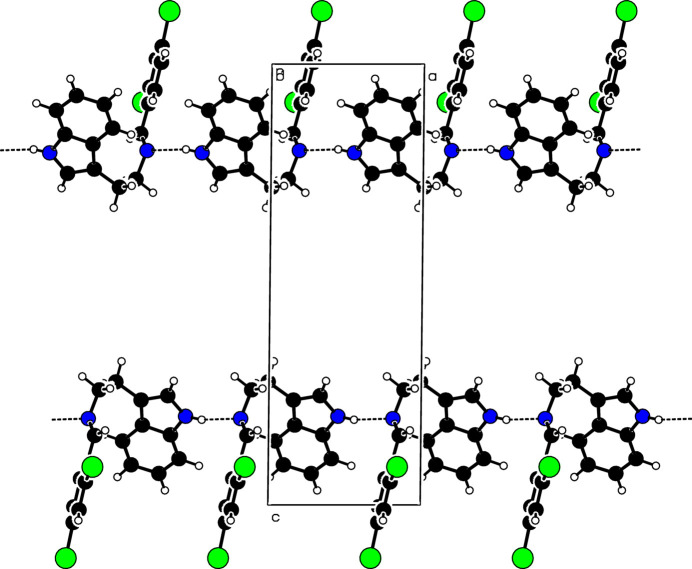
The molecules of the title compound are linked by N—H⋯N hydrogen bonds, generating a C(7) chain extending along the a-axis direction.
Keywords: crystal structure, hydrogen bonding, C—H⋯π interactions
Abstract
In the title compound, C17H14Cl2N2, the molecule exists in an E configuration with respect to the C=N bond of the Schiff base fragment. The dihedral angle between the indole ring system and the benzene ring is 80.86 (12)°. In the crystal, molecules are connected by N—H⋯N hydrogen bonds, generating a C(7) chain extending along the a-axis direction. No aromatic π–π stacking occurs but weak C—H⋯π interactions are observed.

Structure description
Schiff bases are widely used as catalysts, corrosion inhibitors and intermediates in organic synthesis, and also play a potential role in the development of coordination chemistry (Muralisankar et al., 2016 ▸). Indole and its derivatives are useful staring compounds to derive pharmaceutical (Nalli et al., 2020 ▸) and biological (Arumugam et al., 2021 ▸) materials. In the present study, the hydrogen-bonding interactions and C—H⋯π interactions of the title compound are investigated.
The asymmetric unit of the title compound is shown in Fig. 1 ▸. The C=N double bond adopts an E configuration. The bond lengths and angles in the title molecule are normal and agree with those in other indole–imine compounds (e.g., Suresh et al., 2016 ▸; Ho et al., 2006 ▸). The dihedral angle between the C1–C8/N1 indole ring system and the C12–C17 benzene ring is 80.86 (10)°.
Figure 1.
The molecular structure of the title compound showing 50% displacement ellipsoids.
In the extended structure, the N1—H5 group is a hydrogen-bond donor to atom N2 of the imino group (Table 1 ▸). These hydrogen bonds generate a C(7) chain extending along the a-axis direction, as shown in Fig. 2 ▸. There are no π–π interactions in this crystal structure but weak C—H⋯π interactions occur.
Table 1. Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °).
| D—H⋯A | D—H | H⋯A | D⋯A | D—H⋯A |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| N1—H5⋯N2i | 0.83 (3) | 2.17 (3) | 2.971 (3) | 163 (2) |
Symmetry code: (i)
 .
.
Figure 2.
Partial packing diagram for the title compound showing the formation of [100] hydrogen-bonded chains.
A search of the Cambridge Structural Database (Version 5.43, update November 2022; Groom et al., 2016 ▸) for the benzylidene)-[2-(1H-indol-3-yl)-ethyl]-amine skeleton yielded the hits 1-(anthracen-9-yl)-N-[2-(1H- indol-3-yl)ethyl]methanimine (CSD refcode TEGJIB; Faizi et al., 2017 ▸), 2-[2-(1H-indol-3-ylethyliminomethyl)]-5-methylphenol (PEVXEW; Brink et al., 2018 ▸), rac-4-{(E)-[1-cyano-1-cyclohexyl-2-(1H-indol-yl)ethyl]iminomethyl} benzonitrile (OCEWIE; Letessier et al., 2011 ▸), 1H-indole-3-ethylenesalicylaldimine (FAJVIV; Rodriguez et al., 1987 ▸) and 1-(4-chlorophenyl)-2-{[2-(1H-indol-3-yl) ethyl]imino}-2-(4-methoxyphenyl)ethan-1-one (AZUYUS; Li et al., 2021 ▸).
Synthesis and crystallization
The title compound was synthesized by condensing tryptamine, 2-(1H-indol-3-yl)ethan-1-amine (0.01 mmol) and 2,4-dichlorobenzaldehyde (0.01 mmol), which were taken separately, dissolved in 40 ml of ethanol, then mixed, and heated on a water bath for one h, then kept for crystallization. After a few days, colourless plate-shaped crystals were obtained.
Refinement
Crystal data, data collection and structure refinement details are summarized in Table 2 ▸.
Table 2. Experimental details.
| Crystal data | |
| Chemical formula | C17H14Cl2N2 |
| M r | 317.20 |
| Crystal system, space group | Monoclinic, P21/n |
| Temperature (K) | 296 |
| a, b, c (Å) | 7.2107 (8), 10.2179 (13), 20.863 (3) |
| β (°) | 90.562 (4) |
| V (Å3) | 1537.1 (3) |
| Z | 4 |
| Radiation type | Mo Kα |
| μ (mm−1) | 0.42 |
| Crystal size (mm) | 0.52 × 0.34 × 0.13 |
| Data collection | |
| Diffractometer | Agilent Xcalibur, Atlas, Gemini |
| Absorption correction | Multi-scan (SADABS; Krause et al., 2015 ▸) |
| T min, T max | 0.631, 0.746 |
| No. of measured, independent and observed [I > 2σ(I)] reflections | 68672, 3872, 1946 |
| R int | 0.091 |
| (sin θ/λ)max (Å−1) | 0.671 |
| Refinement | |
| R[F 2 > 2σ(F 2)], wR(F 2), S | 0.048, 0.134, 1.01 |
| No. of reflections | 3872 |
| No. of parameters | 246 |
| H-atom treatment | All H-atom parameters refined |
| Δρmax, Δρmin (e Å−3) | 0.20, −0.27 |
Supplementary Material
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) global, I. DOI: 10.1107/S2414314623007800/hb4446sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S2414314623007800/hb4446Isup2.hkl
Supporting information file. DOI: 10.1107/S2414314623007800/hb4446Isup3.cml
CCDC reference: 2290063
Additional supporting information: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report
Acknowledgments
MH thanks SERB-IRE for financial support (Ref. No. SIR/2022/000011]. SJK thanks TANSCHE for financial support (File No. RGP/2019–20/MTWU/ HECP-0080).
full crystallographic data
Crystal data
| C17H14Cl2N2 | F(000) = 656 |
| Mr = 317.20 | Dx = 1.371 Mg m−3 |
| Monoclinic, P21/n | Mo Kα radiation, λ = 0.71073 Å |
| a = 7.2107 (8) Å | Cell parameters from 3778 reflections |
| b = 10.2179 (13) Å | θ = 2.6–29.9° |
| c = 20.863 (3) Å | µ = 0.42 mm−1 |
| β = 90.562 (4)° | T = 296 K |
| V = 1537.1 (3) Å3 | Plate, colourless |
| Z = 4 | 0.52 × 0.34 × 0.13 mm |
Data collection
| Agilent Xcalibur, Atlas, Gemini diffractometer | 1946 reflections with I > 2σ(I) |
| Radiation source: fine-focus sealed tube | Rint = 0.091 |
| ω scans | θmax = 28.5°, θmin = 2.0° |
| Absorption correction: multi-scan (SADABS; Krause et al., 2015) | h = −9→9 |
| Tmin = 0.631, Tmax = 0.746 | k = −13→13 |
| 68672 measured reflections | l = −27→27 |
| 3872 independent reflections |
Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | Primary atom site location: dual |
| Least-squares matrix: full | Hydrogen site location: difference Fourier map |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.048 | All H-atom parameters refined |
| wR(F2) = 0.134 | w = 1/[σ2(Fo2) + (0.0498P)2 + 0.4436P] where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3 |
| S = 1.01 | (Δ/σ)max = 0.001 |
| 3872 reflections | Δρmax = 0.20 e Å−3 |
| 246 parameters | Δρmin = −0.26 e Å−3 |
| 0 restraints |
Special details
| Geometry. All esds (except the esd in the dihedral angle between two l.s. planes) are estimated using the full covariance matrix. The cell esds are taken into account individually in the estimation of esds in distances, angles and torsion angles; correlations between esds in cell parameters are only used when they are defined by crystal symmetry. An approximate (isotropic) treatment of cell esds is used for estimating esds involving l.s. planes. |
| Refinement. All the H atoms were located in a difference Fourier map and allowed to refine freely (C—H = 0.93–0.96 and N—H = 0.83 Å). |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | ||
| Cl2 | 0.82313 (10) | 0.46440 (8) | 0.37941 (3) | 0.0896 (3) | |
| Cl1 | 0.65404 (13) | 0.74406 (7) | 0.58638 (4) | 0.1034 (3) | |
| N2 | 0.6843 (2) | 0.3930 (2) | 0.69593 (9) | 0.0656 (5) | |
| N1 | 0.0458 (3) | 0.2537 (2) | 0.70118 (10) | 0.0701 (6) | |
| C5 | 0.3287 (3) | 0.1772 (2) | 0.68119 (11) | 0.0628 (6) | |
| C8 | 0.3389 (3) | 0.2540 (2) | 0.73804 (11) | 0.0648 (6) | |
| C6 | 0.1440 (3) | 0.1792 (2) | 0.65910 (11) | 0.0631 (6) | |
| C12 | 0.6934 (3) | 0.4814 (2) | 0.58989 (12) | 0.0593 (6) | |
| C7 | 0.1639 (3) | 0.2993 (3) | 0.74787 (13) | 0.0680 (7) | |
| C13 | 0.6992 (3) | 0.5929 (2) | 0.55222 (12) | 0.0641 (6) | |
| C14 | 0.7393 (3) | 0.5892 (3) | 0.48855 (14) | 0.0683 (7) | |
| C15 | 0.7767 (3) | 0.4709 (3) | 0.46026 (12) | 0.0648 (6) | |
| C17 | 0.7315 (3) | 0.3640 (3) | 0.55950 (14) | 0.0675 (7) | |
| C11 | 0.6416 (3) | 0.4833 (3) | 0.65769 (13) | 0.0661 (7) | |
| C16 | 0.7732 (3) | 0.3571 (3) | 0.49571 (14) | 0.0707 (7) | |
| C4 | 0.4574 (4) | 0.1057 (3) | 0.64506 (16) | 0.0818 (8) | |
| C10 | 0.6134 (4) | 0.4015 (3) | 0.76114 (14) | 0.0785 (8) | |
| C1 | 0.0861 (5) | 0.1121 (3) | 0.60482 (14) | 0.0836 (8) | |
| C3 | 0.4003 (6) | 0.0415 (3) | 0.59108 (17) | 0.0979 (11) | |
| C9 | 0.5055 (4) | 0.2801 (3) | 0.77920 (14) | 0.0796 (8) | |
| C2 | 0.2174 (6) | 0.0439 (3) | 0.57140 (17) | 0.0972 (10) | |
| H12 | 0.720 (3) | 0.289 (3) | 0.5830 (12) | 0.082 (8)* | |
| H11 | 0.573 (3) | 0.556 (2) | 0.6692 (10) | 0.065 (7)* | |
| H10 | 0.543 (4) | 0.476 (3) | 0.7641 (12) | 0.081 (9)* | |
| H9 | 0.726 (4) | 0.407 (3) | 0.7916 (13) | 0.099 (9)* | |
| H8 | 0.586 (4) | 0.201 (3) | 0.7761 (12) | 0.091 (9)* | |
| H4 | 0.579 (4) | 0.105 (3) | 0.6598 (12) | 0.083 (9)* | |
| H13 | 0.797 (3) | 0.275 (3) | 0.4752 (12) | 0.076 (8)* | |
| H14 | 0.743 (3) | 0.663 (3) | 0.4649 (12) | 0.082 (8)* | |
| H7 | 0.470 (3) | 0.290 (2) | 0.8258 (12) | 0.078 (7)* | |
| H6 | 0.126 (3) | 0.357 (2) | 0.7814 (10) | 0.068 (7)* | |
| H1 | −0.045 (4) | 0.108 (3) | 0.5888 (13) | 0.106 (10)* | |
| H3 | 0.489 (4) | −0.005 (3) | 0.5634 (15) | 0.119 (11)* | |
| H2 | 0.177 (5) | −0.006 (4) | 0.5331 (17) | 0.132 (13)* | |
| H5 | −0.060 (4) | 0.282 (3) | 0.6933 (12) | 0.082 (9)* |
Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| Cl2 | 0.0795 (5) | 0.1146 (6) | 0.0746 (5) | 0.0090 (4) | 0.0029 (3) | 0.0035 (4) |
| Cl1 | 0.1558 (8) | 0.0600 (4) | 0.0939 (6) | 0.0151 (4) | −0.0242 (5) | −0.0064 (4) |
| N2 | 0.0525 (11) | 0.0758 (14) | 0.0685 (13) | 0.0038 (10) | −0.0010 (9) | 0.0048 (11) |
| N1 | 0.0601 (13) | 0.0747 (15) | 0.0757 (15) | 0.0114 (12) | 0.0050 (11) | 0.0011 (11) |
| C5 | 0.0652 (15) | 0.0551 (14) | 0.0681 (15) | 0.0121 (11) | 0.0125 (11) | 0.0153 (12) |
| C8 | 0.0605 (14) | 0.0739 (16) | 0.0602 (14) | 0.0068 (12) | 0.0087 (11) | 0.0181 (13) |
| C6 | 0.0695 (15) | 0.0528 (14) | 0.0671 (15) | 0.0071 (12) | 0.0078 (12) | 0.0093 (12) |
| C12 | 0.0467 (12) | 0.0621 (15) | 0.0690 (15) | 0.0059 (11) | −0.0094 (10) | −0.0004 (12) |
| C7 | 0.0707 (16) | 0.0718 (17) | 0.0617 (15) | 0.0074 (13) | 0.0119 (13) | 0.0002 (13) |
| C13 | 0.0644 (14) | 0.0555 (15) | 0.0721 (16) | 0.0053 (11) | −0.0151 (12) | 0.0018 (13) |
| C14 | 0.0659 (16) | 0.0587 (16) | 0.0800 (19) | −0.0008 (12) | −0.0136 (13) | 0.0104 (15) |
| C15 | 0.0478 (13) | 0.0780 (18) | 0.0684 (15) | 0.0042 (12) | −0.0071 (10) | 0.0065 (14) |
| C17 | 0.0659 (15) | 0.0596 (16) | 0.0769 (18) | 0.0066 (12) | −0.0027 (12) | 0.0089 (14) |
| C11 | 0.0534 (14) | 0.0663 (17) | 0.0783 (18) | 0.0082 (12) | −0.0057 (12) | −0.0042 (14) |
| C16 | 0.0676 (16) | 0.0640 (17) | 0.0803 (19) | 0.0123 (13) | −0.0014 (13) | −0.0037 (15) |
| C4 | 0.079 (2) | 0.0709 (18) | 0.096 (2) | 0.0228 (15) | 0.0201 (17) | 0.0209 (17) |
| C10 | 0.0702 (18) | 0.096 (2) | 0.0690 (18) | 0.0042 (17) | −0.0010 (14) | −0.0028 (16) |
| C1 | 0.102 (2) | 0.0655 (17) | 0.083 (2) | 0.0028 (17) | −0.0044 (17) | −0.0025 (16) |
| C3 | 0.138 (3) | 0.0652 (19) | 0.091 (2) | 0.031 (2) | 0.032 (2) | −0.0007 (17) |
| C9 | 0.0741 (18) | 0.098 (2) | 0.0663 (18) | 0.0031 (16) | −0.0018 (14) | 0.0154 (16) |
| C2 | 0.137 (3) | 0.0653 (19) | 0.090 (2) | 0.010 (2) | 0.006 (2) | −0.0077 (17) |
Geometric parameters (Å, º)
| Cl2—C15 | 1.724 (3) | C14—H14 | 0.90 (3) |
| Cl1—C13 | 1.733 (2) | C15—C16 | 1.378 (4) |
| N2—C11 | 1.256 (3) | C17—C16 | 1.369 (4) |
| N2—C10 | 1.461 (3) | C17—H12 | 0.92 (3) |
| N1—C6 | 1.365 (3) | C11—H11 | 0.92 (2) |
| N1—C7 | 1.369 (3) | C16—H13 | 0.95 (3) |
| N1—H5 | 0.83 (3) | C4—C3 | 1.364 (5) |
| C5—C6 | 1.405 (3) | C4—H4 | 0.93 (3) |
| C5—C4 | 1.406 (4) | C10—C9 | 1.514 (4) |
| C5—C8 | 1.424 (3) | C10—H10 | 0.92 (3) |
| C8—C7 | 1.362 (3) | C10—H9 | 1.03 (3) |
| C8—C9 | 1.494 (4) | C1—C2 | 1.371 (4) |
| C6—C1 | 1.385 (4) | C1—H1 | 1.00 (3) |
| C12—C13 | 1.385 (3) | C3—C2 | 1.377 (5) |
| C12—C17 | 1.386 (3) | C3—H3 | 0.99 (3) |
| C12—C11 | 1.467 (3) | C9—H8 | 1.00 (3) |
| C7—H6 | 0.96 (2) | C9—H7 | 1.01 (2) |
| C13—C14 | 1.363 (4) | C2—H2 | 0.99 (4) |
| C14—C15 | 1.373 (4) | ||
| C11—N2—C10 | 117.5 (2) | N2—C11—C12 | 122.7 (2) |
| C6—N1—C7 | 108.9 (2) | N2—C11—H11 | 123.5 (14) |
| C6—N1—H5 | 123.4 (18) | C12—C11—H11 | 113.8 (14) |
| C7—N1—H5 | 125.7 (19) | C17—C16—C15 | 118.9 (3) |
| C6—C5—C4 | 117.4 (3) | C17—C16—H13 | 121.4 (15) |
| C6—C5—C8 | 107.8 (2) | C15—C16—H13 | 119.6 (15) |
| C4—C5—C8 | 134.7 (3) | C3—C4—C5 | 119.8 (3) |
| C7—C8—C5 | 105.8 (2) | C3—C4—H4 | 123.2 (17) |
| C7—C8—C9 | 126.5 (3) | C5—C4—H4 | 117.0 (17) |
| C5—C8—C9 | 127.7 (2) | N2—C10—C9 | 111.6 (3) |
| N1—C6—C1 | 130.4 (3) | N2—C10—H10 | 108.1 (16) |
| N1—C6—C5 | 107.1 (2) | C9—C10—H10 | 112.3 (17) |
| C1—C6—C5 | 122.5 (2) | N2—C10—H9 | 107.3 (15) |
| C13—C12—C17 | 116.5 (2) | C9—C10—H9 | 107.4 (16) |
| C13—C12—C11 | 123.1 (2) | H10—C10—H9 | 110 (2) |
| C17—C12—C11 | 120.4 (2) | C2—C1—C6 | 117.6 (3) |
| C8—C7—N1 | 110.4 (2) | C2—C1—H1 | 117.6 (17) |
| C8—C7—H6 | 126.3 (14) | C6—C1—H1 | 124.7 (17) |
| N1—C7—H6 | 123.3 (13) | C4—C3—C2 | 121.2 (3) |
| C14—C13—C12 | 122.5 (2) | C4—C3—H3 | 121.5 (19) |
| C14—C13—Cl1 | 117.9 (2) | C2—C3—H3 | 117.2 (19) |
| C12—C13—Cl1 | 119.5 (2) | C8—C9—C10 | 114.6 (2) |
| C13—C14—C15 | 119.2 (3) | C8—C9—H8 | 106.5 (16) |
| C13—C14—H14 | 121.4 (17) | C10—C9—H8 | 110.3 (15) |
| C15—C14—H14 | 119.4 (17) | C8—C9—H7 | 111.0 (13) |
| C14—C15—C16 | 120.5 (3) | C10—C9—H7 | 107.0 (14) |
| C14—C15—Cl2 | 119.7 (2) | H8—C9—H7 | 107 (2) |
| C16—C15—Cl2 | 119.8 (2) | C1—C2—C3 | 121.4 (3) |
| C16—C17—C12 | 122.4 (3) | C1—C2—H2 | 118 (2) |
| C16—C17—H12 | 120.0 (17) | C3—C2—H2 | 121 (2) |
| C12—C17—H12 | 117.5 (16) | ||
| C6—C5—C8—C7 | −0.3 (3) | C13—C14—C15—Cl2 | 178.70 (17) |
| C4—C5—C8—C7 | 179.1 (3) | C13—C12—C17—C16 | 0.2 (3) |
| C6—C5—C8—C9 | 179.4 (2) | C11—C12—C17—C16 | 177.4 (2) |
| C4—C5—C8—C9 | −1.1 (4) | C10—N2—C11—C12 | −175.7 (2) |
| C7—N1—C6—C1 | 179.5 (3) | C13—C12—C11—N2 | −159.7 (2) |
| C7—N1—C6—C5 | 0.9 (3) | C17—C12—C11—N2 | 23.3 (4) |
| C4—C5—C6—N1 | −179.9 (2) | C12—C17—C16—C15 | −0.3 (4) |
| C8—C5—C6—N1 | −0.4 (3) | C14—C15—C16—C17 | 0.1 (4) |
| C4—C5—C6—C1 | 1.4 (4) | Cl2—C15—C16—C17 | −178.35 (18) |
| C8—C5—C6—C1 | −179.1 (2) | C6—C5—C4—C3 | −0.3 (4) |
| C5—C8—C7—N1 | 0.9 (3) | C8—C5—C4—C3 | −179.7 (3) |
| C9—C8—C7—N1 | −178.9 (2) | C11—N2—C10—C9 | 124.4 (3) |
| C6—N1—C7—C8 | −1.1 (3) | N1—C6—C1—C2 | −179.7 (3) |
| C17—C12—C13—C14 | 0.2 (3) | C5—C6—C1—C2 | −1.4 (4) |
| C11—C12—C13—C14 | −176.9 (2) | C5—C4—C3—C2 | −0.7 (5) |
| C17—C12—C13—Cl1 | −179.82 (17) | C7—C8—C9—C10 | −89.3 (3) |
| C11—C12—C13—Cl1 | 3.1 (3) | C5—C8—C9—C10 | 91.0 (3) |
| C12—C13—C14—C15 | −0.4 (4) | N2—C10—C9—C8 | −60.8 (4) |
| Cl1—C13—C14—C15 | 179.62 (17) | C6—C1—C2—C3 | 0.3 (5) |
| C13—C14—C15—C16 | 0.2 (4) | C4—C3—C2—C1 | 0.8 (5) |
Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, º)
| D—H···A | D—H | H···A | D···A | D—H···A |
| N1—H5···N2i | 0.83 (3) | 2.17 (3) | 2.971 (3) | 163 (2) |
Symmetry code: (i) x−1, y, z.
Funding Statement
Funding for this research was provided by: Department of Science and Technology, Ministry of Science and Technology, India, Science and Engineering Research Board (grant No. SIR/2022/000011); Tamil Nadu State Council for Higher Education (grant No. RGP/2019-20/MTWU/HECP-0080).
References
- Agilent (2012). CrysAlis PRO and CrysAlis RED. Agilent Technologies Ltd, Yarnton, England.
- Arumugam, N., Almansour, A. I., Kumar, R. S., Yeswanthkumar, S., Padmanaban, R., Arun, Y., Kansız, S., Dege, N., Manohar, T. S. & Venketesh, S. (2021). J. Mol. Struct. 1225, 129165–129166.
- Brink, A., Kroon, R. E., Visser, H. G., van Rensburg, C. E. J. & Roodt, A. (2018). New J. Chem. 42, 5193–5203.
- Faizi, M. S. H., Dege, N., Malinkin, S. & Sliva, T. Y. (2017). Acta Cryst. E73, 1329–1332. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Groom, C. R., Bruno, I. J., Lightfoot, M. P. & Ward, S. C. (2016). Acta Cryst. B72, 171–179. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Ho, J. J., Black, D. St C., Messerle, B. A., Clegg, J. K. & Turner, P. T. (2006). Organometallics, 25, 5800–5810.
- Krause, L., Herbst-Irmer, R., Sheldrick, G. M. & Stalke, D. (2015). J. Appl. Cryst. 48, 3–10. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Letessier, J., Schollmeyer, D., Detert, H. & Opatz, T. (2011). Acta Cryst. E67, o3435. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Li, L., Zhang, S., Deng, X., Li, G., Tang, Z. & Zhao, G. (2021). Org. Lett. 23, 6819–6824. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Muralisankar, M., Haribabu, J., Bhuvanesh, N. S. P., Karvembu, R. & Sreekanth, A. (2016). Inorg. Chim. Acta, 449, 82–95.
- Nalli, M., Armijos Rivera, J. I., Masci, D., Coluccia, A., Badia, R., Riveira-Muñoz, E., Brambilla, A., Cinquina, E., Turriziani, O., Falasca, F., Catalano, M., Limatola, C., Esté, J. A., Maga, G., Silvestri, R., Crespan, E. & La Regina, G. (2020). Eur. J. Med. Chem. 208, 112696. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Rodriguez, M. L., Medina de la Rosa, E., Gili, P., Zarza, P. M., Reyes, M. G. M., Medina, A. & Díaz González, M. C. (1987). Acta Cryst. C43, 134–136.
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2015a). Acta Cryst. A71, 3–8.
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2015b). Acta Cryst. C71, 3–8.
- Spek, A. L. (2020). Acta Cryst. E76, 1–11. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Suresh, D., Ferreira, B., Lopes, P. S., Gomes, C. S. B., Krishnamoorthy, P., Charas, A., Vila-Viçosa, D., Morgado, J., Calhorda, M. J., Maçanita, A. L. & Gomes, P. T. (2016). Dalton Trans. 45, 15603–15620. [DOI] [PubMed]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) global, I. DOI: 10.1107/S2414314623007800/hb4446sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S2414314623007800/hb4446Isup2.hkl
Supporting information file. DOI: 10.1107/S2414314623007800/hb4446Isup3.cml
CCDC reference: 2290063
Additional supporting information: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report