Abstract
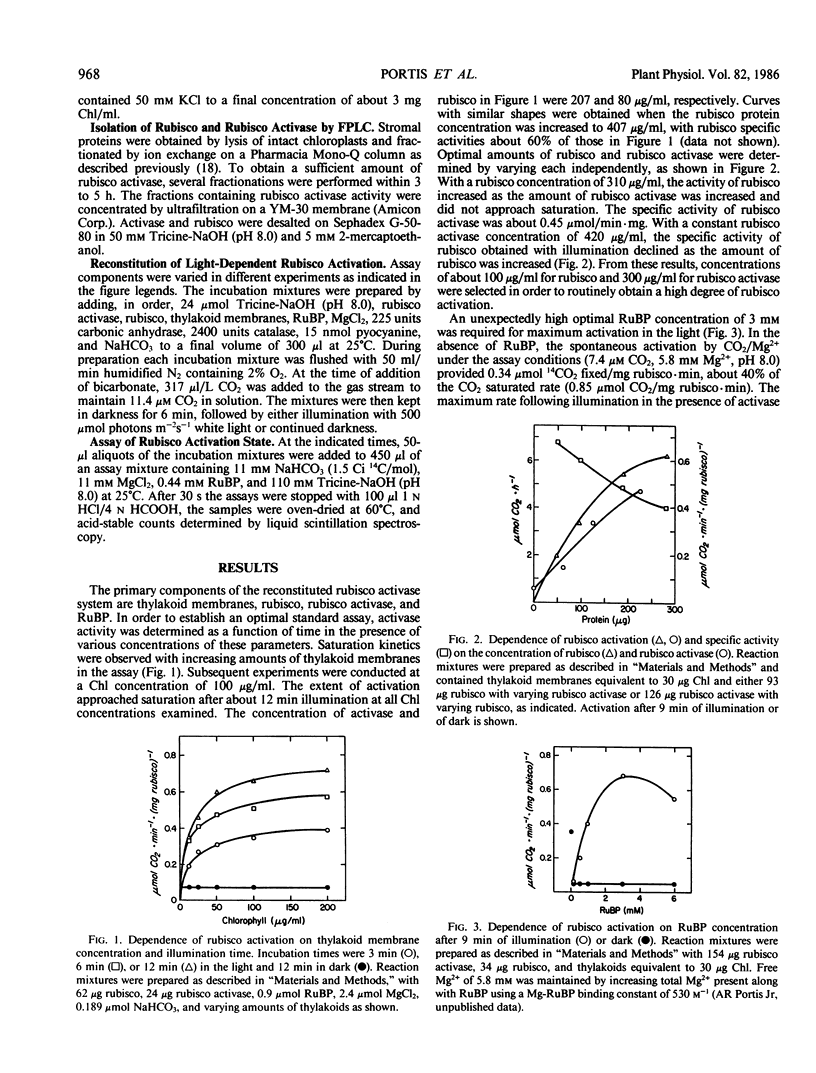
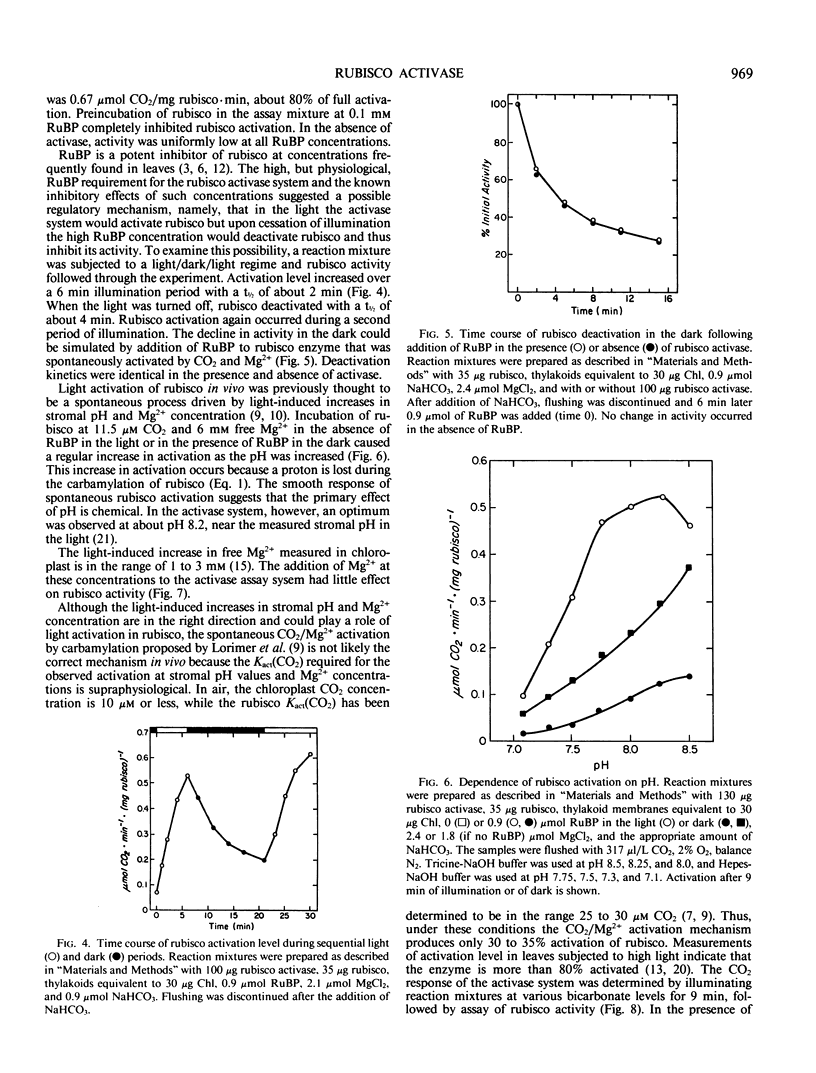
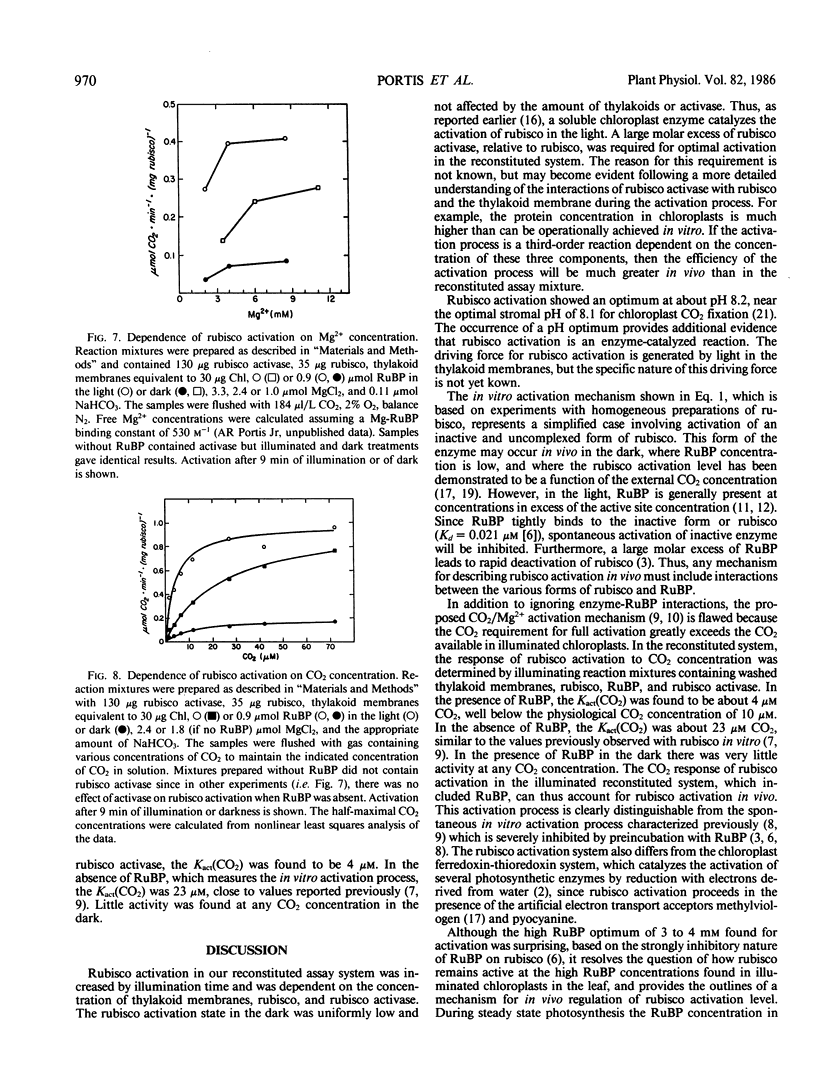
The enzyme-catalyzed activation of ribulosebisphosphate carboxylase/oxygenase (rubisco) was investigated in an illuminated reconstituted system containing thylakoid membranes, rubisco, ribulosebisphosphate (RuBP), MgCl2, carbonic anhydrase, catalase, the artificial electron acceptor pyocyanine, and partially purified rubisco activase. Optimal conditions for light-induced rubisco activation were found to include 100 micrograms per milliliter rubisco, 300 micrograms per milliliter rubisco activase, 3 millimolar RuBP, and 6 millimolar free Mg2+ at pH 8.2. The half-time for rubisco activation was 2 minutes, and was 4 minutes for rubisco deactivation. The rate of rubisco deactivation was identical in the presence and absence of activase. The Kact(CO2) of rubisco activation in the reconstituted system was 4 micromolar CO2, compared to a Kact(CO2) of 25 to 30 micromolar CO2 for the previously reported spontaneous CO2/Mg2+ activation mechanism. The activation process characterized here explains the high degree of rubisco activation at the physiological concentrations of 10 micromolar CO2 and 2 to 4 millimolar RuBP found in intact leaves, conditions which lead to almost complete deactivation of rubisco in vitro.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Belknap W. R., Portis A. R. Exchange Properties of the Activator CO(2) of Spinach Ribulose-1,5-Bisphosphate Carboxylase/Oxygenase. Plant Physiol. 1986 Mar;80(3):707–710. doi: 10.1104/pp.80.3.707. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chu D. K., Bassham J. A. Regulation of ribulose 1,5-diphosphate carboxylase by substrates and other metabolites: further evidence for several types of binding sites. Plant Physiol. 1975 Apr;55(4):720–726. doi: 10.1104/pp.55.4.720. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heldt H. W., Sauer F. The inner membrane of the chloroplast envelope as the site of specific metabolite transport. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1971 Apr 6;234(1):83–91. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(71)90133-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JAGENDORF A. T., MARGULIES M. Inhibition of spinach chloroplast photosynthetic reactions by p-chlorophenyll, 1-dimethylurea. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1960 Oct;90:184–195. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(60)90566-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jordan D. B., Chollet R. Inhibition of ribulose bisphosphate carboxylase by substrate ribulose 1,5-bisphosphate. J Biol Chem. 1983 Nov 25;258(22):13752–13758. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jordan D. B., Ogren W. L. A Sensitive Assay Procedure for Simultaneous Determination of Ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate Carboxylase and Oxygenase Activities. Plant Physiol. 1981 Feb;67(2):237–245. doi: 10.1104/pp.67.2.237. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laing W. A., Christeller J. T. A model for the kinetics of activation and catalysis of ribulose 1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase. Biochem J. 1976 Dec 1;159(3):563–570. doi: 10.1042/bj1590563. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lorimer G. H., Badger M. R., Andrews T. J. The activation of ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase by carbon dioxide and magnesium ions. Equilibria, kinetics, a suggested mechanism, and physiological implications. Biochemistry. 1976 Feb 10;15(3):529–536. doi: 10.1021/bi00648a012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lorimer G. H., Miziorko H. M. Carbamate formation on the epsilon-amino group of a lysyl residue as the basis for the activation of ribulosebisphosphate carboxylase by CO2 and Mg2+. Biochemistry. 1980 Nov 11;19(23):5321–5328. doi: 10.1021/bi00564a027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mott K. A., Jensen R. G., O'leary J. W., Berry J. A. Photosynthesis and Ribulose 1,5-Bisphosphate Concentrations in Intact Leaves of Xanthium strumarium L. Plant Physiol. 1984 Dec;76(4):968–971. doi: 10.1104/pp.76.4.968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PON N. G., RABIN B. R., CALVIN M. MECHANISM OF THE CARBOXYDISMUTASE REACTION. I. THE EFFECT OF PRELIMINARY INCUBATION OF SUBSTRATES, METAL ION AND ENZYME ON ACTIVITY. Biochem Z. 1963;338:7–19. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perchorowicz J. T., Jensen R. G. Photosynthesis and Activation of Ribulose Bisphosphate Carboxylase in Wheat Seedlings : Regulation by CO(2) and O(2). Plant Physiol. 1983 Apr;71(4):955–960. doi: 10.1104/pp.71.4.955. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perchorowicz J. T., Raynes D. A., Jensen R. G. Light limitation of photosynthesis and activation of ribulose bisphosphate carboxylase in wheat seedlings. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 May;78(5):2985–2989. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.5.2985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Portis A. R. Evidence of a Low Stromal Mg Concentration in Intact Chloroplasts in the Dark: I. STUDIES WITH THE IONOPHORE A23187. Plant Physiol. 1981 May;67(5):985–989. doi: 10.1104/pp.67.5.985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salvucci M. E., Portis A. R., Jr, Ogren W. L. Purification of ribulose-1, 5-bisphosphate carboxylase/oxygenase with high specific activity by fast protein liquid chromatography. Anal Biochem. 1986 Feb 15;153(1):97–101. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(86)90066-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salvucci M. E., Portis A. R., Ogren W. L. Light and CO(2) Response of Ribulose-1,5-Bisphosphate Carboxylase/Oxygenase Activation in Arabidopsis Leaves. Plant Physiol. 1986 Mar;80(3):655–659. doi: 10.1104/pp.80.3.655. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Somerville C. R., Portis A. R., Ogren W. L. A Mutant of Arabidopsis thaliana Which Lacks Activation of RuBP Carboxylase In Vivo. Plant Physiol. 1982 Aug;70(2):381–387. doi: 10.1104/pp.70.2.381. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Werdan K., Heldt H. W., Milovancev M. The role of pH in the regulation of carbon fixation in the chloroplast stroma. Studies on CO2 fixation in the light and dark. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1975 Aug 11;396(2):276–292. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(75)90041-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


