Abstract
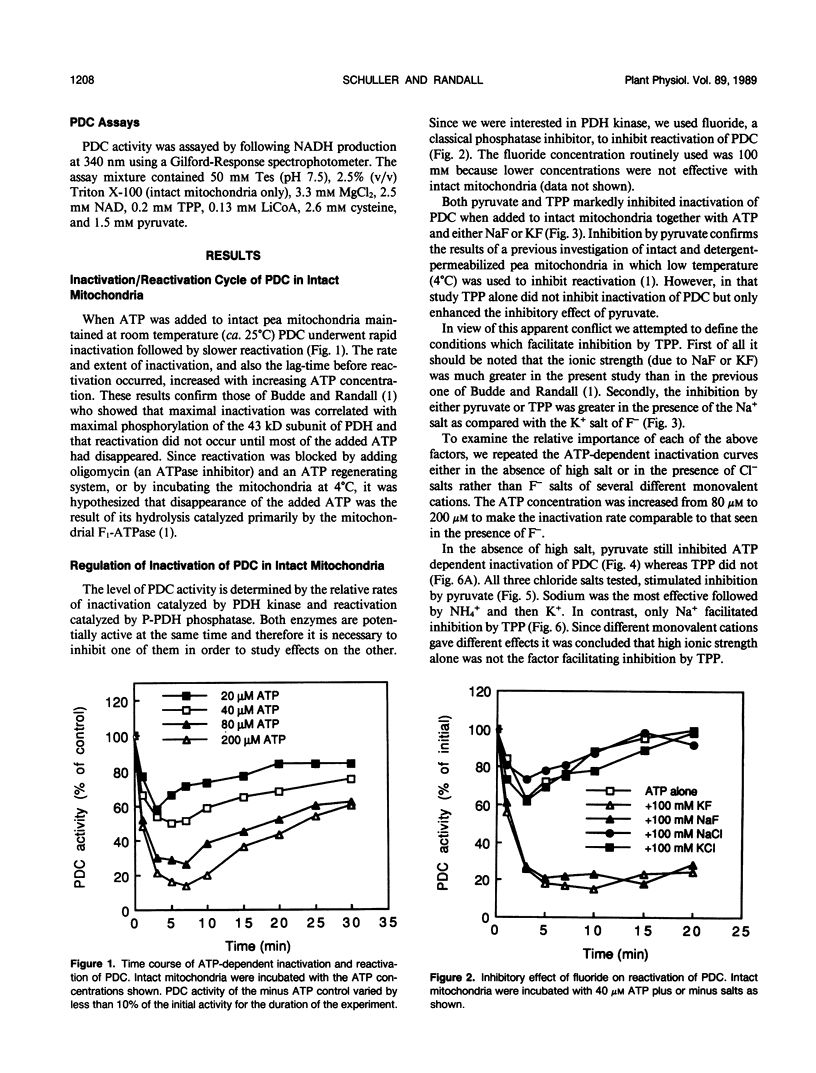
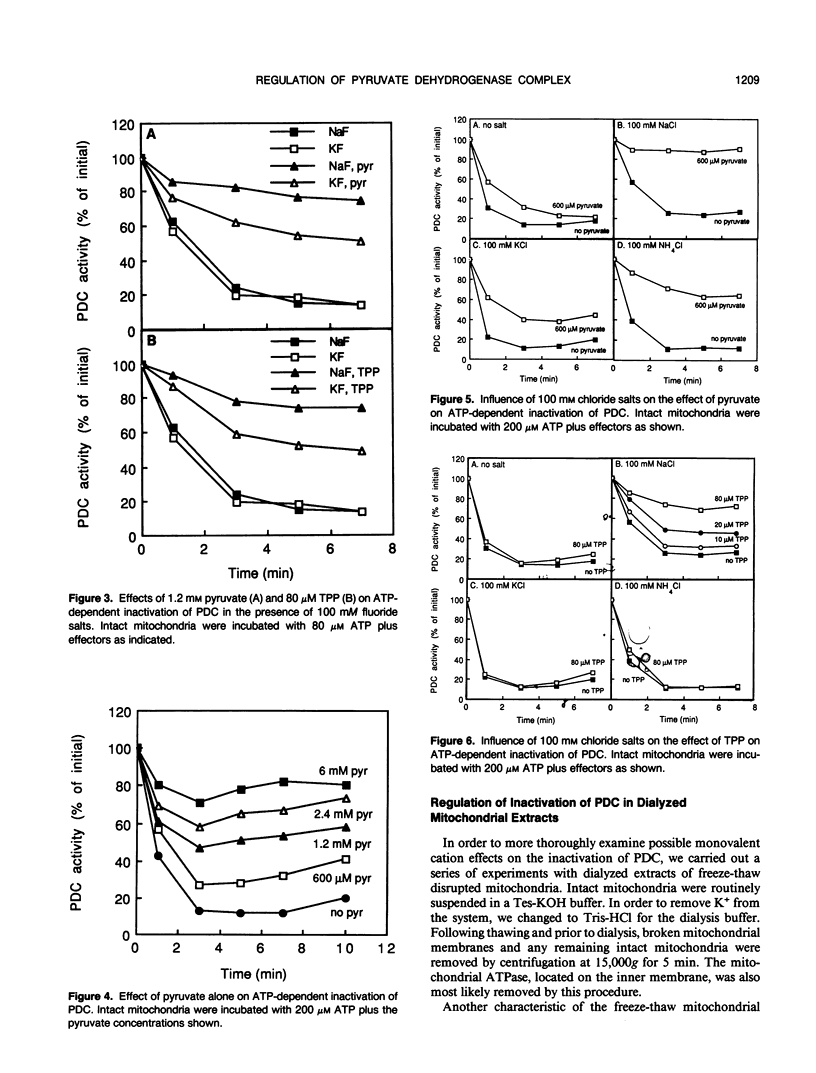
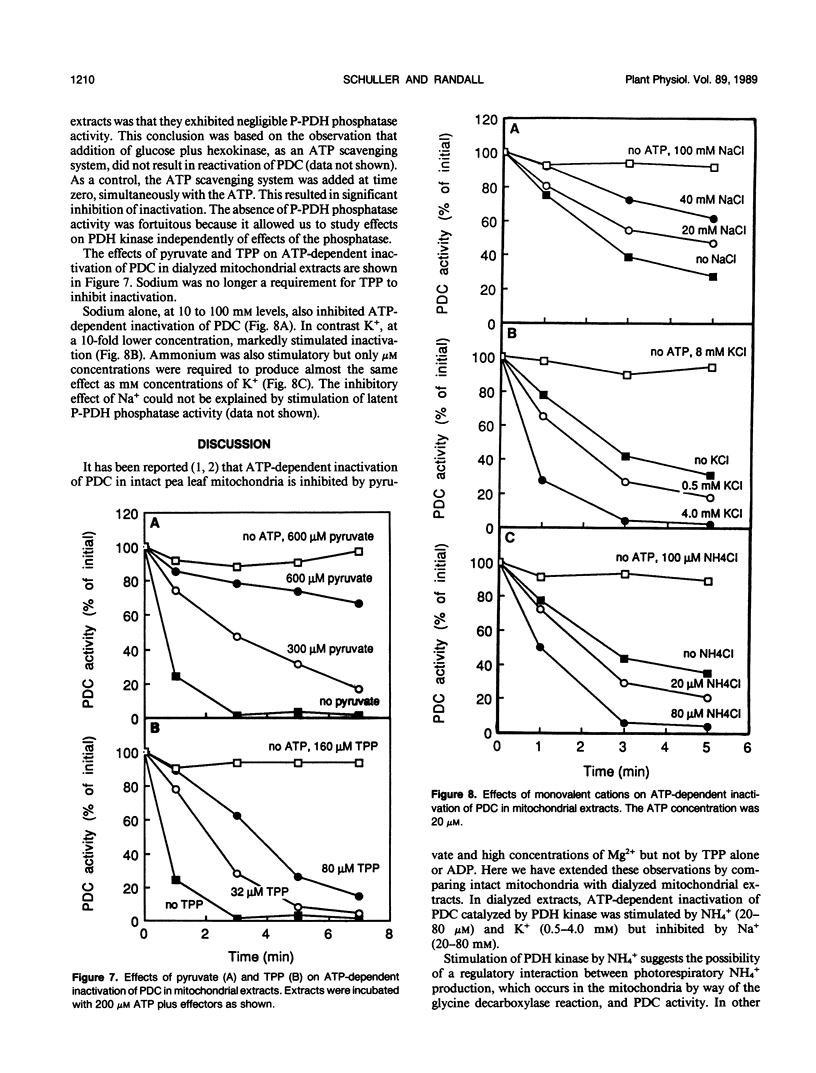
Inactivation of the pyruvate dehydrogenase complex catalyzed by pyruvate dehydrogenase kinase was studied using intact mitochondria purified from green leaf tissue of pea (Pisum sativum L.) and dialyzed mitochondrial extracts. Thiamine pyrophosphate was inhibitory in dialyzed extracts but not in intact mitochondria, except in the presence of high concentrations of Na+. NH4+, at concentrations as low as 20 micromolar, markedly stimulated inactivation in dialyzed extracts. K+ in the range 1 to 10 millimolar also enhanced inactivation. In contrast, Na+ was without affect at lower concentrations but was inhibitory at 10 to 100 millimolar levels. The effect of NH4+ is discussed in relation to a possible regulatory interaction between photorespiratory NH4+ production and the entry of carbon into the tricarboxylic acid cycle by way of the pyruvate dehydrogenase complex.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Budde R. J., Fang T. K., Randall D. D. Regulation of the phosphorylation of mitochondrial pyruvate dehydrogenase complex in situ: effects of respiratory substrates and calcium. Plant Physiol. 1988 Dec;88(4):1031–1036. doi: 10.1104/pp.88.4.1031. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Budde R. J., Randall D. D. Regulation of pea mitochondrial pyruvate dehydrogenase complex activity: inhibition of ATP-dependent inactivation. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1987 Nov 1;258(2):600–606. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(87)90382-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Budde R. J., Randall D. D. Regulation of steady state pyruvate dehydrogenase complex activity in plant mitochondria : reactivation constraints. Plant Physiol. 1988 Dec;88(4):1026–1030. doi: 10.1104/pp.88.4.1026. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Denton R. M., Randle P. J., Bridges B. J., Cooper R. H., Kerbey A. L., Pask H. T., Severson D. L., Stansbie D., Whitehouse S. Regulation of mammalian pyruvate dehydrogenase. Mol Cell Biochem. 1975 Oct 31;9(1):27–53. doi: 10.1007/BF01731731. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gardeström P., Wigge B. Influence of Photorespiration on ATP/ADP Ratios in the Chloroplasts, Mitochondria, and Cytosol, Studied by Rapid Fractionation of Barley (Hordeum vulgare) Protoplasts. Plant Physiol. 1988 Sep;88(1):69–76. doi: 10.1104/pp.88.1.69. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hucho F., Randall D. D., Roche T. E., Burgett M. W., Pelley J. W., Reed L. J. -Keto acid dehydrogenase complexes. XVII. Kinetic and regulatory properties of pyruvate dehydrogenase kinase and pyruvate dehydrogenase phosphatase from bovine kidney and heart. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1972 Jul;151(1):328–340. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(72)90504-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin F., Winspear M. J., Macfarlane J. D., Oaks A. Effect of Methionine Sulfoximine on the Accumulation of Ammonia in C(3) and C(4) Leaves : The Relationship between NH(3) Accumulation and Photorespiratory Activity. Plant Physiol. 1983 Jan;71(1):177–181. doi: 10.1104/pp.71.1.177. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miernyk J. A., Randall D. D. Some kinetic and regulatory properties of the pea mitochondrial pyruvate dehydrogenase complex. Plant Physiol. 1987 Feb;83(2):306–310. doi: 10.1104/pp.83.2.306. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller G., Evans H. J. The Influence of Salts on Pyruvate Kinase from Tissues of Higher Plants. Plant Physiol. 1957 Jul;32(4):346–354. doi: 10.1104/pp.32.4.346. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morris P. F., Layzell D. B., Canvin D. T. Ammonia Production and Assimilation in Glutamate Synthase Mutants of Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant Physiol. 1988 May;87(1):148–154. doi: 10.1104/pp.87.1.148. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson J. B., Evans H. J. Properties of pyruvate kinase from soybean nodule cytosol. Plant Physiol. 1978 Jun;61(6):909–914. doi: 10.1104/pp.61.6.909. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Randall D. D., Williams M., Rapp B. J. Phosphorylation-dephosphorylation of pyruvate dehydrogenase complex from pea leaf mitochondria. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1981 Apr 1;207(2):437–444. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(81)90051-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubin P. M., Randall D. D. Regulation of plant pyruvate dehydrogenase complex by phosphorylation. Plant Physiol. 1977 Jul;60(1):34–39. doi: 10.1104/pp.60.1.34. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubin P. M., Zahler W. L., Randall D. D. Plant pyruvate dehydrogenase complex: analysis of the kinetic properties and metabolite regulation. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1978 May;188(1):70–77. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(78)90357-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomlinson J. D., Turner J. F. Pyruvate kinase of higher plants. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 Nov 2;329(1):128–139. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(73)90015-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


