Abstract
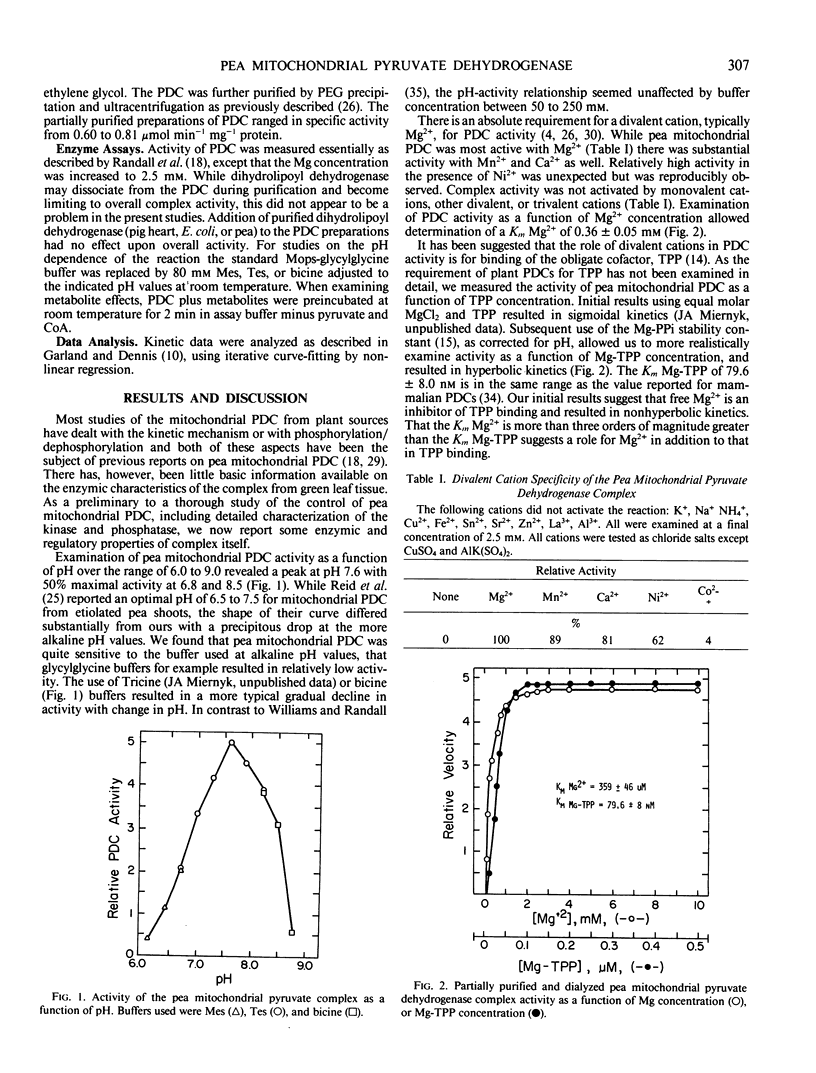
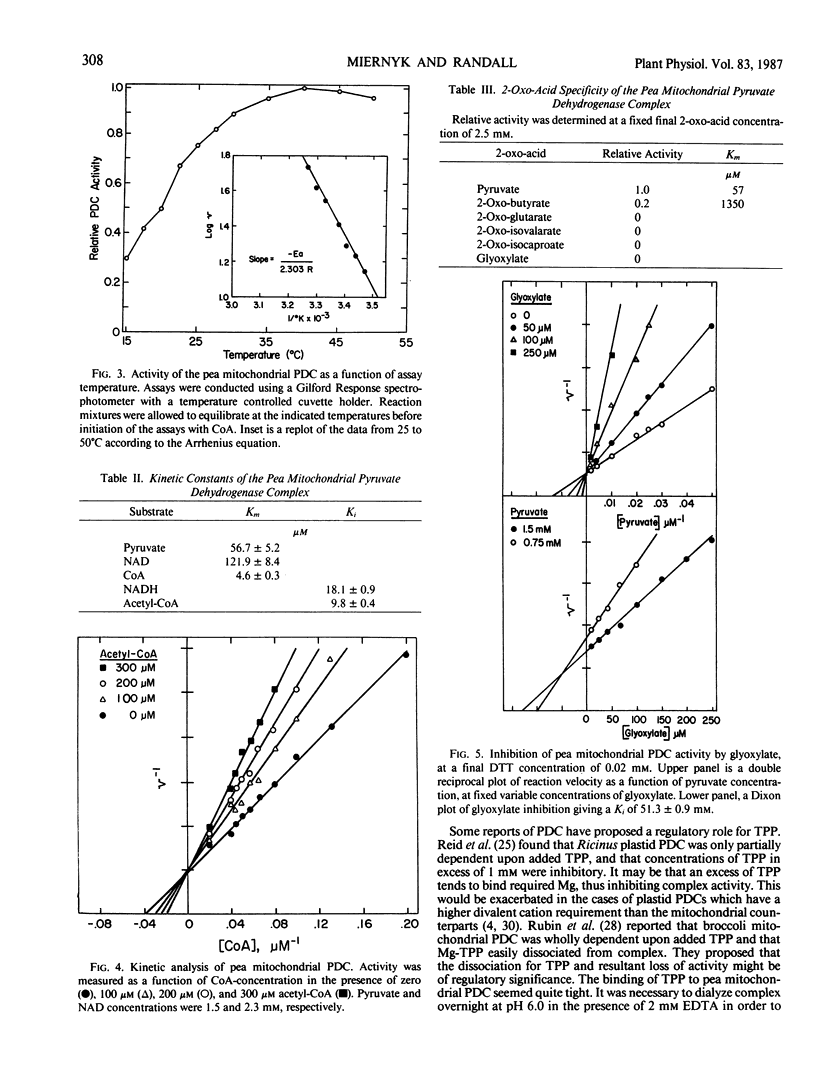
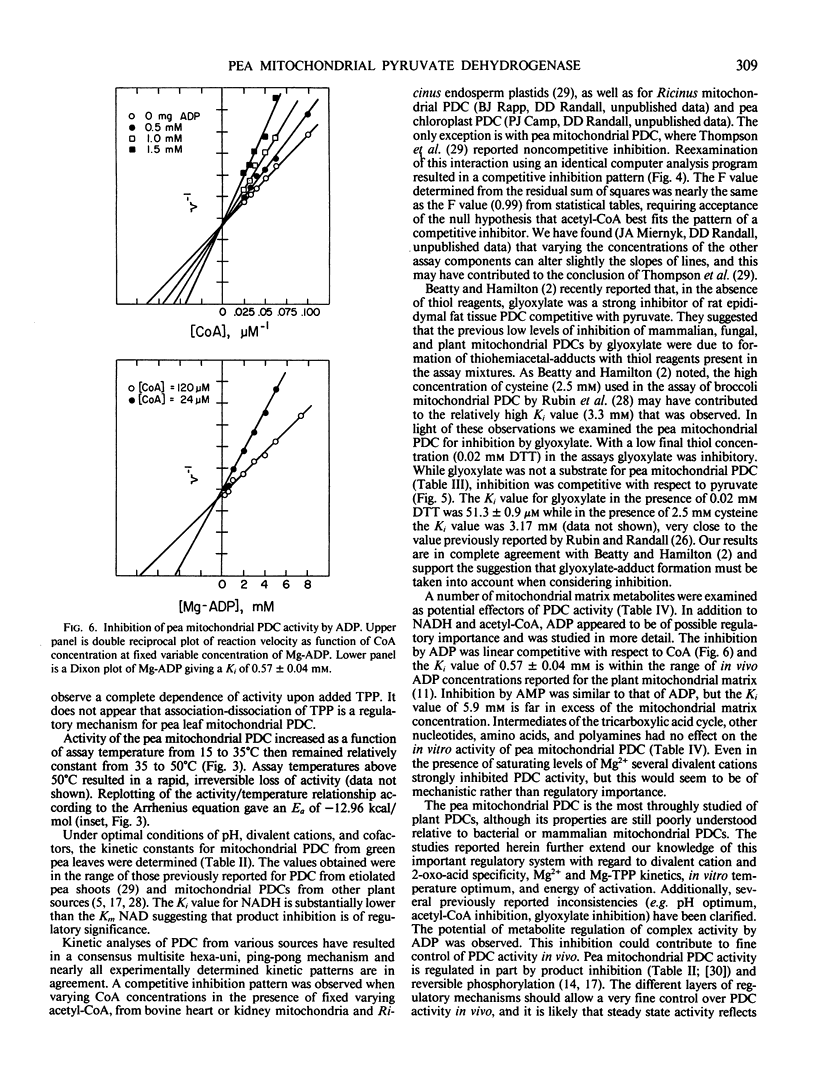
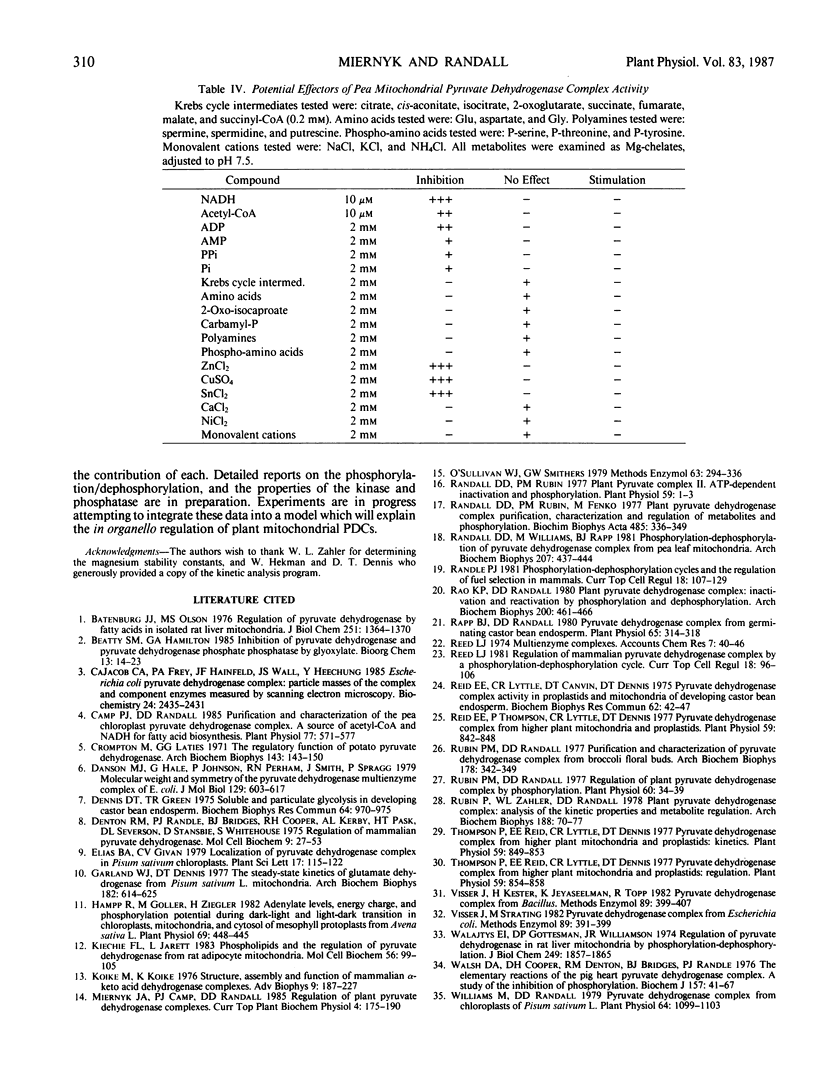
The pyruvate dehydrogenase complex was isolated, partially purified, and characterized from green pea (Pisum sativum L., cv Little Marvel) leaf mitochondria. The pH optimum for the overall reaction was 7.6. The divalent cation requirement was best satisfied by Mg2+. Reaction velocity was maximal at 40°C. Pyruvate was a better substrate than 2-oxo-butyrate; other 2-oxo-acids were not substrates. Michaelis constants for substrates were; pyruvate, 57 micromolar; NAD, 122 micromolar; Coenzyme-A, 5 micromolar; Mg2+, 0.36 millimolar; Mg-thiamine pyrophosphate, 80 nanomolar. The products, NADH and acetyl-Coenzyme-A, were linear competitive inhibitors with respect to NAD and Coenzyme A. Inhibition constants were 18 and 10 micromolar, respectively. Glyoxylate inhibited complex activity only in the absence of thiol reagents. Glyoxylate inhibition was competitive with respect to pyruvate with an inhibition constant of 51 micromolar. Among mitochondrial metabolites examined as potential effectors, only ADP with an inhibition constant of 0.57 millimolar could be of physiological significance.
Full text
PDF
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Batenburg J. J., Olson M. S. Regulation of pyruvate dehydrogenase by fatty acid in isolated rat liver mitochondria. J Biol Chem. 1976 Mar 10;251(5):1364–1370. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CaJacob C. A., Frey P. A., Hainfeld J. F., Wall J. S., Yang H. Escherichia coli pyruvate dehydrogenase complex: particle masses of the complex and component enzymes measured by scanning transmission electron microscopy. Biochemistry. 1985 May 7;24(10):2425–2431. doi: 10.1021/bi00331a006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Camp P. J., Randall D. D. Purification and Characterization of the Pea Chloroplast Pyruvate Dehydrogenase Complex : A Source of Acetyl-CoA and NADH for Fatty Acid Biosynthesis. Plant Physiol. 1985 Mar;77(3):571–577. doi: 10.1104/pp.77.3.571. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crompton M., Laties G. G. The regulatory function of potato pyruvate dehydrogenase. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1971 Mar;143(1):143–150. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(71)90194-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Danson M. J., Hale G., Johnson P., Perham R. N., Smith J., Spragg P. Molecular weight and symmetry of the pyruvate dehydrogenase multienzyme complex of Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol. 1979 Apr 25;129(4):603–617. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(79)90471-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dennis D. T., Green T. R. Soluble and particulate glycolysis in developing castor bean endosperm. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1975 Jan 2;64(3):970–975. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(75)90142-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Denton R. M., Randle P. J., Bridges B. J., Cooper R. H., Kerbey A. L., Pask H. T., Severson D. L., Stansbie D., Whitehouse S. Regulation of mammalian pyruvate dehydrogenase. Mol Cell Biochem. 1975 Oct 31;9(1):27–53. doi: 10.1007/BF01731731. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garland W. J., Dennis D. T. Steady-state kinetics of glutamate dehydrogenase from Pisum sativum L. mitochondria. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1977 Aug;182(2):614–625. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(77)90542-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hampp R., Goller M., Ziegler H. Adenylate Levels, Energy Charge, and Phosphorylation Potential during Dark-Light and Light-Dark Transition in Chloroplasts, Mitochondria, and Cytosol of Mesophyll Protoplasts from Avena sativa L. Plant Physiol. 1982 Feb;69(2):448–455. doi: 10.1104/pp.69.2.448. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kiechle F. L., Jarett L. Phospholipids and the regulation of pyruvate dehydrogenase from rat adipocyte mitochondria. Mol Cell Biochem. 1983;56(2):99–105. doi: 10.1007/BF00227209. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koike M., Koike K. Structure, assembly and function of mammalian alpha-keto acid dehydrogenase complexes. Adv Biophys. 1976:187–227. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Sullivan W. J., Smithers G. W. Stability constants for biologically important metal-ligand complexes. Methods Enzymol. 1979;63:294–336. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(79)63014-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Randall D. D., Rubin P. M., Fenko M. Plant pyruvate dehydrogenase complex purification, characterization and regulation by metabolites and phosphorylation. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1977 Dec 8;485(2):336–349. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(77)90169-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Randall D. D., Rubin P. M. Plant Pyruvate Dehydrogenase Complex: II. ATP-Dependent Inactivation and Phosphorylation. Plant Physiol. 1977 Jan;59(1):1–3. doi: 10.1104/pp.59.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Randall D. D., Williams M., Rapp B. J. Phosphorylation-dephosphorylation of pyruvate dehydrogenase complex from pea leaf mitochondria. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1981 Apr 1;207(2):437–444. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(81)90051-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Randle P. J. Phosphorylation-dephosphorylation cycles and the regulation of fuel selection in mammals. Curr Top Cell Regul. 1981;18:107–129. doi: 10.1016/b978-0-12-152818-8.50013-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rao K. P., Randall D. D. Plant pyruvate dehydrogenase complex: inactivation and reactivation by phosphorylation and dephosphorylation. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1980 Apr 1;200(2):461–466. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(80)90377-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rapp B. J., Randall D. D. Pyruvate dehydrogenase complex from germinating castor bean endosperm. Plant Physiol. 1980 Feb;65(2):314–318. doi: 10.1104/pp.65.2.314. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reed L. J. Regulation of mammalian pyruvate dehydrogenase complex by a phosphorylation-dephosphorylation cycle. Curr Top Cell Regul. 1981;18:95–106. doi: 10.1016/b978-0-12-152818-8.50012-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reid E. E., Lyttle C. R., Canvin D. T., Dennis D. T. Pyruvate dehydrogenase complex activity in proplastids and mitochondria of developing castor bean endosperm. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1975 Jan 6;62(1):42–47. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(75)80402-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reid E. E., Thompson P., Lyttle C. R., Dennis D. T. Pyruvate dehydrogenase complex from higher plant mitochondria and proplastids. Plant Physiol. 1977 May;59(5):842–848. doi: 10.1104/pp.59.5.842. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubin P. M., Randall D. D. Purification and characterization of pyruvate dehydrogenase complex from borccoli floral buds. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1977 Jan 30;178(2):342–349. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(77)90202-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubin P. M., Randall D. D. Regulation of plant pyruvate dehydrogenase complex by phosphorylation. Plant Physiol. 1977 Jul;60(1):34–39. doi: 10.1104/pp.60.1.34. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubin P. M., Zahler W. L., Randall D. D. Plant pyruvate dehydrogenase complex: analysis of the kinetic properties and metabolite regulation. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1978 May;188(1):70–77. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(78)90357-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson P., Reid E. E., Lyttle C. R., Dennis D. T. Pyruvate dehydrogenase complex from higher plant mitochondria and proplastids: kinetics. Plant Physiol. 1977 May;59(5):849–853. doi: 10.1104/pp.59.5.849. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson P., Reid E. E., Lyttle C. R., Dennis D. T. Pyruvate dehydrogenase complex from higher plant mitochondria and proplastids: regulation. Plant Physiol. 1977 May;59(5):854–858. doi: 10.1104/pp.59.5.854. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Visser J., Kester H., Jeyaseelan K., Topp R. Pyruvate dehydrogenase complex from Bacillus. Methods Enzymol. 1982;89(Pt 500):399–407. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(82)89070-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Visser J., Strating M. Pyruvate dehydrogenase complex from Escherichia coli. Methods Enzymol. 1982;89(Pt 500):391–399. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(82)89069-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walajtys E. I., Gottesman D. P., Williamson J. R. Regulation of pyruvate dehydrogenase in rat liver mitochondria by phosphorylation-dephosphorylation. J Biol Chem. 1974 Mar 25;249(6):1857–1865. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walsh D. A., Cooper R. H., Denton R. M., Bridges B. J., Randle P. J. The elementary reactions of the pig heart pyruvate dehydrogenase complex. A study of the inhibition by phosphorylation. Biochem J. 1976 Jul 1;157(1):41–67. doi: 10.1042/bj1570041. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams M., Randall D. D. Pyruvate Dehydrogenase Complex from Chloroplasts of Pisum sativum L. Plant Physiol. 1979 Dec;64(6):1099–1103. doi: 10.1104/pp.64.6.1099. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


