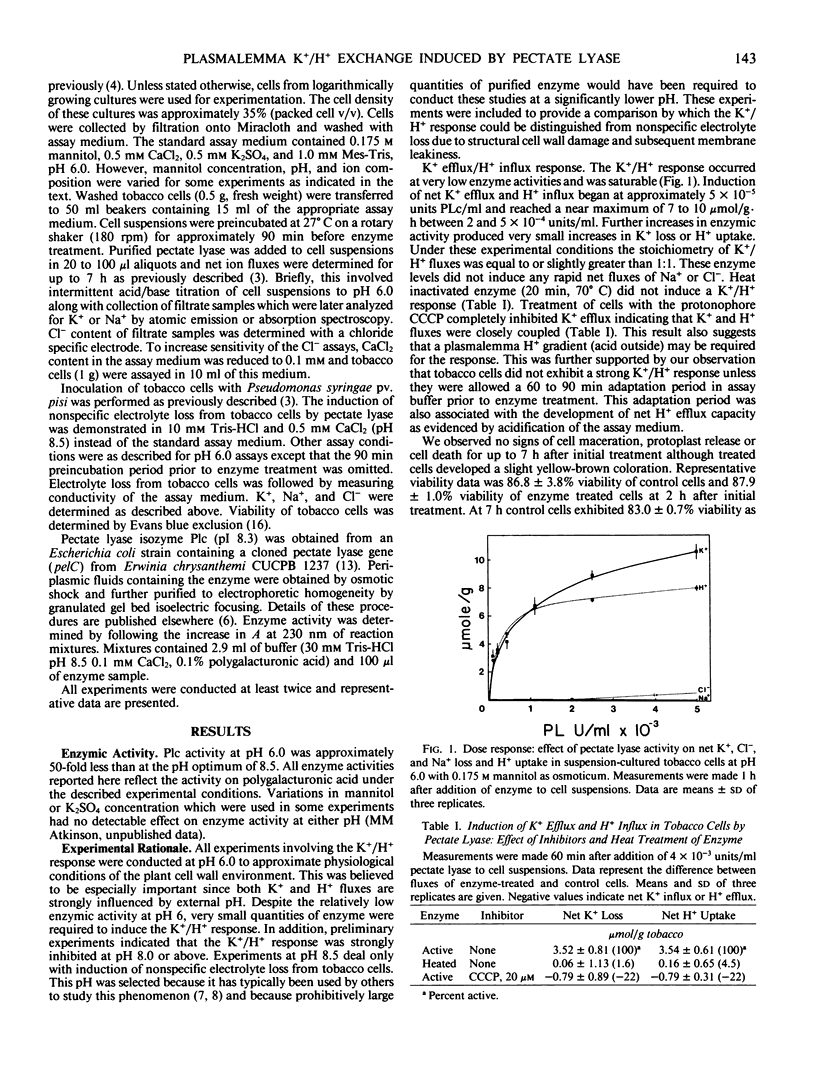
Abstract
A purified pectate lyase isozyme derived from Erwinia chrysanthemi induced rapid net K+ efflux and H+ influx in suspension-cultured tobacco cells. Comparable fluxes of other ions (Na+, Cl−) were not observed. The K+ efflux/H+ influx response began within 15 minutes after addition of enzyme to cell suspensions and continued for approximately 1 hour after which cells resumed the net H+ efflux exhibited prior to enzyme treatment. The response was not prolonged by a second enzyme dose 1 hour after the first. The K+/H+ response was characterized by saturation at low enzymic activity (2 × 10−3 units per milliliter), and inhibition by the protonophore, carbonyl cyanide m-chlorophenylhydrazone, and was not associated with membrane leakiness caused by structural cell wall damage. The total K+ loss and H+ uptake induced by enzyme was one-fourth to one-third that induced by Pseudomonas syringae pv. pisi and did not reduce cell viability. These results indicate that pectate lyase induces a K+ efflux/H+ influx response in tobacco similar to but of shorter duration than that induced by P. syringae pv. pisi during the hypersensitive response. Pectate lyase or other cell wall degrading enzymes may therefore influence the induction of hypersensitivity.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson J. D., Mattoo A. K., Lieberman M. Induction of ethylene biosynthesis in tobacco leaf discs by cell wall disesting enzymes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1982 Jul 30;107(2):588–596. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(82)91532-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Atkinson M. M., Huang J. S., Knopp J. A. The Hypersensitive Reaction of Tobacco to Pseudomonas syringae pv. pisi: Activation of a Plasmalemma K/H Exchange Mechanism. Plant Physiol. 1985 Nov;79(3):843–847. doi: 10.1104/pp.79.3.843. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bishop P. D., Pearce G., Bryant J. E., Ryan C. A. Isolation and characterization of the proteinase inhibitor-inducing factor from tomato leaves. Identity and activity of poly- and oligogalacturonide fragments. J Biol Chem. 1984 Nov 10;259(21):13172–13177. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bruce R. J., West C. A. Elicitation of Casbene Synthetase Activity in Castor Bean : THE ROLE OF PECTIC FRAGMENTS OF THE PLANT CELL WALL IN ELICITATION BY A FUNGAL ENDOPOLYGALACTURONASE. Plant Physiol. 1982 May;69(5):1181–1188. doi: 10.1104/pp.69.5.1181. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collmer A., Schoedel C., Roeder D. L., Ried J. L., Rissler J. F. Molecular cloning in Escherichia coli of Erwinia chrysanthemi genes encoding multiple forms of pectate lyase. J Bacteriol. 1985 Mar;161(3):913–920. doi: 10.1128/jb.161.3.913-920.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis K. R., Lyon G. D., Darvill A. G., Albersheim P. Host-Pathogen Interactions : XXV. Endopolygalacturonic Acid Lyase from Erwinia carotovora Elicits Phytoalexin Accumulation by Releasing Plant Cell Wall Fragments. Plant Physiol. 1984 Jan;74(1):52–60. doi: 10.1104/pp.74.1.52. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gardner J. M., Kado C. I. Polygalacturonic acid trans-eliminase in the osmotic shock fluid of Erwinia rubrifaciens: characterization of the purified enzyme and its effect on plant cells. J Bacteriol. 1976 Jul;127(1):451–460. doi: 10.1128/jb.127.1.451-460.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jin D. F., West C. A. Characteristics of galacturonic Acid oligomers as elicitors of casbene synthetase activity in castor bean seedlings. Plant Physiol. 1984 Apr;74(4):989–992. doi: 10.1104/pp.74.4.989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keifer D. W., Lucas W. J. Potassium Channels in Chara corallina: CONTROL AND INTERACTION WITH THE ELECTROGENIC H PUMP. Plant Physiol. 1982 Apr;69(4):781–788. doi: 10.1104/pp.69.4.781. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee S. C., West C. A. Polygalacturonase from Rhizopus stolonifer, an Elicitor of Casbene Synthetase Activity in Castor Bean (Ricinus communis L.) Seedlings. Plant Physiol. 1981 Apr;67(4):633–639. doi: 10.1104/pp.67.4.633. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nothnagel E. A., McNeil M., Albersheim P., Dell A. Host-Pathogen Interactions : XXII. A Galacturonic Acid Oligosaccharide from Plant Cell Walls Elicits Phytoalexins. Plant Physiol. 1983 Apr;71(4):916–926. doi: 10.1104/pp.71.4.916. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roby D., Toppan A., Esquerré-Tugayé M. T. Cell surfaces in plant-microorganism interactions : v. Elicitors of fungal and of plant origin trigger the synthesis of ethylene and of cell wall hydroxyproline-rich glycoprotein in plants. Plant Physiol. 1985 Mar;77(3):700–704. doi: 10.1104/pp.77.3.700. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stevens C. F. Biophysical studies of ion channels. Science. 1984 Sep 21;225(4668):1346–1350. doi: 10.1126/science.6089347. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker-Simmons M., Jin D., West C. A., Hadwiger L., Ryan C. A. Comparison of proteinase inhibitor-inducing activities and phytoalexin elicitor activities of a pure fungal endopolygalacturonase, pectic fragments, and chitosans. Plant Physiol. 1984 Nov;76(3):833–836. doi: 10.1104/pp.76.3.833. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


