Abstract
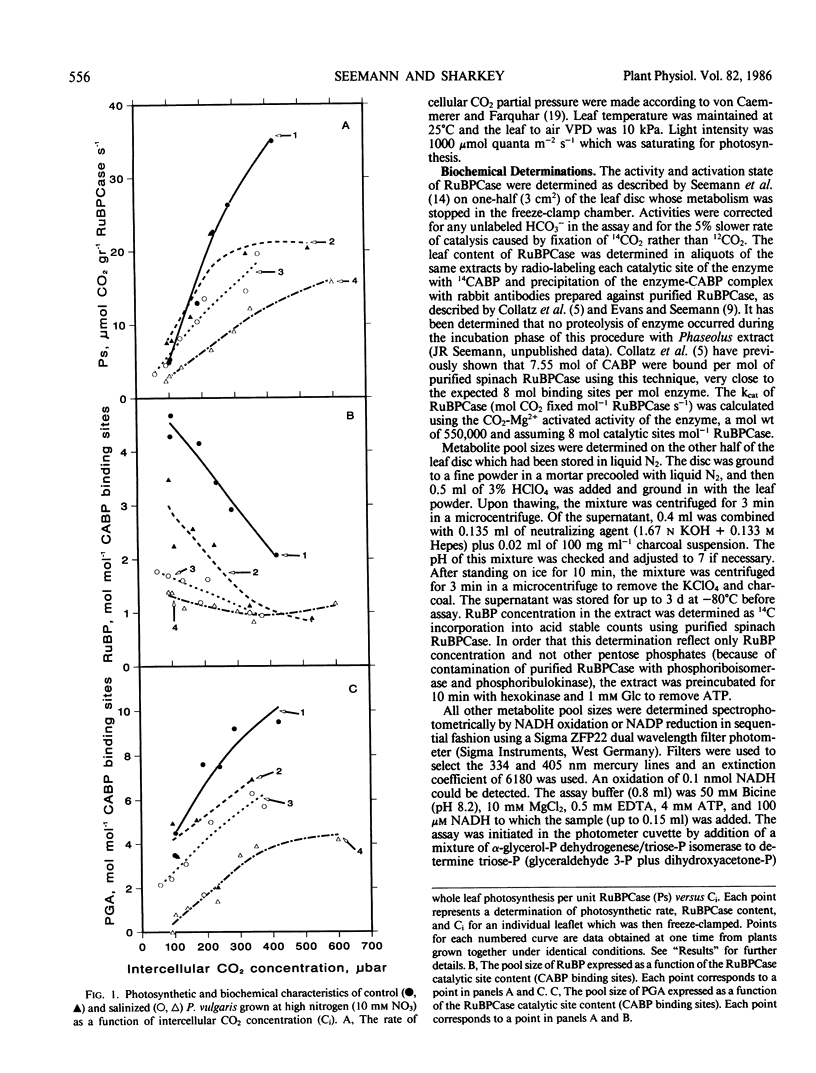
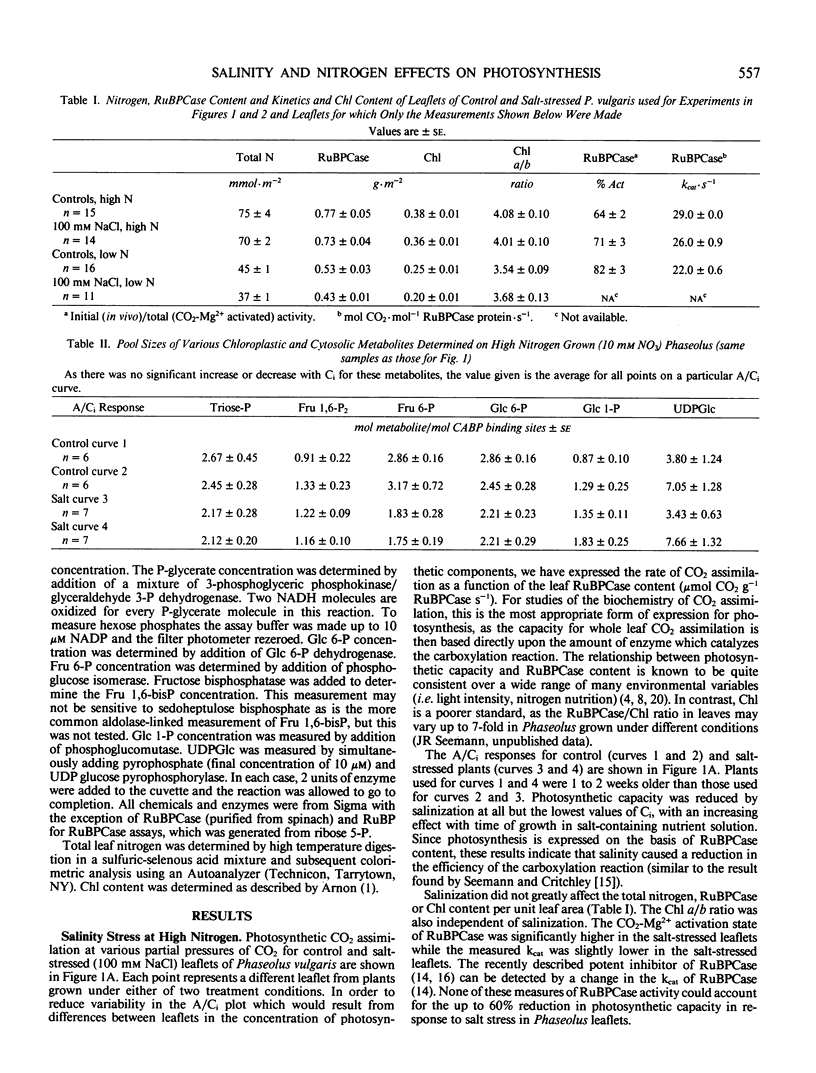
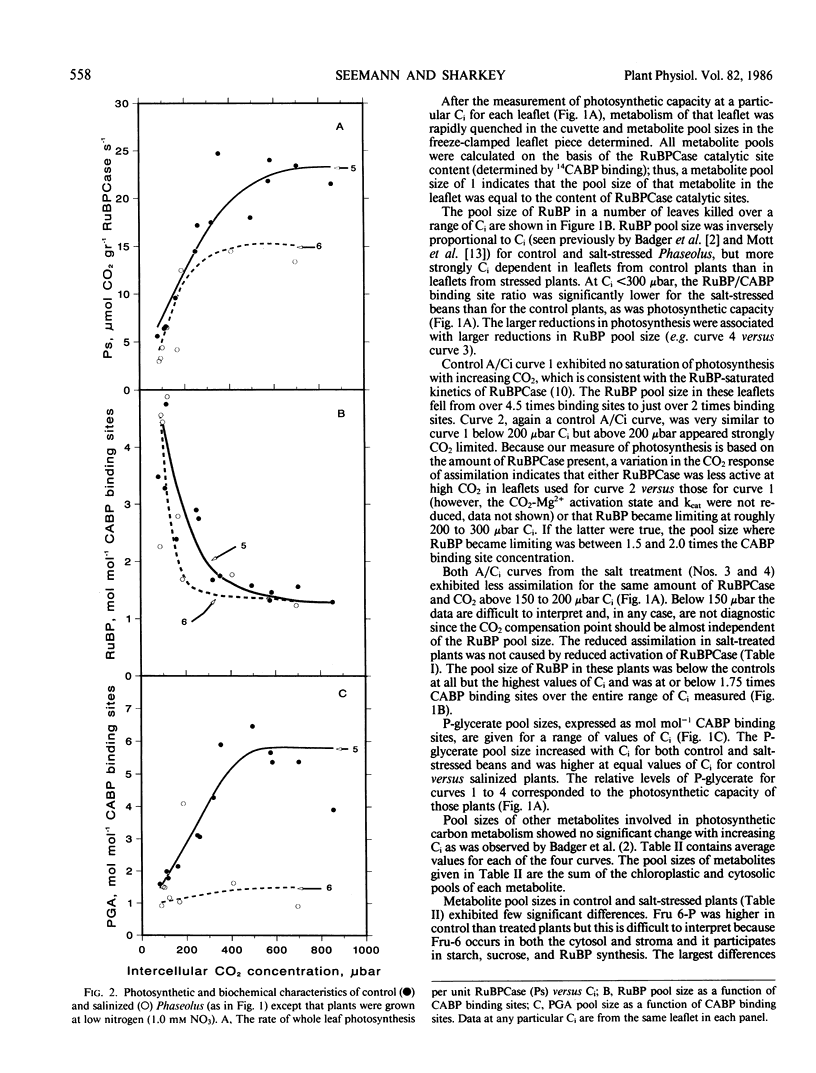
Salinity (100 millimolar NaCl) was found to reduce photosynthetic capacity independent of stomatal closure in Phaseolus vulgaris. This reduction was shown to be a consequence of a reduction in the efficiency of ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate (RuBP) carboxylase (RuBPCase) rather than a reduction in the leaf content of photosynthetic machinery. In control plants, photosynthesis became RuBP-limited at approximately 1.75 moles RuBP per mole 2-carboxyarabinitol bisphosphate binding sites. Salinization caused the RuBP pool size to reach this limiting value for CO2 fixation at much lower values of intercellular CO2. Plants grown at low nitrogen and ± NaCl became RuBP limited at similar RuBP pool sizes as the high nitrogen-grown plants. At limiting RuBP pool sizes and equal values of intercellular CO2 photosynthetic capacity of salt-stressed plants was less than control plants. This effect of salinity on RuBPCase activity could not be explained by deactivation of the enzyme or inhibitor synthesis. Thus, salinity reduced photosynthetic capacity by reducing both the RuBP pool size by an effect on RuBP regeneration capacity and RuBPCase activity by an unknown mechanism when RuBP was limiting.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arnon D. I. COPPER ENZYMES IN ISOLATED CHLOROPLASTS. POLYPHENOLOXIDASE IN BETA VULGARIS. Plant Physiol. 1949 Jan;24(1):1–15. doi: 10.1104/pp.24.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ball M. C., Farquhar G. D. Photosynthetic and Stomatal Responses of the Grey Mangrove, Avicennia marina, to Transient Salinity Conditions. Plant Physiol. 1984 Jan;74(1):7–11. doi: 10.1104/pp.74.1.7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Downton W. J., Grant W. J., Robinson S. P. Photosynthetic and stomatal responses of spinach leaves to salt stress. Plant Physiol. 1985 May;78(1):85–88. doi: 10.1104/pp.78.1.85. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans J. R. Nitrogen and Photosynthesis in the Flag Leaf of Wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). Plant Physiol. 1983 Jun;72(2):297–302. doi: 10.1104/pp.72.2.297. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans J. R., Seemann J. R. Differences between Wheat Genotypes in Specific Activity of Ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate Carboxylase and the Relationship to Photosynthesis. Plant Physiol. 1984 Apr;74(4):759–765. doi: 10.1104/pp.74.4.759. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mott K. A., Jensen R. G., O'leary J. W., Berry J. A. Photosynthesis and Ribulose 1,5-Bisphosphate Concentrations in Intact Leaves of Xanthium strumarium L. Plant Physiol. 1984 Dec;76(4):968–971. doi: 10.1104/pp.76.4.968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seemann J. R., Berry J. A., Freas S. M., Krump M. A. Regulation of ribulose bisphosphate carboxylase activity in vivo by a light-modulated inhibitor of catalysis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Dec;82(23):8024–8028. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.23.8024. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Servaites J. C. Binding of a Phosphorylated Inhibitor to Ribulose Bisphosphate Carboxylase/Oxygenase during the Night. Plant Physiol. 1985 Aug;78(4):839–843. doi: 10.1104/pp.78.4.839. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharkey T. D., Seemann J. R., Berry J. A. Regulation of Ribulose-1,5-Bisphosphate Carboxylase Activity in Response to Changing Partial Pressure of O(2) and Light in Phaseolus vulgaris. Plant Physiol. 1986 Jul;81(3):788–791. doi: 10.1104/pp.81.3.788. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


