allow this mechanism to participate in the diurnal regulation of Rubisco activity as PFD changed at its normal rate. Furthermore, under natural conditions this regulatory mechanism was found to be important in controlling Rubisco activity over approximately the same range of PFD as did changes in activation state of the enzyme. Finally, this regulation of Rubisco activity resulted in relatively similar and saturating RuBP pool sizes for photosynthesis at all but the lowest PFD values in all three species.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Berry J. A., Lorimer G. H., Pierce J., Seemann J. R., Meek J., Freas S. Isolation, identification, and synthesis of 2-carboxyarabinitol 1-phosphate, a diurnal regulator of ribulose-bisphosphate carboxylase activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Feb;84(3):734–738. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.3.734. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brooks A., Portis A. R. Protein-bound ribulose bisphosphate correlates with deactivation of ribulose bisphosphate carboxylase in leaves. Plant Physiol. 1988 May;87(1):244–249. doi: 10.1104/pp.87.1.244. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chu D. K., Bassham J. A. Regulation of ribulose 1,5-diphosphate carboxylase by substrates and other metabolites: further evidence for several types of binding sites. Plant Physiol. 1975 Apr;55(4):720–726. doi: 10.1104/pp.55.4.720. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jordan D. B., Chollet R. Inhibition of ribulose bisphosphate carboxylase by substrate ribulose 1,5-bisphosphate. J Biol Chem. 1983 Nov 25;258(22):13752–13758. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kobza J., Edwards G. E. Influences of leaf temperature on photosynthetic carbon metabolism in wheat. Plant Physiol. 1987 Jan;83(1):69–74. doi: 10.1104/pp.83.1.69. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kobza J., Seemann J. R. Light-dependent kinetics of 2-carboxyarabinitol 1-phosphate metabolism and ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase activity in vivo. Plant Physiol. 1989 Jan;89(1):174–179. doi: 10.1104/pp.89.1.174. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kobza J., Seemann J. R. Mechanisms for light-dependent regulation of ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase activity and photosynthesis in intact leaves. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jun;85(11):3815–3819. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.11.3815. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laing W. A., Christeller J. T. A model for the kinetics of activation and catalysis of ribulose 1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase. Biochem J. 1976 Dec 1;159(3):563–570. doi: 10.1042/bj1590563. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miziorko H. M., Lorimer G. H. Ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase-oxygenase. Annu Rev Biochem. 1983;52:507–535. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.52.070183.002451. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mott K. A., Jensen R. G., O'leary J. W., Berry J. A. Photosynthesis and Ribulose 1,5-Bisphosphate Concentrations in Intact Leaves of Xanthium strumarium L. Plant Physiol. 1984 Dec;76(4):968–971. doi: 10.1104/pp.76.4.968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perchorowicz J. T., Raynes D. A., Jensen R. G. Light limitation of photosynthesis and activation of ribulose bisphosphate carboxylase in wheat seedlings. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 May;78(5):2985–2989. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.5.2985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robinson S. P., Portis A. R. Involvement of stromal ATP in the light activation of ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase/oxygenase in intact isolated chloroplasts. Plant Physiol. 1988 Jan;86(1):293–298. doi: 10.1104/pp.86.1.293. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robinson S. P., Streusand V. J., Chatfield J. M., Portis A. R. Purification and assay of rubisco activase from leaves. Plant Physiol. 1988 Dec;88(4):1008–1014. doi: 10.1104/pp.88.4.1008. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salvucci M. E., Anderson J. C. Factors affecting the activation state and the level of total activity of ribulose bisphosphate carboxylase in tobacco protoplasts. Plant Physiol. 1987 Sep;85(1):66–71. doi: 10.1104/pp.85.1.66. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seemann J. R., Berry J. A., Freas S. M., Krump M. A. Regulation of ribulose bisphosphate carboxylase activity in vivo by a light-modulated inhibitor of catalysis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Dec;82(23):8024–8028. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.23.8024. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seemann J. R., Kirschbaum M. U., Sharkey T. D., Pearcy R. W. Regulation of Ribulose-1,5-Bisphosphate Carboxylase Activity in Alocasia macrorrhiza in Response to Step Changes in Irradiance. Plant Physiol. 1988 Sep;88(1):148–152. doi: 10.1104/pp.88.1.148. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seemann J. R., Sharkey T. D. Salinity and Nitrogen Effects on Photosynthesis, Ribulose-1,5-Bisphosphate Carboxylase and Metabolite Pool Sizes in Phaseolus vulgaris L. Plant Physiol. 1986 Oct;82(2):555–560. doi: 10.1104/pp.82.2.555. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seemann J. R., Sharkey T. D. The Effect of Abscisic Acid and Other Inhibitors on Photosynthetic Capacity and the Biochemistry of CO(2) Assimilation. Plant Physiol. 1987 Jul;84(3):696–700. doi: 10.1104/pp.84.3.696. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Servaites J. C. Binding of a Phosphorylated Inhibitor to Ribulose Bisphosphate Carboxylase/Oxygenase during the Night. Plant Physiol. 1985 Aug;78(4):839–843. doi: 10.1104/pp.78.4.839. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vu C. V., Allen L. H., Bowes G. Effects of Light and Elevated Atmospheric CO(2) on the Ribulose Bisphosphate Carboxylase Activity and Ribulose Bisphosphate Level of Soybean Leaves. Plant Physiol. 1983 Nov;73(3):729–734. doi: 10.1104/pp.73.3.729. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


