Abstract
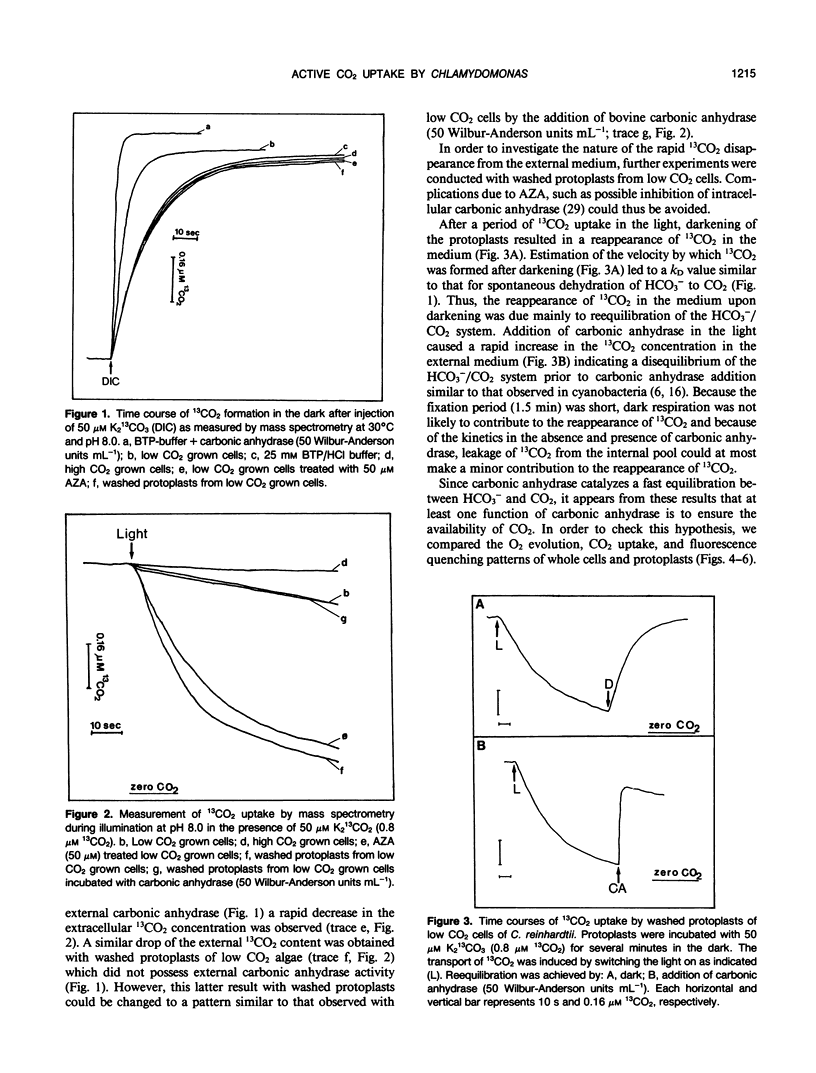
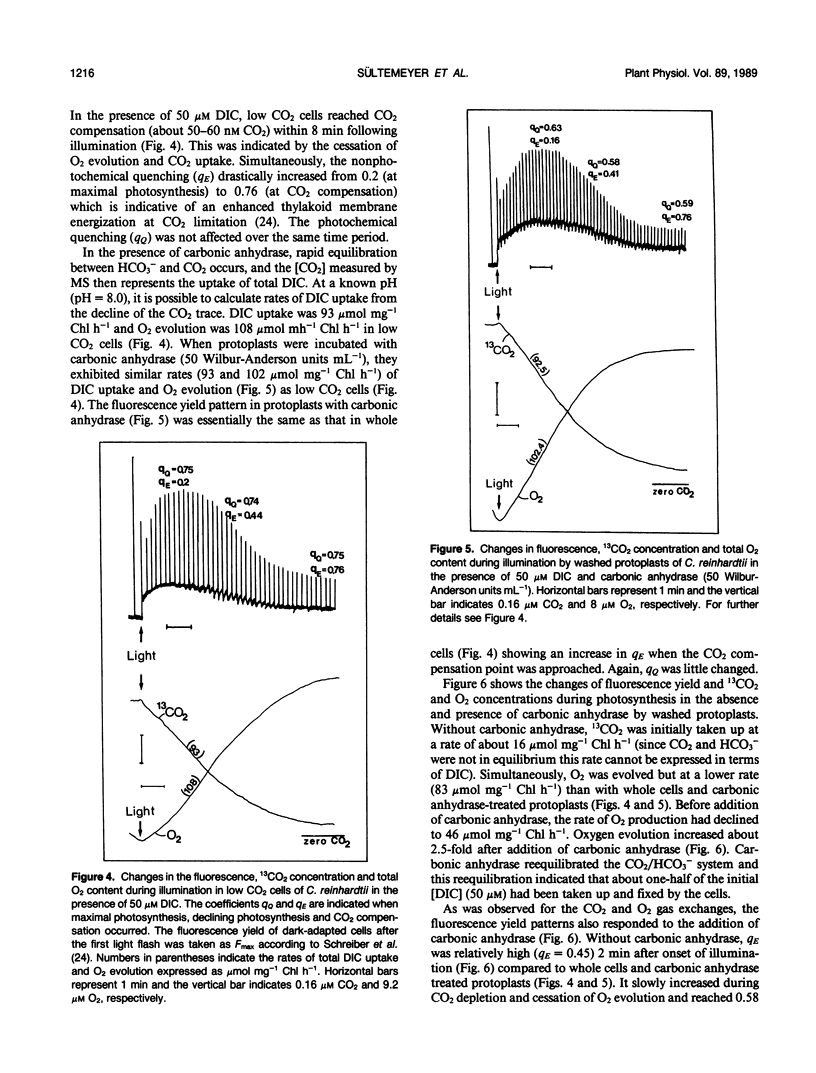
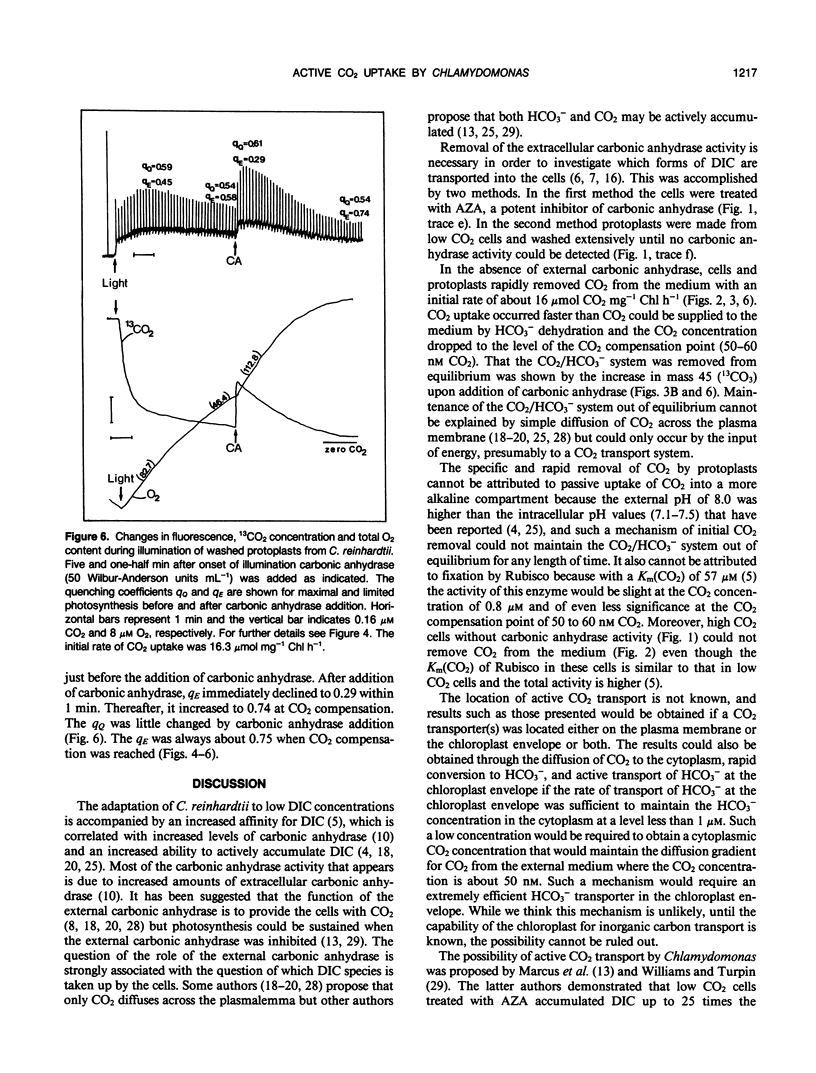
Mass spectrometric measurements of dissolved free 13CO2 were used to monitor CO2 uptake by air grown (low CO2) cells and protoplasts from the green alga Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. In the presence of 50 micromolar dissolved inorganic carbon and light, protoplasts which had been washed free of external carbonic anhydrase reduced the 13CO2 concentration in the medium to close to zero. Similar results were obtained with low CO2 cells treated with 50 micromolar acetazolamide. Addition of carbonic anhydrase to protoplasts after the period of rapid CO2 uptake revealed that the removal of CO2 from the medium in the light was due to selective and active CO2 transport rather than uptake of total dissolved inorganic carbon. In the light, low CO2 cells and protoplasts incubated with carbonic anhydrase took up CO2 at an apparently low rate which reflected the uptake of total dissolved inorganic carbon. No net CO2 uptake occurred in the dark. Measurement of chlorophyll a fluorescence yield with low CO2 cells and washed protoplasts showed that variable fluorescence was mainly influenced by energy quenching which was reciprocally related to photosynthetic activity with its highest value at the CO2 compensation point. During the linear uptake of CO2, low CO2 cells and protoplasts incubated with carbonic anhydrase showed similar rates of net O2 evolution (102 and 108 micromoles per milligram of chlorophyll per hour, respectively). The rate of net O2 evolution (83 micromoles per milligram of chlorophyll per hour) with washed protoplasts was 20 to 30% lower during the period of rapid CO2 uptake and decreased to a still lower value of 46 micromoles per milligram of chlorophyll per hour when most of the free CO2 had been removed from the medium. The addition of carbonic anhydrase at this point resulted in more than a doubling of the rate of O2 evolution. These results show low CO2 cells of Chlamydomonas are able to transport both CO2 and HCO3− but CO2 is preferentially removed from the medium. The external carbonic anhydrase is important in the supply to the cells of free CO2 from the dehydration of HCO3−.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Badger M. R., Andrews T. J. Photosynthesis and Inorganic Carbon Usage by the Marine Cyanobacterium, Synechococcus sp. Plant Physiol. 1982 Aug;70(2):517–523. doi: 10.1104/pp.70.2.517. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Badger M. R., Bassett M., Comins H. N. A Model for HCO(3) Accumulation and Photosynthesis in the Cyanobacterium Synechococcus sp: Theoretical Predictions and Experimental Observations. Plant Physiol. 1985 Feb;77(2):465–471. doi: 10.1104/pp.77.2.465. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Badger M. R., Kaplan A., Berry J. A. Internal Inorganic Carbon Pool of Chlamydomonas reinhardtii: EVIDENCE FOR A CARBON DIOXIDE-CONCENTRATING MECHANISM. Plant Physiol. 1980 Sep;66(3):407–413. doi: 10.1104/pp.66.3.407. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Espie G. S., Miller A. G., Birch D. G., Canvin D. T. Simultaneous Transport of CO(2) and HCO(3) by the Cyanobacterium Synechococcus UTEX 625. Plant Physiol. 1988 Jul;87(3):551–554. doi: 10.1104/pp.87.3.551. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller A. G., Colman B. Active transport and accumulation of bicarbonate by a unicellular cyanobacterium. J Bacteriol. 1980 Sep;143(3):1253–1259. doi: 10.1128/jb.143.3.1253-1259.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller A. G., Espie G. S., Canvin D. T. Active Transport of CO(2) by the Cyanobacterium Synechococcus UTEX 625 : Measurement by Mass Spectrometry. Plant Physiol. 1988 Mar;86(3):677–683. doi: 10.1104/pp.86.3.677. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller A. G., Turpin D. H., Canvin D. T. Growth and Photosynthesis of the Cyanobacterium Synechococcus leopoliensis in HCO(3)-Limited Chemostats. Plant Physiol. 1984 Aug;75(4):1064–1070. doi: 10.1104/pp.75.4.1064. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moroney J. V., Husic H. D., Tolbert N. E. Effect of Carbonic Anhydrase Inhibitors on Inorganic Carbon Accumulation by Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. Plant Physiol. 1985 Sep;79(1):177–183. doi: 10.1104/pp.79.1.177. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moroney J. V., Kitayama M., Togasaki R. K., Tolbert N. E. Evidence for Inorganic Carbon Transport by Intact Chloroplasts of Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. Plant Physiol. 1987 Mar;83(3):460–463. doi: 10.1104/pp.83.3.460. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moroney J. V., Tolbert N. E. Inorganic Carbon Uptake by Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. Plant Physiol. 1985 Feb;77(2):253–258. doi: 10.1104/pp.77.2.253. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palmqvist K., Sjöberg S., Samuelsson G. Induction of Inorganic Carbon Accumulation in the Unicellular Green Algae Scenedesmus obliquus and Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. Plant Physiol. 1988 Jun;87(2):437–442. doi: 10.1104/pp.87.2.437. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlösser U. G., Sachs H., Robinson D. G. Isolation of protoplasts by means of a "species-specific" autolysine in Chlamydomonas. Protoplasma. 1976;88(1):51–64. doi: 10.1007/BF01280359. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams T. G., Turpin D. H. The Role of External Carbonic Anhydrase in Inorganic Carbon Acquisition by Chlamydomonas reinhardii at Alkaline pH. Plant Physiol. 1987 Jan;83(1):92–96. doi: 10.1104/pp.83.1.92. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


