Abstract
The difficulty of detection at an early stage and the ease of developing resistance to chemotherapy render ovarian cancer (OVC) difficult to cure. Although several novel cancer therapies have been developed recently, drug resistance remains a concern since chemotherapy remains as the most commonly used treatment for cancer patients. Therefore, there is an urgent need to reclaim potential combination treatments for OVC. So far, there have been several research targeting the endocannabinoid system (ECS) in cancer. Among the various cannabinoid-based drugs, endocannabinoids, which are lipid molecules generated in the body, have been reported to produce many anti-tumor effects; however, research investigating the anti-chemoresistance effect of endocannabinoids in OVC remains unclear. In this study, we aimed to combine endocannabinoids, anandamide (AEA), and 2-arachidonoylglycerol (2-AG) with chemotherapeutic drugs as a combination approach to treat OVC. Our results showed that OVC cells expressed both cannabinoid receptors (CBR), CB1 and CB2, suggesting the possibility of endocannabinoid system (ECS) as a target. We found that the anti-chemoresistance effect mediated by endocannabinoids was caused by upregulation of ceramide levels, leading to severe endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress and increased autophagy in chemoresistant cancer cells. Therefore, chemoresistant cancer cell growth was inhibited, and cell apoptosis was induced under combined treatments. Based on our results, endocannabinoids overcomed chemoresistance of OVC cells in vitro. Our findings suggest that drugs targeting ECS may have the potential to be adjuvants for chemotherapy by increasing the efficacy of chemotherapeutic drugs and decreasing their side effects.
Keywords: Ovarian cancer, chemoresistance, endocannabinoid system, ER stress, autophagy
Introduction
Although ovarian cancer (OVC) is relatively rare in women compared to other types of cancer, its high fatality makes it the leading cause of death in gynecological cancer [1]. The reason that the mortality rate of OVC remains obstinately high may be due to its unapparent signs at the early stage and its tendency to relapse after a 2- to 10-year treatment, thus easily developing chemoresistance to platinum- or taxane-based drugs. Chemoresistance remains an important issue since chemotherapy is still the most commonly used treatment despite the development of several novel cancer treatments, such as immunotherapies or therapeutic cancer vaccines [2]. For these novel cancer treatments to be widely applied in clinics, decades of development are still required to mature the techniques and reduce costs. Therefore, during the transition period of cancer treatment, it is still worthwhile to explore new treatments to overcome chemoresistance in OVC and to improve the poor prognosis of cancer patients.
The involvement of ER stress in the development of drug resistance has long been discussed. ER stress can be activated by the outside environment, such as hypoxia, changes of tumor microenvironment or cytotoxic therapy, and inner conditions, such as dysregulated metabolism and altered transcription of oncogenes [3]. Activation of ER stress could either benefit cancer cell proliferation, metastasis and chemoresistance, or hinder cancer progression by inducing cell apoptosis. Some studies have found that persistent and moderate ER stress may promote drug resistance by increasing the expression of NF-κB or anti-apoptotic proteins, such as the Bcl-2 family [4], while other studies have shown that severe ER stress restrains tumor growth [5,6]. Hence, interfering with ER homeostasis and triggering a lethal ER stress response by the combination of standard therapies with other drugs that modulate ER stress may be considered for cancer patients. Autophagy, the downstream signaling pathway of ER stress, has also been implicated in the development of chemoresistance. Autophagy is a process by which cells strike a balance between survival and death through the degradation of myriad proteins and organelles, and as such, maintains well-behaved protein functions [7]. It plays a complex role in cancer cell survival. Although some studies have found that autophagy activation increases chemoresistance in some cancers, others have suggested a lack of autophagy may also promote tumor growth [8]. Therefore, either insufficient or excessive autophagy can lead to cell apoptosis [9].
The endocannabinoid system (ECS), which includes cannabinoid receptors 1 and 2 (CB1 and CB2), endogenous cannabinoids (endocannabinoids), and their degradation enzymes, controls miscellaneous physiological capabilities, and their pleiotropic nature renders it feasible for use as targeted molecular therapy in many diseases [10]. To date, many cannabinoid-based drugs have been used for medical purposes and investigated in several diseases, such as mental disorders, neurodegenerative disorders, epilepsy and cancer [11,12]. The application of the two best-known endocannabinoids, AEA and 2-AG, has also been studied, especially in cancer [13-15]. Both AEA and 2-AG have been reported to elicit various anti-tumor effects, including the inhibition of the cell cycle, cell migration, invasion, and the induction of cell death in a variety of cancers, such as glioma, melanoma, lung cancer, breast cancer, and prostate cancer [16,17]. Moreover, previous studies have found the existence of ECS in the ovarian surface epithelium and fallopian tube, which are potential origins of ovarian tumors [18-21], thus suggesting the possibility of targeting ECS to treat OVC. Another study also reported that higher CB1 expression levels were positively correlated with the severity of OVC [22], indicating that CB1 may promote tumorigenesis or aggravate cancer progression. Despite of the above findings, the exact role of ECS in the development of OVC remains unclear [23], and whether endocannabinoids, AEA and 2-AG, can be used as “adjuvants” for boosting the therapeutic efficacy of standard chemotherapy has not been investigated in OVC so far. Therefore, we aimed to decipher the ability of endocannabinoids to reverse chemoresistance in OVC.
Based on previous research indicating that some cannabinoid-based drugs are capable of inducing apoptosis leading to tumor retardation by enhancing ER stress and autophagy [24-27], we also found that the overwhelming ER stress and autophagy triggered by endocannabinoids could overcome the chemoresistance in OVC, thus inducing chemoresistant cancer cell death under combined treatments. These findings are also consistent with previous research reporting that several cannabinoid-based drugs exert their anti-tumor effects through the activation of ER stress and autophagy in various cancers [28,29]. Our study demonstrates the mechanism underlying endocannabinoid-induced reversion of chemoresistance and highlights the potential use of endocannabinoids in OVC.
Materials and methods
Cell lines and culture
ES2 (RRID: CVCL_3509) and IGROV1 (RRID: CVCL_1304) OVC cell lines were cultured in McCoy’s 5A (Sigma, #M4892) and RPMI 1640 (Gibco, #31800022) media supplemented with 10% fetal bovine serum and 1% penicillin/streptomycin, respectively. Normal ovarian epithelial cells (IOSE398, HOSE6-3, and HOSE11-12) were cultured in 1:1 ratio of MCDB 105 (Sigma, #M6395) and M199 (Sigma, #M0393) media. The cells were incubated under 5% CO2 at 37°C. Cell lines had been authenticated by short tandem repeat profiling and had been routinely tested for mycoplasma. Cisplatin-resistant cells were selected by sequential drug treatments until they could survive with 2 μM cisplatin (Sigma, #P4394). Paclitaxel-resistant cells were selected until they could tolerate with 0.01 μg/mL (for ES2 cell line) or 0.1 μg/mL (for IGROV1 cell line) paclitaxel (Sigma, #T7402).
Chemical compounds and cell toxicity analysis
Chemical compounds including AEA (Cayman, #90050), 2-AG (Cayman, #62160), myriocin (Sigma, #M1177), cisplatin (Sigma, #P4394), paclitaxel (Sigma, #T7402) and chloroquine (Cayman, #14194) were used in this study. For cell toxicity analysis, both ES2 and IGROV1 OVC cell lines were seeded in 3-cm dish for 18-24 h, followed by treatment with different concentrations of endocannabinoids and chemotherapeutic drugs for 48 h. The cells were fixed in 4% paraformaldehyde (Alfa Aesar, #43368) was stained with 1 μg/mL Hoechst 33342 (Sigma, #14533) for 1 h. Images of each dish were taken under an inverted microscope, and the cell numbers were counted using ImageJ software. IC50 values for each drug were analyzed using OriginLab software.
Western blotting
Cells were lysed in radioimmune precipitation assay (RIPA) buffer containing 150 mM NaCl, 10 mM EDTA, 50 mM Tris-HCl at pH 7.4, 1% NP-40, 0.004% sodium azide, 0.5% sodium deoxycholate, 0.1% SDS, and protease inhibitor cocktail (MilliporeSigma, #11836153001) and supplemented with 1 mM NaF, 1 mM PMSF, and 1 mM Na3VO4. Proteins from whole cell lysates were separated by SDS-PAGE gel and electroblotted onto nitrocellulose membrane, which was incubated with several primary antibodies (Supplementary Table 1). The immunocomplexes were incubated with horseradish peroxidase-conjugated IgG and detected using an enhanced chemiluminescence (ECL) detection kit (Amersham, #RPN2236).
Immunofluorescence staining and confocal image
Cells seeded in a 3-cm glass bottom dish for 18-24 h were fixed, permeabilized, and blocked with 4% paraformaldehyde, 0.5% Triton X-100, and CAS-BlockTM Histochemical Reagent (Life Technologies, #008120) respectively and then incubated with primary antibodies against CB1 (Cayman, #101500), CB2 (Cayman, #101550), ceramide (Sigma, #C8104), and LC3 (MBL, #PM036) at 4°C overnight. Alexa 488- or 543-conjugated secondary antibodies (Invitrogen) along with 1 μg/mL Hoechst 33342, was stained for 1 h at room temperature. Immunofluorescence images were taken under an inverted microscope or Olympus FluoView laser scanning confocal microscope (FV3000, Olympus) equipped with 405 nm, 488 nm, and 543 nm lasers.
Cell cycle arrest analysis
Cells were treated with endocannabinoids or chemotherapeutic drugs for 48 h, trypsinized, washed twice with PBS and centrifuged at 300 g for 10 min. The cells were fixed with ethanol for 1 h at 4°C. Next, 100 μg/mL RNase A (Bio Basic, #RB0437) was added for 15 min, followed by 40 μg/mL propidium iodide (PI; Sigma, #P4170) staining for 30 min. Cells were filtered using an 80 μm nylon mesh, and the cell cycle was examined using a CytoFLEX flow cytometer (Beckman Coulter).
Apoptosis flow cytometry
After treatment with endocannabinoids and chemotherapeutic drugs for 48 h, cells were trypsinized, washed twice with PBS and centrifuged at 300 g for 5 min. An Annexin V/PI staining kit (Invitrogen, #V13242) was used to detect apoptotic cells. Live cells were stained with annexin V and PI for 15 min and suspended in 1-fold annexin binding buffer. After filtration through 80 μm nylon mesh, CytoFLEX flow cytometer (Beckman Coulter) was used to quantify the percentage of apoptotic cells.
Clinical samples of OVC patients and immunohistochemistry (IHC)
Paraffin-embedded clinical OVC samples, including normal ovarian tissue and serous or clear cell tumor tissues, were obtained from Human Biobank of the Research Center of Clinical Medicine at NCKU Hospital. The study was approved by the Human Research Ethics Committee of NCKU Hospital (IRB: B-ER-107-356). Immunohistochemistry (IHC) was performed according to a standard protocol. Clinical samples were deparaffinized, and antigen retrieval was performed using citrate buffer. Endogenous peroxidase was removed by 6% H2O2 and blocked with SuperBlockTM T20 blocking buffer (Thermo, #37516). Samples were then incubated with serum, CB1 (Cayman, #101500), or CB2 (Cayman, #101550) antibodies overnight at 4°C, followed by the incubtaion of secondary antibodies conjugated with IgG-HRP for 1 h. In the final step, samples were stained with diaminobenzidine (DAB, Thermo, #34002) chromogen counterstained with hematoxylin. Slides were mounted using a mounting medium (Leica Biosystems, #3801731), and images were taken under an inverted microscope.
RNA extraction, reverse transcription and quantitative PCR analysis
Total RNA was extracted by TRIzol reagent (Life Technologies, #15596018). Chloroform (Sigma, #c2432), 100% isopropanol (Sigma, #19516) and 75% ethanol were used to extract RNA. In the following, RNA pellet was heated at 55°C and was dissolved in DEPC-water (Protech, #PT-P560). RNA purity and concentration were measured by microplate readers (SpectraMax ABS Plus, Molecular Devices) at the absorbance of 230/260/280 nm. cDNA synthesis was subsequently performed using PrimeScript RT Reagent Kit (Takara, #RR037A) by MiniAmp Plus thermal cycler (Applied Biosystems, Waltham, MA, USA). StepOnePlus Real-Time PCR System (Applied Biosystems) was used to perform qPCR analysis. Severl primers for homo sapiens (Supplementary Table 2) [30] and SYBR Green Master (Applied Biosystems, #A25741) were used to detect DNA expression levels. The Ct value of targeted genes was relative to that of GAPDH (reference gene) in each cell line, and the comparative Ct value of targeted genes in chemoresistant cell lines was normalized with wild-type cell lines.
Statistical analysis
All values are reported as mean ± standard error of the mean (SEM). One-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) was used to analyze multiple groups. Statistical analyses were performed using SPSS and OriginLab. Statistical significance was set at P<0.05.
Data availability
The raw data of KM plot analysis in Figure 1A were obtained from Kaplan-Meier Plotter at http://kmplot.com. The derived data and other original data, materials and analysis generated in this study are available from corresponding author on request.
Figure 1.
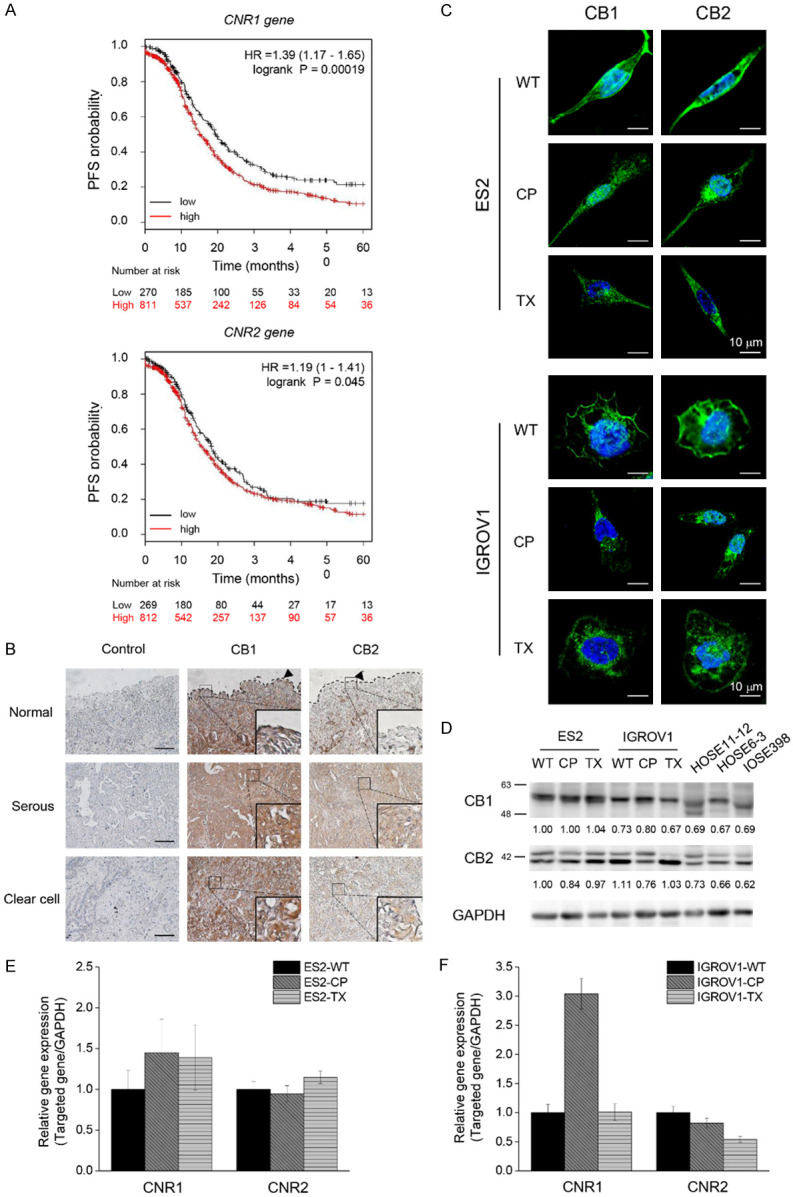
Existence of CB1 and CB2 in OVC. A. Kaplan-Meier plots showed the high and low expression levels of CNR1 and CNR2 genes in OVC cohort study. Log rank p-value and hazard ratio (HR) are shown in the figures. B. Representative images of CB1 or CB2 immunoreactivity in ovarian tissues. Images of serum control were presented on the left panel. In the middle and the right panels, brown color intensity represented the expression of CB1 and CB2. Enlarged images were shown in the lower right corner. Dotted lines displayed the location of normal epithelium. Scale bars, 100 μm. C. Representative images taken by confocal microscopy showed that both ES2 and IGROV1 cell lines expressed CB1 and CB2 (green). Nucleus was stained by Hoechst dye (blue). D. Comparison of CB1 and CB2 Western blotting between cancer cell lines (ES2 and IGROV1) and normal cell lines (HOSE11-12, HOSE6-3, IOSE398). GAPDH was served as the internal control. E, F. CNR1 and CNR2 mRNA expression levels in OVC cells. The Ct value of CNR1 and CNR2 was compared to GAPDH mRNA level in each cell line, and the comparative Ct value of CNR1 and CNR2 in chemoresistant cells was normalized with wild-type cells. The Y axis showed the fold change of CNR1 and CNR2 mRNA expression levels between wild-type and chemoresistant cells. The experiments were repeated for at least three times. Bars represent mean ± SEM. WT: wild-type, non-chemoresistant cell line, CP: cisplatin-resistant cell line, TX: paclitaxel-resistant cell line.
Results
Higher mRNA expression of CB1 and CB2 genes predicts poor prognosis and the expression of CBR in OVC
To determine the relationship between ECS and survival rate, Kaplan-Meier plotter (KM plotter) database [31] was used to analyze the progression-free survival (PFS) of 1081 OVC patients in stages III and IV. Patients with endometrioid and serous OVC were treated with different types of chemotherapy, including cisplatin, carboplatin, paclitaxel, docetaxel, avastin, topotecan, and gemcitabine, and all of them received optimal or suboptimal debulking surgery. We found a higher expression of CNR1 or CNR2 genes predicted a lower survival rate in cancer patients, suggesting that changes in endocannabinoid signaling may be related to cancer relapse, chemoresistance, and metastasis (Figure 1A). Consistent with the results mentioned above, the higher expression of CB1 and CB2 could be observed in serous or clear cell types of ovarian tumors than in normal epithelium (Figure 1B). To determine whether the endocannabinoid system could be targeted in OVC, we performed immunofluorescence to identify CB1 and CB2 expression in epithelial OVC cells. We found that CB1 and CB2 were mainly located on the cell membranes of wild-type and chemoresistant (CP, cisplatin-resistant; TX, paclitaxel-resistant) ES2 and IGROV1 cell lines, with a few in the cytosol (Figure 1C). Further Western blotting showed the existence of cannabinoid receptors in OVC cells and normal ovarian epithelial cells. The expression of CB1 in the cisplatin-resistant IGROV1 cell line was also higher than that in wild-type or paclitaxel-resistant IGROV1 cell lines. In addition, the multiple bands of CB2 observed in the immunoblot may be due to alternative splicing in the cells (Figure 1D). We also found the mRNA of CNR1 in chemoresistant cell lines also showed higher expression level when comopared to wild-type cell lines, whereas there was no significant difference of mRNA expression of CNR2 between each cell lines (Figure 1E, 1F). These results suggest that the endocannabinoid system is a potential target for treating OVC.
Combined treatments of endocannabinoids and chemotherapy decreases the viability of OVC cells
To address the anti-tumor effects of endocannabinoids, we first treated both wild-type and chemoresistant cells with AEA or 2-AG. Based on these results, we found that chemoresistant cancer cells were also refractory to endocannabinoids compared to their wild-type counterparts (Figure 2A, 2B). In addition, the IC50 values of cisplatin in resistant cell lines were approximately 20-fold (for ES2 cells) and 8-fold (for IGROV1 cells) higher than those in their wild-type counterparts. On the other hand, the IC50 value of paclitaxel in resistant ES2 cells was approximately 6-fold higher than that in the wild-type, while the IC50 value of paclitaxel could not be calculated for paclitaxel-resistant IGROV1 (Figure 2C, 2D). We combined IC30 and IC50 values of AEA and 2-AG calculated from the wild-type curve (Figure 2A, 2B; black line) with chemotherapy to treat chemoresistant cancer cells. The combined treatments impeded the percentage of cells and lowered the IC50 values of cisplatin and paclitaxel in chemoresistant cells, indicating that endocannabinoids can potentiate the therapeutic efficacy of chemotherapy and reverse chemoresistance. As expected, the inhibition of cancer cell growth under IC30 and IC50 values of endocannabinoids did not have significant difference, suggesting IC30 of endocannabinoids was enough to produce the anti-tumor effects (Figure 2E-H). Therefore, we investigated the mechanism underlying the chemosensitization effects of IC30 of endocannabinoids in subsequent experiments. As previous studies have reported the biphasic effects of cannabinoid-based drugs, we also found that endocannabinoids possess biphasic properties on cancer cell growth. We treated cancer cells with lower concentrations of endocannabinoids and found cell growth was promoted at nanomolar concentrations (Supplementary Figure 1A, 1B) and was inhibited at higher concentrations. The tendency of endocannabinoids in nanomolar-range to promote cell growth was observed.
Figure 2.
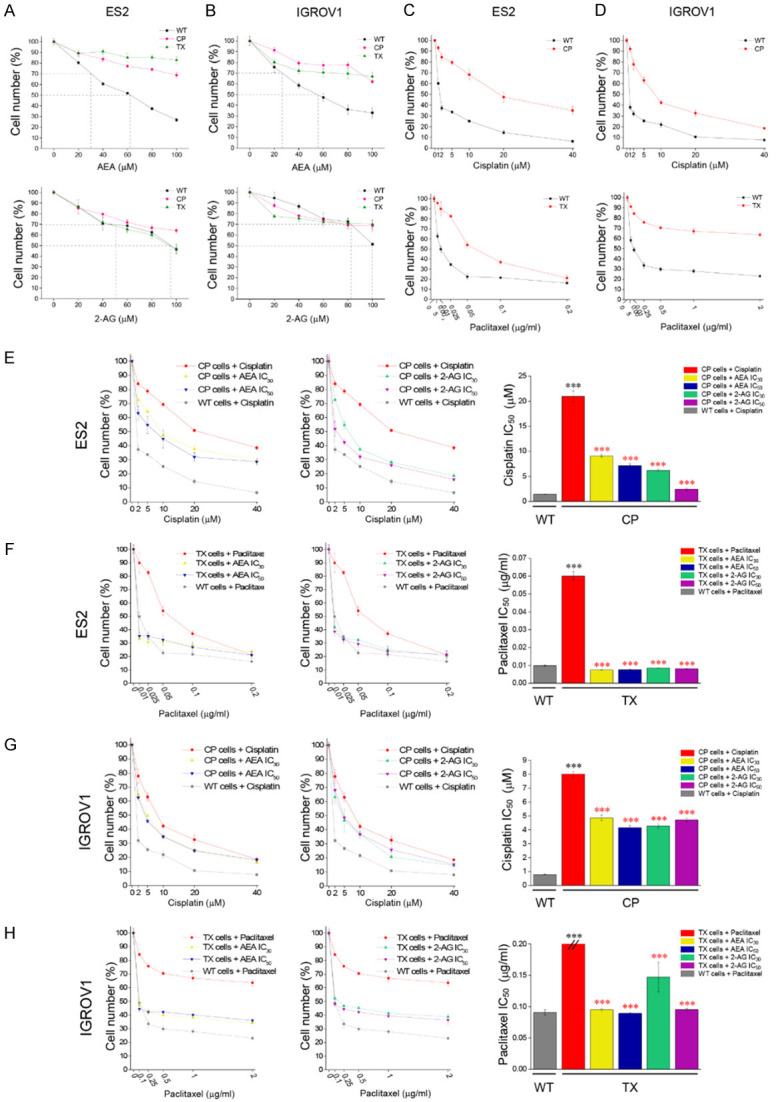
Cell toxicity of endocannabinoids and chemotherapeutic drugs on OVC cell growth. A, B. AEA and 2-AG were treated for 48 h at 0-100 μM on ES2 and IGROV1 cell lines. C and D. Cisplatin (0-40 μM) and paclitaxel (0-0.2 μg/mL) were treated for 48 h on both ES2 and IGROV1 cell lines. E-H. Different concentration of cisplatin or paclitaxel were combined with endocannabinoids to treat both ES2 and IGROV1 cell lines. In the left and middle images, red solid line represents CP- or TX-resistant cell lines. Yellow/blue or green/purple solid lines represent the addition of IC30 or IC50 values of AEA or 2-AG respectively on cisplatin- or paclitaxel-resistant cell lines. Gray dotted line represents wild-type cell line. In the right panels, IC50 values of cisplatin or paclitaxel were analyzed and compared between wild-type or chemoresistant cell lines. Black asterisk symbolized the IC50 comparison between wild-type and resistant cell lines, while red asterisk represented the IC50 comparison between the treatment of chemotherapeutic drugs alone and combined treatments with several conditions in resistant cell lines. ***P<0.001 by one-way ANOVA. All experiments were repeated for three independent experiments. Bars represent mean ± SEM.
Endocannabinoid-induced ceramide causes the activation of ER stress pathways
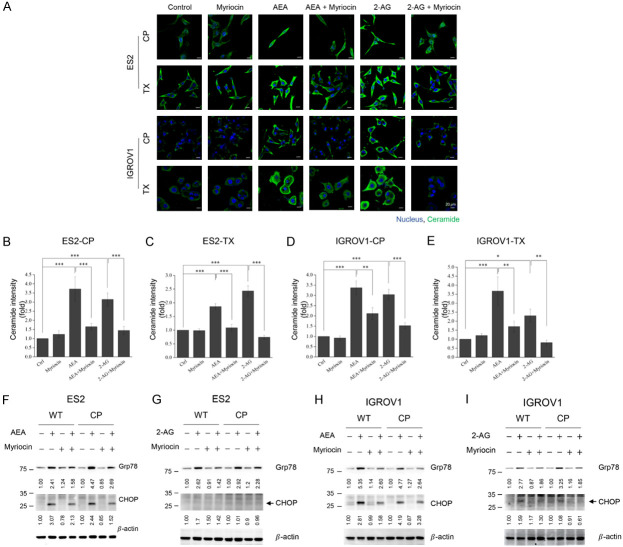
While analyzing the chemosensitization mechanism of endocannabinoids, we first investigated whether endocannabinoids could arrest or delay cell cycle progression and inhibit cell proliferation to improve chemotherapeutic efficacy. Chemoresistant cells were incubated with chemotherapy alone or in combination for 24 h. However, neither chemotherapy nor combined treatments arrested or delayed the cell cycle (Supplementary Figure 2A, 2B). Endocannabinoids themselves also could not arrest the cell cycle in wild-type cancer cells (Supplementary Figure 2C, 2D). Hence, the inhibition of cell number by combined treatments may be caused by other mechanisms. In this study, we found that both AEA and 2-AG upregulated ceramide levels, and the increase in ceramide levels could be prevented by pretreatment with the ceramide synthase inhibitor, myriocin (Figure 3A). Quantification results also showed a significant difference in ceramide intensity between control groups and endocannabinoid-treated groups (Figure 3B-E). We further investigated whether endocannabinoids activated ER stress by upregulating ceramide levels. Incubation with AEA increased the levels of glucose-regulated protein (GRP78/BiP), of which elevation could be seen as ER stress activation, as well as the downstream protein CHOP, in both wild-type and cisplatin-resistant cancer cells (Figure 3F, 3H). In addition, 2-AG significantly increased GRP78 levels but slightly increased CHOP expression (Figure 3G, 3I). Pre-treatment with myriocin alleviated ER stress, indicating that ER stress was stimulated by endocannabinoid-induced ceramide upregulation (Figure 3F-I).
Figure 3.
Endocannabinoids up-regulate ceramide levels and induce ER stress in chemoresistant cells. A. Chemoresistant cancer cells were pre-treated with 2 μM myriocin for 1 h and were incubated with IC30 of AEA or 2-AG for 24 h. Antibody against ceramide was used, and the nucleus was stained by Hoechst dye (blue). Representative images were shown, and all images were taken by confocal microscopy. B-E. The fold change of ceramide intensity was quantified. The results were analyzed from three independent experiments. F-I. Wild-type and cisplatin-resistant cancer cells were pre-treated with 2 μM myriocin for 1 h and were incubated IC30 of AEA or 2-AG for 48 h. Antibodies against Grp78 and CHOP were used for immunoblotting analysis. β-actin was served as the internal control. Arrowhead indicates the position of CHOP proteins on the immunoblots. Bars represent mean ± SEM. *P<0.05, **P<0.01, ***P<0.001 by one-way ANOVA.
Activation of various ER stress pathways and autophagy induced by endocannabinoids and combined treatments
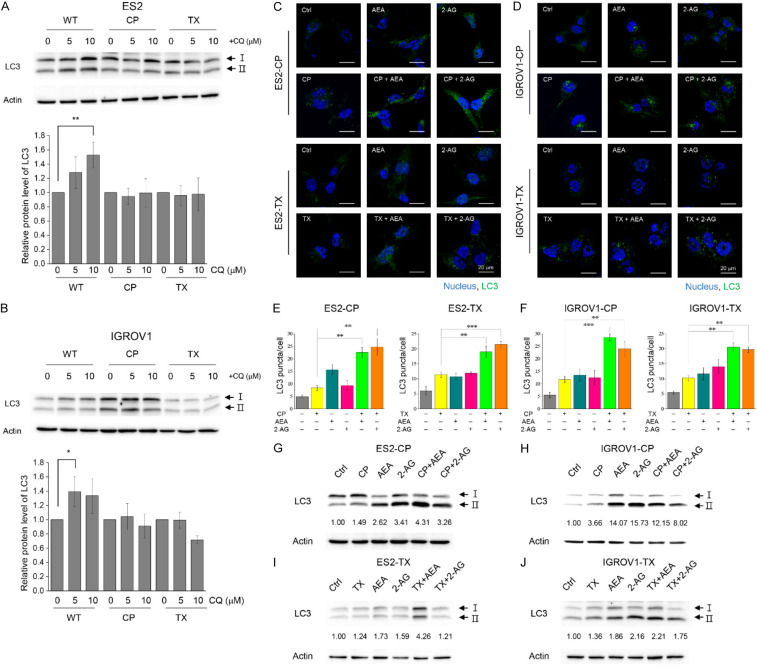
Because the chemotherapeutic drugs used in this study target different molecular levels; for instance, cisplatin interacts with DNA, and paclitaxel functions as microtubule-stabilizing agent, we preliminary investigated the activation of ER stress pathways induced by combined treatments in cisplatin-resistant cells to explore the chemosensitization effects of endocannabinoids. Cisplatin alone could not activate any ER stress pathways in resistant cell lines; however, the activation of three well-known ER stress pathways, including cleavage of ATF6α, phosphorylation of IRE1α, phosphorylation of eIF2α of which upstream signal is PERK, and CHOP expression, was elevated under AEA alone, 2-AG alone or combined treatments in a time-dependent manner in general (Figure 4A-D). The results indicated that both AEA and 2-AG induced ER stress on which AEA exerted a stronger impact in cisplatin-resistant cells. Moreover, ER stress activation induced by endocannabinoids was also observed in non-chemoresistant wild-type cancer cells (Supplementary Figure 3). Due to the crosslink between ER stress and autophagy, we tested basal level of autophagy in cancer cells by using chloroquine (CQ), which inhibits the fusion of autophagosome with lysosome, in the following. The results showed that in wild-type cells, LC3-II was higher under CQ treatments compared to control group. However, there was no changes of LC3-II in chemoresistant cells under CQ treatments (Figure 5A, 5B), suggesting the innate regulatory ability of autophagy in chemoresistant cells could refrain the autophagy activation. We next hypothesized endocannabinoids may produce anti-chemoresistance effect by enhancing autophagy level in chemoresistant cells since it has been reported that up-regulation of ceramide and ER stress activation lead to elevation of autophagy. Immunofluorescence results showed that both AEA and 2-AG slightly increased the conversion of LC3-I to LC3-II, which is a process indicating the formation of autophagosomes. Under combined treatments, LC3-II puncta were dramatically elevated in both chemoresistant ES2 (Figure 5C, 5E) and IGROV1 (Figure 5D, 5F) cell lines. Immunoblots also showed an increase in LC3-II formation after incubation with endocannabinoids or their combination (Figure 5G-J). We also tested whether endocannabinoids induced autophagy in wild-type cells and found no LC3 lipidation under endocannabinoid treatments (Supplementary Figure 4). Moreover, myriocin had been found to decrease LC3-II expression in chemoresistant cells, suggesting ceramide induced by endocannabinoids also led to autophagy formation (Supplementary Figure 5). Taken together, endocannabinoids exert chemosensitizing effects by activating ER stress and increasing autophagy levels in chemoresistant OVC.
Figure 4.
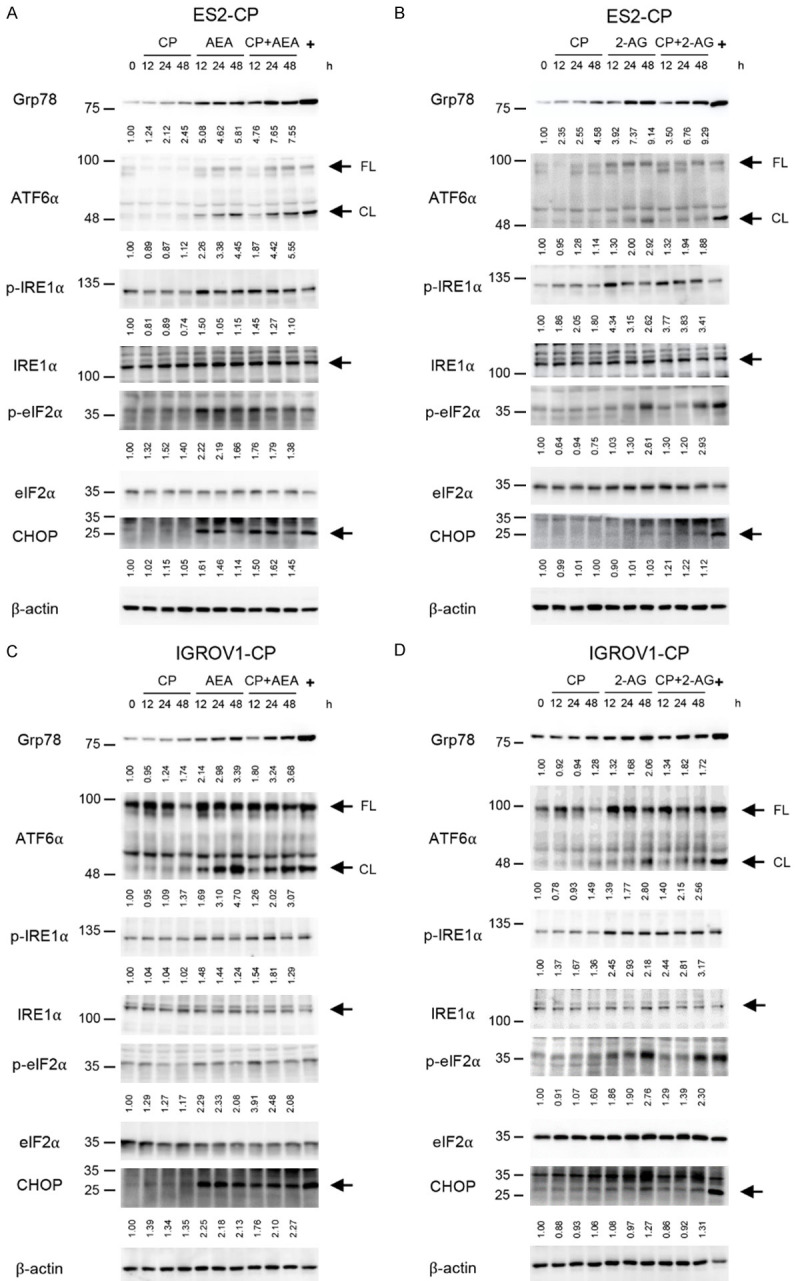
Activation of ER stress in chemoresistant cancer cells under the treatments of endocannabinoids and chemotherapeutic drugs. A-D. Cisplatin-resistant ES2 and IGROV1 cell lines were treated with 2 mM cisplatin and IC30 of AEA and 2-AG for 12, 24 and 48 h. Antibodies against ER stress-related proteins, including Grp78, ATF6α, phospho-IRE1α (p-IRE1α), IRE1α, phospho-eIF2α (p-eIF2α) and eIF2α were used in the immunoblotting analysis. 10 μg/mL tunicamycin was served as positive control (+) of ER stress. β-actin was served as the internal control. FL: full-length form, CL: cleaved form.
Figure 5.
Basal level autophagy in OVC cells and enhancement of autophagy under combination of endocannabinoids and chemotherapeutic drugs. (A, B) Representative LC3 immunoblots and quantification of relative protein level of LC3-II from 3 independent experiments were shown. The protein level of LC3-II was divided by control group in each cell lines. Cells were treated with 5 and 10 μM CQ for 24 h. Actin was served as internal control. Bars represent mean ± SD. (C, D) 10 μM cisplatin, 0.01 μg/mL (for ES2-TX) or 0.1 μg/mL (for IGROV1-TX) paclitaxel and IC30 of AEA or 2-AG were used for treating cisplatin- or paclitaxel-resistant ES2 and IGROV1 cell lines. All drugs were incubated for 48 h. Autophagy was detected by LC3 antibody (green), and the nucleus was stained by Hoechst dye (blue). The images were taken by confocal microscopy. (E, F) Quantification of LC3 puncta per cell from (A and B) was analyzed. The experiments were repeated for three independent experiments. Bars represent mean ± SEM. (G-J) Western blot analysis of LC3 in ES2 and IGROV1 cell lines treated with AEA/2-AG and cisplatin/paclitaxel for 36 h. *P<0.05, **P<0.01, ***P<0.001 by one-way ANOVA.
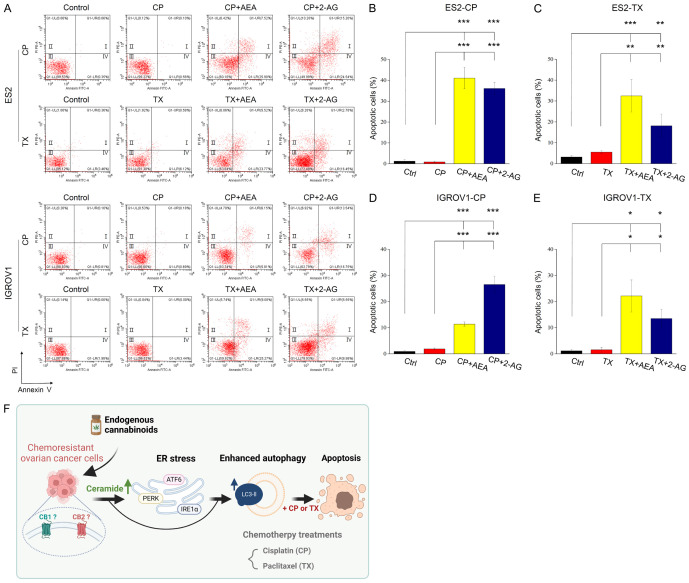
Combined treatments induce apoptosis in chemoresistant cancer cells
Finally, we investigated whether endocannabinoids improve the efficacy of chemotherapeutic drugs to induce apoptosis instead of necrosis. The results showed that combining endocannabinoids with cisplatin or paclitaxel significantly increased the number of cells in the first (I) and fourth (IV) quadrants, which represent the late-stage and the early-stage of apoptotic cells respectively, by flow cytometry assay (Figure 6A); however, cisplatin or paclitaxel alone did not cause apoptosis in chemoresistant cells (Figure 6B-E). Consistent with Figure 2, IC30 value of endocannabinoids could not significantly induce apoptosis in chemoresistant cancer cells (Supplementary Figure 6). In conclusion, our results suggest that endocannabinoids promote the efficacy of chemotherapeutic drugs and reverse chemoresistance by upregulating ceramide, triggering ER stress, and enhancing autophagic levels, thereby inducing apoptosis in chemoresistant OVC cells (Figure 6F).
Figure 6.
Endocannabinoids combined with chemotherapeutic drugs induce apoptosis in chemoresistant cancer cells. A. Chemoresistant cancer cells were treated with 2 mM cisplatin, 0.01 μg/mL (for ES2-TX) or 0.1 μg/mL (for IGROV1-TX) paclitaxel and IC30 of AEA or 2-AG for 48 h. Annexin V and propidium iodide were used to quantify apoptosis. Representative images of flow cytometry were shown. B-E. Quantification of the percentage of apoptotic cells was analyzed from three independent experiments. The bars represent mean ± SEM. F. Schematic diagram shows the mechanism about how endocannabinoids reverse chemoresistance in OVC. *P<0.05, **P<0.01, ***P<0.001 by one-way ANOVA.
Discussion
In this study, we combined endocannabinoids with chemotherapeutic drugs to develop a potential therapy for women with intractable OVC, as well as shed some light on the signaling pathway of the endocannabinoid system in ovarian tumors. From bioinformatics, we found higher expression of CNR1 and CNR2 genes was related to poor prognosis. This finding is consistent with previous research showing a strong CB1 intensity in aggressive ovarian tumor tissues [22]. We also found the existence of both CB1 and CB2 in clinical samples and OVC cells, allowing the possibility to apply endocannabinoids for cancer treatment. Although in chemoresistant OVC cells, endocannabinoids could not induce cell death by themselves, we hypothesized that endocannabinoids help reduce chemoresistance by promoting the unfolded protein response (UPR), which in turn increases ER stress loading in cancer cells.
To explain the upregulation of CB1 and CB2 in cancer cells compared to that in normal cells, we reasoned that the endocannabinoid system produces biphasic effects on cancer cell growth through CB1 or CB2 activation. This assumption was based on previous results indicating that changes in endocannabinoid levels correspond to pathological alterations, thereby warranting a concentration-dependent biphasic manner that has been discovered under a variety of physiological conditions [32-34]. By treating cancer cells with a low tone (nanomolar concentration) of endocannabinoids, we found that both AEA and 2-AG accelerated tumor cell proliferation while impeding tumor growth at a higher tone (micromolar concentration; Supplementary Figure 1). In addition, previous studies have analyzed the levels of AEA and 2-AG in follicular fluid and observed a nanomolar tone of AEA and 2-AG in human and mouse models [35,36]. Therefore, our findings suggest that cancer cells may benefit from the nanomolar range of endocannabinoids that originally exist in peripheral tissues, while they may be persecuted by the micromolar range of endocannabinoids given by the outside environment. These results indicate that endocannabinoids can regulate tumor progression depending on their concentration levels under pathophysiological circumstances.
Since it has been reported that cannabinoid-based drugs could increase ceramide levels through the activation of both CB1 and CB2, and thus inducing cancer cell apoptosis [37,38], we also examined whether endocannabinoids could upregulate ceramide levels in OVC. Our results showed that both AEA and 2-AG significantly increased ceramide levels; moreover, endocannabinoid-induced ER stress was suppressed by ceramide synthase inhibitor, indicating that the production of ceramide triggered UPR in OVC cells. In another aspect, more and more research has found the crosslink between ER stress and autophagy and has proposed that severe ER stress is a potent factor for autophagic induction [39,40]. Our results also showed that the combination of endocannabinoids and chemotherapeutic drugs activated severe ER stress after 24 h and significantly increased autophagic levels after 48 h in chemoresistant cancer cells.
The role of autophagy in tumor progression is debated for several years. Either excessive or insufficient autophagic levels has been reported to benefit tumor progression. In our study, we found that the basal level of autophagy was higher in WT cells than that in chemoresistant cells after blocking the fusion of autophagosome and lysosome by CQ treatment (Figure 5A, 5B). In addition, we also observed a higher level of autophagy in cisplatin-resistant IGROV1 cells than that in wild-type or paclitaxel-resistant IGROV1 cells with or without CQ treatment. According to the results mentioned above, we proposed that the dysregulated innate mechanisms of autophagy in chemoresistant OVC cells help cancer avoid the accumulation of autophagosome, thus preventing excessive autophagy and leading to their chemoresistance ability. Therefore, the ability of endocannabinoids to induce excessive autophagic levels in chemoresistant cancer cells by ceramide production and ER stress activation produces the anti-chemoresistance effect. Compared with chemoresistant cancer cells, endocannabinoids did not increase autophagy levels in non-chemoresistant wild-type cancer cells. Finally, we confirmed that the combined treatments dramatically induced apoptosis in chemoresistant cancer cells which essentially lack the response to cisplatin or paclitaxel.
In conclusion, we provided the developmental basis of endocannabinoid treatments as an adjuvant for chemotherapy to promote therapeutic outcomes and reduce side effects. There is a possibility that combining endocannabinoids with chemotherapy is a promising avenue for treating OVC during the transition period from traditional cancer therapies to precision cancer medicine.
Acknowledgements
We thank the technical services provided by the Bioimaging Core Facility of the National Core Facility for Biopharmaceuticals, Ministry of Science and Technology, Taiwan. This work was supported by the National Science and Technology Council of Taiwan [112-2740-B-006-002 and 112-2314-B-006-076].
Disclosure of conflict of interest
None.
Abbreviations
- 2-AG
2-Arachidonoylglycerol
- AEA
Anandamide
- CBR
Cannabinoid receptor
- CP
Cisplatin
- CL
Cleaved form
- ECS
Endocannabinoid system
- ER
Endoplasmic reticulum
- FL
Full-length form
- HR
Hazard ratio
- OVC
Ovarian cancer
- TX
Paclitaxel
- WT
Wild-type
Supporting Information
References
- 1.Siegel RL, Miller KD, Fuchs HE, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2021. CA Cancer J Clin. 2021;71:7–33. doi: 10.3322/caac.21654. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Shaik B, Zafar T, Balasubramanian K, Gupta SP. An overview of ovarian cancer: molecular processes involved and development of target-based chemotherapeutics. Curr Top Med Chem. 2021;21:329–46. doi: 10.2174/1568026620999201111155426. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Chen X, Cubillos-Ruiz JR. Endoplasmic reticulum stress signals in the tumour and its microenvironment. Nat Rev Cancer. 2021;21:71–88. doi: 10.1038/s41568-020-00312-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Cao S, Tang J, Huang Y, Li G, Li Z, Cai W, Yuan Y, Liu J, Huang X, Zhang H. The road of solid tumor survival: from drug-induced endoplasmic reticulum stress to drug resistance. Front Mol Biosci. 2021;8:620514. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2021.620514. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Lhomond S, Avril T, Dejeans N, Voutetakis K, Doultsinos D, McMahon M, Pineau R, Obacz J, Papadodima O, Jouan F, Bourien H, Logotheti M, Jégou G, Pallares-Lupon N, Schmit K, Le Reste PJ, Etcheverry A, Mosser J, Barroso K, Vauléon E, Maurel M, Samali A, Patterson JB, Pluquet O, Hetz C, Quillien V, Chatziioannou A, Chevet E. Dual IRE1 RNase functions dictate glioblastoma development. EMBO Mol Med. 2018;10:e7929. doi: 10.15252/emmm.201707929. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Lam M, Marsters SA, Ashkenazi A, Walter P. Misfolded proteins bind and activate death receptor 5 to trigger apoptosis during unresolved endoplasmic reticulum stress. Elife. 2020;9:e52291. doi: 10.7554/eLife.52291. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Ichim G, Tait SW. A fate worse than death: apoptosis as an oncogenic process. Nat Rev Cancer. 2016;16:539–48. doi: 10.1038/nrc.2016.58. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Li X, Zhou Y, Li Y, Yang L, Ma Y, Peng X, Yang S, Liu J, Li H. Autophagy: a novel mechanism of chemoresistance in cancers. Biomed Pharmacother. 2019;119:109415. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2019.109415. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Taylor MA, Das BC, Ray SK. Targeting autophagy for combating chemoresistance and radioresistance in glioblastoma. Apoptosis. 2018;23:563–575. doi: 10.1007/s10495-018-1480-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Sharma C, Sadek B, Goyal SN, Sinha S, Kamal MA, Ojha S. Small molecules from nature targeting G-protein coupled cannabinoid receptors: potential leads for drug discovery and development. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2015;2015:238482. doi: 10.1155/2015/238482. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Ligresti A, De Petrocellis L, Di Marzo V. From phytocannabinoids to cannabinoid receptors and endocannabinoids: pleiotropic physiological and pathological roles through complex pharmacology. Physiol Rev. 2016;96:1593–659. doi: 10.1152/physrev.00002.2016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Di Marzo V. Targeting the endocannabinoid system: to enhance or reduce? Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2008;7:438–55. doi: 10.1038/nrd2553. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Velasco G, Sánchez C, Guzmán M. Towards the use of cannabinoids as antitumour agents. Nat Rev Cancer. 2012;12:436–44. doi: 10.1038/nrc3247. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Tegeder I. Endocannabinoids as guardians of metastasis. Int J Mol Sci. 2016;17:230. doi: 10.3390/ijms17020230. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Schwarz R, Ramer R, Hinz B. Targeting the endocannabinoid system as a potential anticancer approach. Drug Metab Rev. 2018;50:26–53. doi: 10.1080/03602532.2018.1428344. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Guindon J, Hohmann AG. The endocannabinoid system and cancer: therapeutic implication. Br J Pharmacol. 2011;163:1447–63. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.2011.01327.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Pisanti S, Picardi P, D’Alessandro A, Laezza C, Bifulco M. The endocannabinoid signaling system in cancer. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 2013;34:273–82. doi: 10.1016/j.tips.2013.03.003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.El-Talatini MR, Taylor AH, Elson JC, Brown L, Davidson AC, Konje JC. Localisation and function of the endocannabinoid system in the human ovary. PLoS One. 2009;4:e4579. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0004579. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Kurman RJ, Shih IM. The origin and pathogenesis of epithelial ovarian cancer: a proposed unifying theory. Am J Surg Pathol. 2010;34:433–43. doi: 10.1097/PAS.0b013e3181cf3d79. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Gebeh AK, Willets JM, Marczylo EL, Taylor AH, Konje JC. Ectopic pregnancy is associated with high anandamide levels and aberrant expression of FAAH and CB1 in fallopian tubes. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2012;97:2827–35. doi: 10.1210/jc.2012-1780. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Cecconi S, Rossi G, Castellucci A, D’Andrea G, Maccarrone M. Endocannabinoid signaling in mammalian ovary. Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol. 2014;178:6–11. doi: 10.1016/j.ejogrb.2014.04.011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Messalli EM, Grauso F, Luise R, Angelini A, Rossiello R. Cannabinoid receptor type 1 immunoreactivity and disease severity in human epithelial ovarian tumors. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2014;211:234, e1–6. doi: 10.1016/j.ajog.2014.04.004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Ayakannu T, Taylor AH, Willets JM, Konje JC. The evolving role of the endocannabinoid system in gynaecological cancer. Hum Reprod Update. 2015;21:517–35. doi: 10.1093/humupd/dmv022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Calvaruso G, Pellerito O, Notaro A, Giuliano M. Cannabinoid-associated cell death mechanisms in tumor models (review) Int J Oncol. 2012;41:407–13. doi: 10.3892/ijo.2012.1476. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Carracedo A, Gironella M, Lorente M, Garcia S, Guzmán M, Velasco G, Iovanna JL. Cannabinoids induce apoptosis of pancreatic tumor cells via endoplasmic reticulum stress-related genes. Cancer Res. 2006;66:6748–55. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-06-0169. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Vara D, Salazar M, Olea-Herrero N, Guzmán M, Velasco G, Díaz-Laviada I. Anti-tumoral action of cannabinoids on hepatocellular carcinoma: role of AMPK-dependent activation of autophagy. Cell Death Differ. 2011;18:1099–111. doi: 10.1038/cdd.2011.32. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Armstrong JL, Hill DS, McKee CS, Hernandez-Tiedra S, Lorente M, Lopez-Valero I, Eleni Anagnostou M, Babatunde F, Corazzari M, Redfern CPF, Velasco G, Lovat PE. Exploiting cannabinoid-induced cytotoxic autophagy to drive melanoma cell death. J Invest Dermatol. 2015;135:1629–37. doi: 10.1038/jid.2015.45. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Herrera B, Carracedo A, Diez-Zaera M, Gómez del Pulgar T, Guzmán M, Velasco G. The CB2 cannabinoid receptor signals apoptosis via ceramide-dependent activation of the mitochondrial intrinsic pathway. Exp Cell Res. 2006;312:2121–31. doi: 10.1016/j.yexcr.2006.03.009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Salazar M, Carracedo A, Salanueva IJ, Hernández-Tiedra S, Lorente M, Egia A, Vázquez P, Blázquez C, Torres S, García S, Nowak J, Fimia GM, Piacentini M, Cecconi F, Pandolfi PP, González-Feria L, Iovanna JL, Guzmán M, Boya P, Velasco G. Cannabinoid action induced autophagy-mediated cell death through stimulation of ER stress in human glioma cells. J Clin Invest. 2009;119:1359–72. doi: 10.1172/JCI37948. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Khan MI, Sobocińska AA, Brodaczewska KK, Zielniok K, Gajewska M, Kieda C, Czarnecka AM, Szczylik C. Involvement of the CB2 cannabinoid receptor in cell growth inhibition and G0/G1 cell cycle arrest via the cannabinoid agonist WIN 55,212-2 in renal cell carcinoma. BMC Cancer. 2018;18:583. doi: 10.1186/s12885-018-4496-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Gyorffy B, Lánczky A, Szállási Z. Implementing an online tool for genome-wide validation of survival-associated biomarkers in ovarian-cancer using microarray data of 1287 patients. Endocr Relat Cancer. 2012;19:197–208. doi: 10.1530/ERC-11-0329. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Christie S, O’Rielly R, Li H, Wittert GA, Page AJ. Biphasic effects of methanandamide on murine gastric vagal afferent mechanosensitivity. J Physiol. 2020;598:139–50. doi: 10.1113/JP278696. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Rodríguez-Manzo G, Canseco-Alba A. Biphasic effects of anandamide on behavioural responses: emphasis on copulatory behaviour. Behav Pharmacol. 2015;26:607–15. doi: 10.1097/FBP.0000000000000154. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Lin Y, Shia KS, Hsiao WC, Hsieh WP, Yeh TK, Tseng SL, Hsu CY, Chao YS, Hung MS. Biphasic suppression of appetite by cannabinoid CB1 receptor antagonists with distinct functional activities. Pharmacol Res. 2010;62:337–43. doi: 10.1016/j.phrs.2010.06.001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Fuchs Weizman N, Wyse BA, Szaraz P, Defer M, Jahangiri S, Librach CL. Cannabis alters epigenetic integrity and endocannabinoid signalling in the human follicular niche. Hum Reprod. 2021;36:1922–31. doi: 10.1093/humrep/deab104. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Blanton HL, McHann MC, De Selle H, Dancel CL, Redondo JL, Molehin D, German NA, Trasti S, Pruitt K, Castro-Piedras I, Guindon J. Chronic administration of xannabinoid receptor 2 agonist (JWH-133) increases ectopic ovarian tumor gowth and endocannabinoids (anandamide and 2-arachidonoyl glycerol) levels in immunocompromised SCID female mice. Front Pharmacol. 2022;13:823132. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.823132. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Gustafsson K, Sander B, Bielawski J, Hannun YA, Flygare J. Potentiation of cannabinoid-induced cytotoxicity in mantle cell lymphoma through modulation of ceramide metabolism. Mol Cancer Res. 2009;7:1086–98. doi: 10.1158/1541-7786.MCR-08-0361. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Bettiga A, Aureli M, Colciago G, Murdica V, Moschini M, Lucianò R, Canals D, Hannun Y, Hedlund P, Lavorgna G, Colombo R, Bassi R, Samarani M, Montorsi F, Salonia A, Benigni F. Bladder cancer cell growth and motility implicate cannabinoid 2 receptor-mediated modifications of sphingolipids metabolism. Sci Rep. 2017;7:42157. doi: 10.1038/srep42157. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Song S, Tan J, Miao Y, Zhang Q. Crosstalk of ER stress-mediated autophagy and ER-phagy: involvement of UPR and the core autophagy machinery. J Cell Physiol. 2018;233:3867–74. doi: 10.1002/jcp.26137. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Lin Y, Jiang M, Chen W, Zhao T, Wei Y. Cancer and ER stress: mutual crosstalk between autophagy, oxidative stress and inflammatory response. Biomed Pharmacother. 2019;118:109249. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2019.109249. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Data Availability Statement
The raw data of KM plot analysis in Figure 1A were obtained from Kaplan-Meier Plotter at http://kmplot.com. The derived data and other original data, materials and analysis generated in this study are available from corresponding author on request.
Figure 1.

Existence of CB1 and CB2 in OVC. A. Kaplan-Meier plots showed the high and low expression levels of CNR1 and CNR2 genes in OVC cohort study. Log rank p-value and hazard ratio (HR) are shown in the figures. B. Representative images of CB1 or CB2 immunoreactivity in ovarian tissues. Images of serum control were presented on the left panel. In the middle and the right panels, brown color intensity represented the expression of CB1 and CB2. Enlarged images were shown in the lower right corner. Dotted lines displayed the location of normal epithelium. Scale bars, 100 μm. C. Representative images taken by confocal microscopy showed that both ES2 and IGROV1 cell lines expressed CB1 and CB2 (green). Nucleus was stained by Hoechst dye (blue). D. Comparison of CB1 and CB2 Western blotting between cancer cell lines (ES2 and IGROV1) and normal cell lines (HOSE11-12, HOSE6-3, IOSE398). GAPDH was served as the internal control. E, F. CNR1 and CNR2 mRNA expression levels in OVC cells. The Ct value of CNR1 and CNR2 was compared to GAPDH mRNA level in each cell line, and the comparative Ct value of CNR1 and CNR2 in chemoresistant cells was normalized with wild-type cells. The Y axis showed the fold change of CNR1 and CNR2 mRNA expression levels between wild-type and chemoresistant cells. The experiments were repeated for at least three times. Bars represent mean ± SEM. WT: wild-type, non-chemoresistant cell line, CP: cisplatin-resistant cell line, TX: paclitaxel-resistant cell line.