Abstract
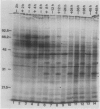
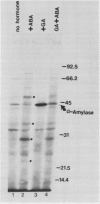
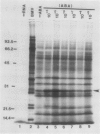
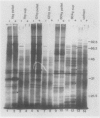
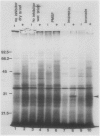
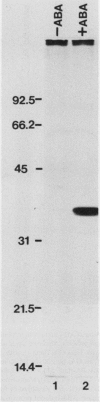
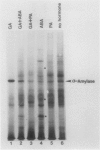
As part of a continuing effort to elucidate the mode of action of abscisic acid (ABA) in barley (Hordeum vulgare L. cv Himalaya) aleurone layers, we have investigated the induction of several polypeptides by ABA in this tissue. There were nine ABA-induced polypeptides as observed by one-dimensional sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis, and considerably more (at least 16 spots) on a two-dimensional gel. These proteins started to show enhanced synthesis 2 to 4 hours after ABA treatment, and their synthesis continued for at least 48 hours. In vitro translation using total RNA isolated from ABA-treated aleurone layers indicated that translatable mRNA levels of these proteins essentially paralleled the levels of in vivo synthesized proteins. The most abundant of the ABA-induced proteins was a 29 kilodalton polypeptide which was also synthesized in tissue incubated without ABA. In vivo synthesis of this protein declined as ABA concentration was decreased, with 1 nanomolar ABA approaching control level. Cell fractionation experiments located the 29 kilodalton major ABA-induced protein in 1,000g and 13,000g pellets; most other induced proteins were in the 80,000g supernatant. The 29 kilodalton protein appeared to be sensitive to degradation by sulfhydryl type proteases. As expected, the induction of these proteins by ABA was suppressed by gibberellic acid. Phaseic acid, the first stable metabolite of ABA, suppressed the gibberellic acid-enhanced α-amylase synthesis but was unable to induce the ABA-induced proteins. None of the ABA-induced proteins were secreted into the incubation medium. A 36 kilodalton ABA-induced protein showed cross-reactivity with antibody against a barley lectin specific for glucosamine, galactosamine, and mannosamine.
Full text
PDF








Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bray E. A., Beachy R. N. Regulation by ABA of beta-Conglycinin Expression in Cultured Developing Soybean Cotyledons. Plant Physiol. 1985 Nov;79(3):746–750. doi: 10.1104/pp.79.3.746. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper P., Ho T. H., Hauptmann R. M. Tissue specificity of the heat-shock response in maize. Plant Physiol. 1984 Jun;75(2):431–441. doi: 10.1104/pp.75.2.431. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dashek W. V., Singh B. N., Walton D. C. Abscisic Acid localization and metabolism in barley aleurone layers. Plant Physiol. 1979 Jul;64(1):43–48. doi: 10.1104/pp.64.1.43. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hammerton R. W., Ho T. H. Hormonal regulation of the development of protease and carboxypeptidase activities in barley aleurone layers. Plant Physiol. 1986 Mar;80(3):692–697. doi: 10.1104/pp.80.3.692. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hickman S., Theodorakis J. L., Greco J. M., Brown P. H. Processing of MOPC 315 immunoglobulin A oligosaccharides: evidence for endoplasmic reticulum and trans Golgi alpha 1,2-mannosidase activity. J Cell Biol. 1984 Feb;98(2):407–416. doi: 10.1083/jcb.98.2.407. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ho D. T. Response of barley aleurone layers to abscisic Acid. Plant Physiol. 1976 Feb;57(2):175–178. doi: 10.1104/pp.57.2.175. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ihle J. N., Dure L., 3rd Hormonal regulation of translation inhibition requiring RNA synthesis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1970 Mar 27;38(6):995–1001. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(70)90338-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jen G., Thach R. E. Inhibition of host translation in encephalomyocarditis virus-infected L cells: a novel mechanism. J Virol. 1982 Jul;43(1):250–261. doi: 10.1128/jvi.43.1.250-261.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mishkind M. L., Raikhel N. V., Palevitz B. A., Keegstra K. The cell biology of wheat germ agglutinin and related lectins. Prog Clin Biol Res. 1983;138:163–176. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mozer T. J. Control of protein synthesis in barley aleurone layers by the plant hormones gibberellic acid and abscisic acid. Cell. 1980 Jun;20(2):479–485. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90634-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Farrell P. H. High resolution two-dimensional electrophoresis of proteins. J Biol Chem. 1975 May 25;250(10):4007–4021. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Partridge J., Shannon L., Gumpf D. A barley lectin that binds free amino sugars. I. Purification and characterization. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Dec 21;451(2):470–483. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(76)90142-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peumans W. J., Stinissen H. M., Carlier A. R. Isolation and partial characterization of wheat-germ-agglutinin-like lectins from rye (Secale cereale) and barley (Hordeum vulgare) embryos. Biochem J. 1982 Apr 1;203(1):239–243. doi: 10.1042/bj2030239. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rogers J. C., Milliman C. Coordinate increase in major transcripts from the high pI alpha-amylase multigene family in barley aleurone cells stimulated with gibberellic acid. J Biol Chem. 1984 Oct 10;259(19):12234–12240. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharkey T. D., Raschke K. Effects of phaseic Acid and dihydrophaseic Acid on stomata and the photosynthetic apparatus. Plant Physiol. 1980 Feb;65(2):291–297. doi: 10.1104/pp.65.2.291. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singh N. K., Handa A. K., Hasegawa P. M., Bressan R. A. Proteins Associated with Adaptation of Cultured Tobacco Cells to NaCl. Plant Physiol. 1985 Sep;79(1):126–137. doi: 10.1104/pp.79.1.126. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Triplett B. A., Quatrano R. S. Timing, localization, and control of wheat germ agglutinin synthesis in developing wheat embryos. Dev Biol. 1982 Jun;91(2):491–496. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(82)90057-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uknes S. J., Ho T. H. Mode of action of abscisic Acid in barley aleurone layers : abscisic Acid induces its own conversion to phaseic Acid. Plant Physiol. 1984 Aug;75(4):1126–1132. doi: 10.1104/pp.75.4.1126. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]