Abstract
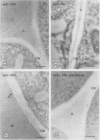
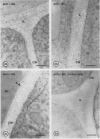
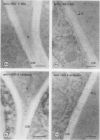
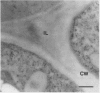
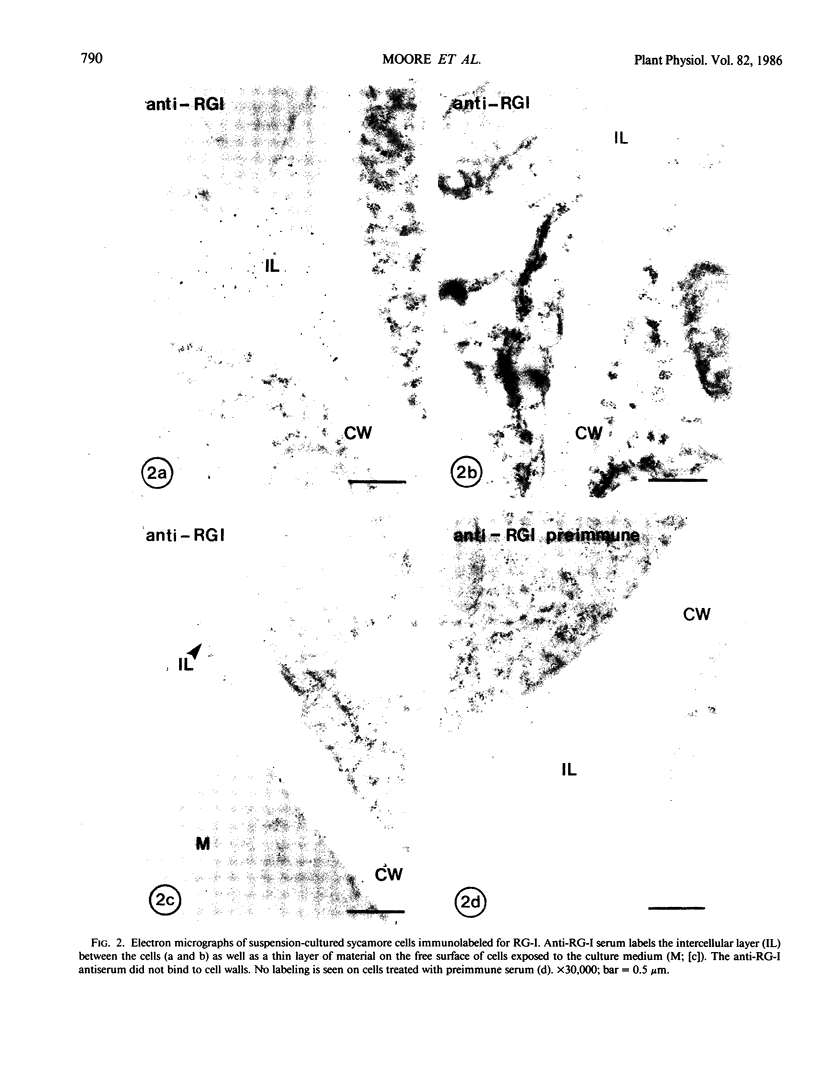
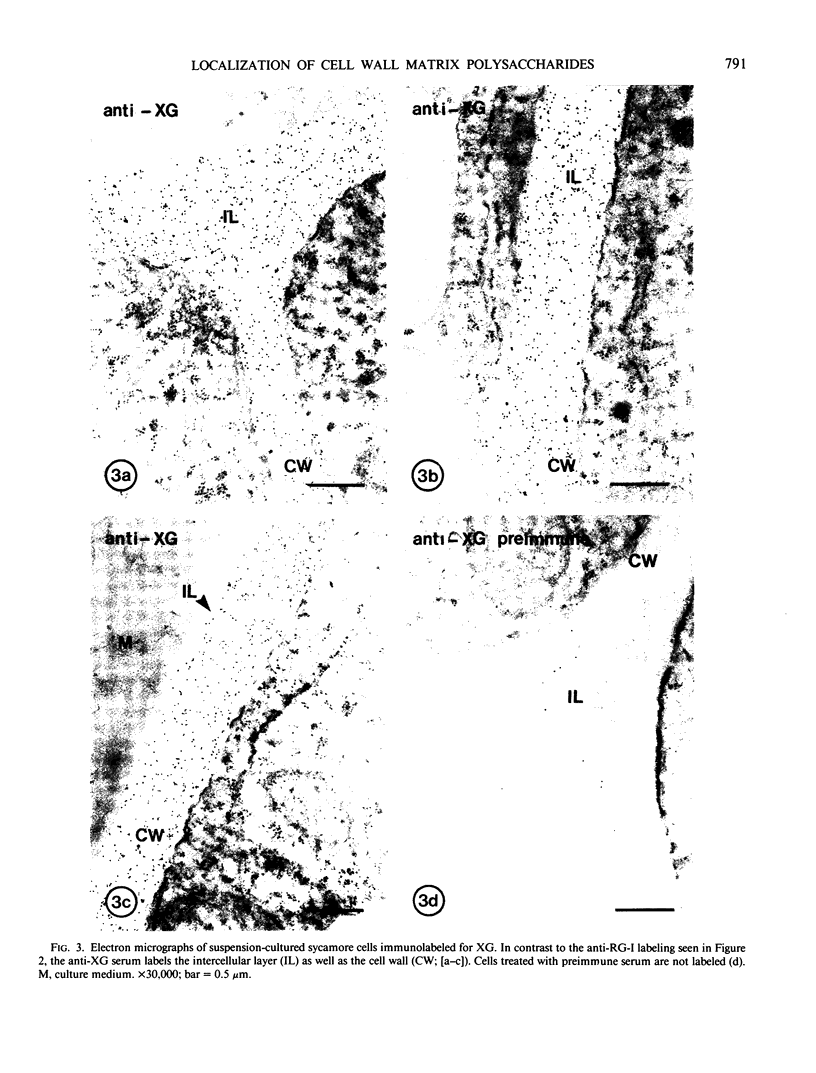
Plant cell walls serve several functions: they impart rigidity to the plant, provide a physical and chemical barrier between the cell and its environment, and regulate the size and shape of each cell. Chemical studies have provided information on the biochemical composition of the plant cell walls as well as detailed knowledge of individual cell wall molecules. In contrast, very little is known about the distribution of specific cell wall components around individual cells and throughout tissues. To address this problem, we have produced polyclonal antibodies against two cell wall matrix components; rhamnogalacturonan I (RG-I), a pectic polysaccharide, and xyloglucan (XG), a hemicellulose. By using the antibiodies as specific markers we have been able to localize these polymers on thin sections of suspension-cultured sycamore cells (Acer pseudoplatanus). Our results reveal that each molecule has a unique distribution. XG is localized throughout the entire wall and middle lamella. RG-I is restricted to the middle lamella and is especially evident in the junctions between cells. These observations indicate that plant cell walls may have more distinct chemical (and functional?) domains than previously envisaged.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ALBERSHEIM P., MUHLETHALER K., FREY-WYSSLING A. Stained pectin as seen in the electron microscope. J Biophys Biochem Cytol. 1960 Oct;8:501–506. doi: 10.1083/jcb.8.2.501. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bauer W. D., Talmadge K. W., Keegstra K., Albersheim P. The Structure of Plant Cell Walls: II. The Hemicellulose of the Walls of Suspension-cultured Sycamore Cells. Plant Physiol. 1973 Jan;51(1):174–187. doi: 10.1104/pp.51.1.174. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown R. M., Jr Cellulose microfibril assembly and orientation: recent developments. J Cell Sci Suppl. 1985;2:13–32. doi: 10.1242/jcs.1985.supplement_2.2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Darvill A. G., McNeil M., Albersheim P. Structure of Plant Cell Walls: VIII. A New Pectic Polysaccharide. Plant Physiol. 1978 Sep;62(3):418–422. doi: 10.1104/pp.62.3.418. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- English P. D., Maglothin A., Keegstra K., Albersheim P. A Cell Wall-degrading Endopolygalacturonase Secreted by Colletotrichum lindemuthianum. Plant Physiol. 1972 Mar;49(3):293–298. doi: 10.1104/pp.49.3.293. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giddings T. H., Jr, Brower D. L., Staehelin L. A. Visualization of particle complexes in the plasma membrane of Micrasterias denticulata associated with the formation of cellulose fibrils in primary and secondary cell walls. J Cell Biol. 1980 Feb;84(2):327–339. doi: 10.1083/jcb.84.2.327. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris P. J., Northcote D. H. Polysaccharide formation in plant Golgi bodies. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1971 Apr 20;237(1):56–64. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(71)90029-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LETHAM D. S. The separation of plant cells with ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid. Exp Cell Res. 1960 Nov;21:353–360. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(60)90267-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Labavitch J. M., Ray P. M. Relationship between Promotion of Xyloglucan Metabolism and Induction of Elongation by Indoleacetic Acid. Plant Physiol. 1974 Oct;54(4):499–502. doi: 10.1104/pp.54.4.499. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLean I. W., Nakane P. K. Periodate-lysine-paraformaldehyde fixative. A new fixation for immunoelectron microscopy. J Histochem Cytochem. 1974 Dec;22(12):1077–1083. doi: 10.1177/22.12.1077. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McNeil M., Darvill A. G., Albersheim P. Structure of Plant Cell Walls: X. RHAMNOGALACTURONAN I, A STRUCTURALLY COMPLEX PECTIC POLYSACCHARIDE IN THE WALLS OF SUSPENSION-CULTURED SYCAMORE CELLS. Plant Physiol. 1980 Dec;66(6):1128–1134. doi: 10.1104/pp.66.6.1128. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McNeil M., Darvill A. G., Fry S. C., Albersheim P. Structure and function of the primary cell walls of plants. Annu Rev Biochem. 1984;53:625–663. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.53.070184.003205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Powell D. A., Morris E. R., Gidley M. J., Rees D. A. Conformations and interactions of pectins. II. Influences of residue sequence on chain association in calcium pectate gels. J Mol Biol. 1982 Mar 15;155(4):517–531. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90485-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ray P. M., Shininger T. L., Ray M. M. ISOLATION OF beta-GLUCAN SYNTHETASE PARTICLES FROM PLANT CELLS AND IDENTIFICATION WITH GOLGI MEMBRANES. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1969 Oct;64(2):605–612. doi: 10.1073/pnas.64.2.605. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruel K., Joseleau J. P. Use of enzyme-gold complexes for the ultrastructural localization of hemicelluloses in the plant cell wall. Histochemistry. 1984;81(6):573–580. doi: 10.1007/BF00489537. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryan C. A., Bishop P., Pearce G. A sycamore cell wall polysaccharide and a chemically related tomato leaf polysaccharide possess similar proteinase inhibitor-inducing activities. Plant Physiol. 1981 Sep;68(3):616–618. doi: 10.1104/pp.68.3.616. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Talmadge K. W., Keegstra K., Bauer W. D., Albersheim P. The Structure of Plant Cell Walls: I. The Macromolecular Components of the Walls of Suspension-cultured Sycamore Cells with a Detailed Analysis of the Pectic Polysaccharides. Plant Physiol. 1973 Jan;51(1):158–173. doi: 10.1104/pp.51.1.158. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Valent B. S., Albersheim P. The structure of plant cell walls: v. On the binding of xyloglucan to cellulose fibers. Plant Physiol. 1974 Jul;54(1):105–108. doi: 10.1104/pp.54.1.105. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vreeland V. Localization of a cell wall polysaccharide in a brown alga with labeled antibody. J Histochem Cytochem. 1970 May;18(5):371–373. doi: 10.1177/18.5.371. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- York W. S., Darvill A. G., Albersheim P. Inhibition of 2,4-dichlorophenoxyacetic Acid-stimulated elongation of pea stem segments by a xyloglucan oligosaccharide. Plant Physiol. 1984 Jun;75(2):295–297. doi: 10.1104/pp.75.2.295. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]