Abstract
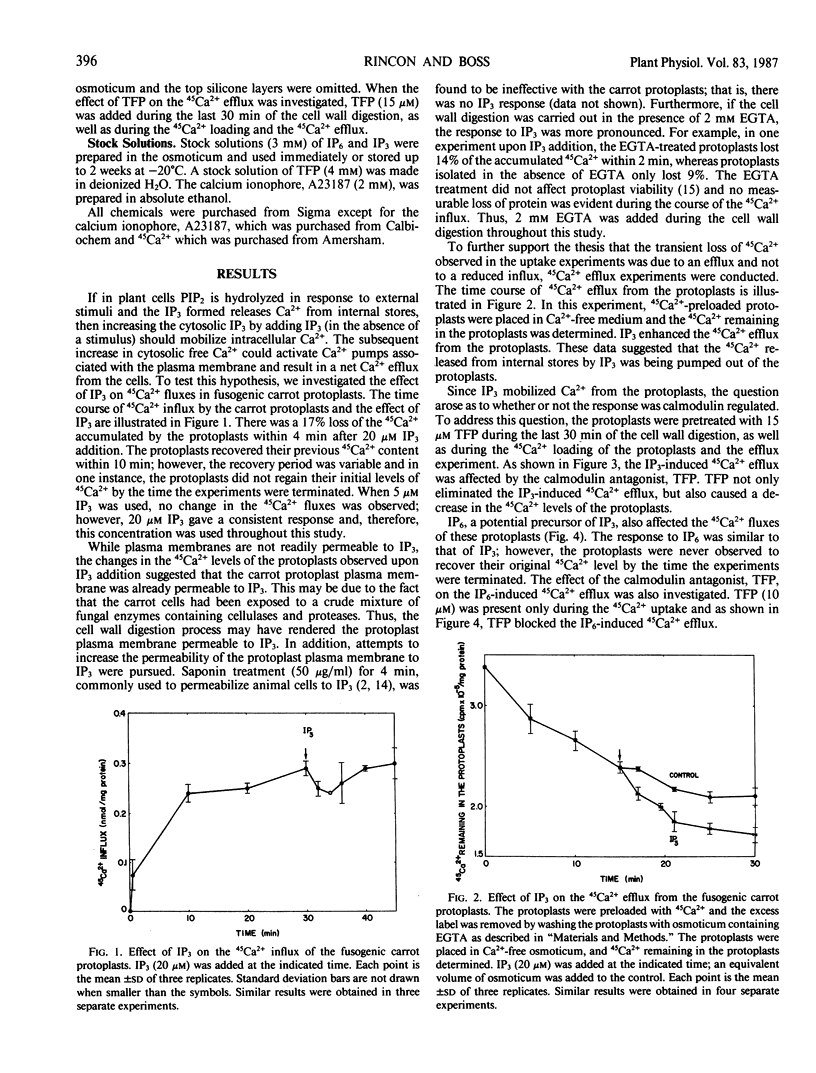
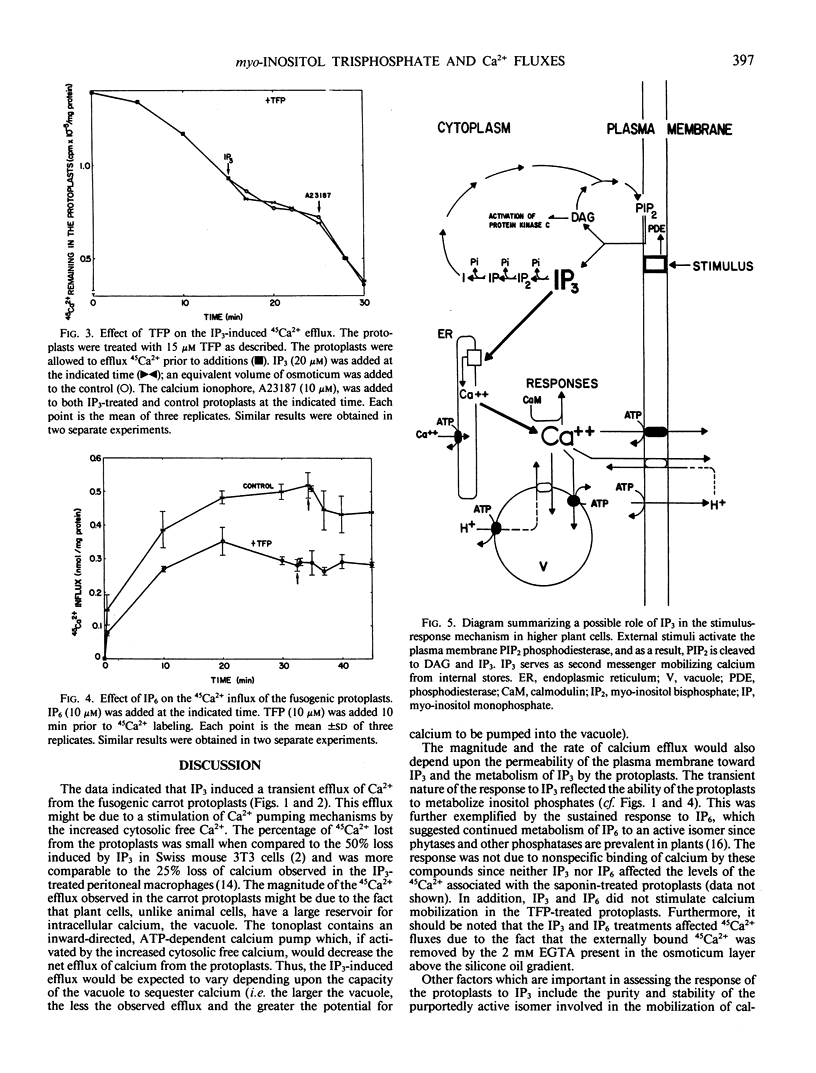
To determine whether or not inositol trisphosphate (IP3) mobilizes calcium in higher plant cells, we investigated the effect of IP3 on Ca2+ fluxes in fusogenic carrot (Daucus carota L.) protoplasts. The protoplasts were incubated in 45Ca2+-containing medium and the 45Ca2+ associated with the protoplasts was monitored with time. Addition of IP3 (20 micromolar) caused a 17% net loss of the accumulated 45Ca2+ within 4 minutes. There was a reuptake of 45Ca2+ and the protoplasts recovered to their initial value by 10 minutes. Phytic acid (IP6), also stimulated 45Ca2+ efflux from the protoplasts. Both the IP3− and the IP6−induced 45Ca2+ efflux were inhibited by the calmodulin antagonist, trifluoperazine.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Berridge M. J., Heslop J. P., Irvine R. F., Brown K. D. Inositol trisphosphate formation and calcium mobilization in Swiss 3T3 cells in response to platelet-derived growth factor. Biochem J. 1984 Aug 15;222(1):195–201. doi: 10.1042/bj2220195. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berridge M. J. Rapid accumulation of inositol trisphosphate reveals that agonists hydrolyse polyphosphoinositides instead of phosphatidylinositol. Biochem J. 1983 Jun 15;212(3):849–858. doi: 10.1042/bj2120849. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boss W. F., Massel M. O. Polyphosphoinositides are present in plant tissue culture cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1985 Nov 15;132(3):1018–1023. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(85)91908-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Creba J. A., Downes C. P., Hawkins P. T., Brewster G., Michell R. H., Kirk C. J. Rapid breakdown of phosphatidylinositol 4-phosphate and phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate in rat hepatocytes stimulated by vasopressin and other Ca2+-mobilizing hormones. Biochem J. 1983 Jun 15;212(3):733–747. doi: 10.1042/bj2120733. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drøbak B. K., Ferguson I. B. Release of Ca2+ from plant hypocotyl microsomes by inositol-1,4,5-trisphosphate. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1985 Aug 15;130(3):1241–1246. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(85)91747-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grimes H. D., Boss W. F. Intracellular calcium and calmodulin involvement in protoplast fusion. Plant Physiol. 1985 Sep;79(1):253–258. doi: 10.1104/pp.79.1.253. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirata M., Suematsu E., Hashimoto T., Hamachi T., Koga T. Release of Ca2+ from a non-mitochondrial store site in peritoneal macrophages treated with saponin by inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate. Biochem J. 1984 Oct 1;223(1):229–236. doi: 10.1042/bj2230229. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michell B. Inositol phosphates. Profusion and confusion. Nature. 1986 Jan 16;319(6050):176–177. doi: 10.1038/319176a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishizuka Y. Turnover of inositol phospholipids and signal transduction. Science. 1984 Sep 21;225(4668):1365–1370. doi: 10.1126/science.6147898. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Streb H., Irvine R. F., Berridge M. J., Schulz I. Release of Ca2+ from a nonmitochondrial intracellular store in pancreatic acinar cells by inositol-1,4,5-trisphosphate. Nature. 1983 Nov 3;306(5938):67–69. doi: 10.1038/306067a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trewavas A. J., Sexton R., Kelly P. Polarity, calcium and abscission: molecular bases for developmental plasticity in plants. J Embryol Exp Morphol. 1984 Nov;83 (Suppl):179–195. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


