Abstract
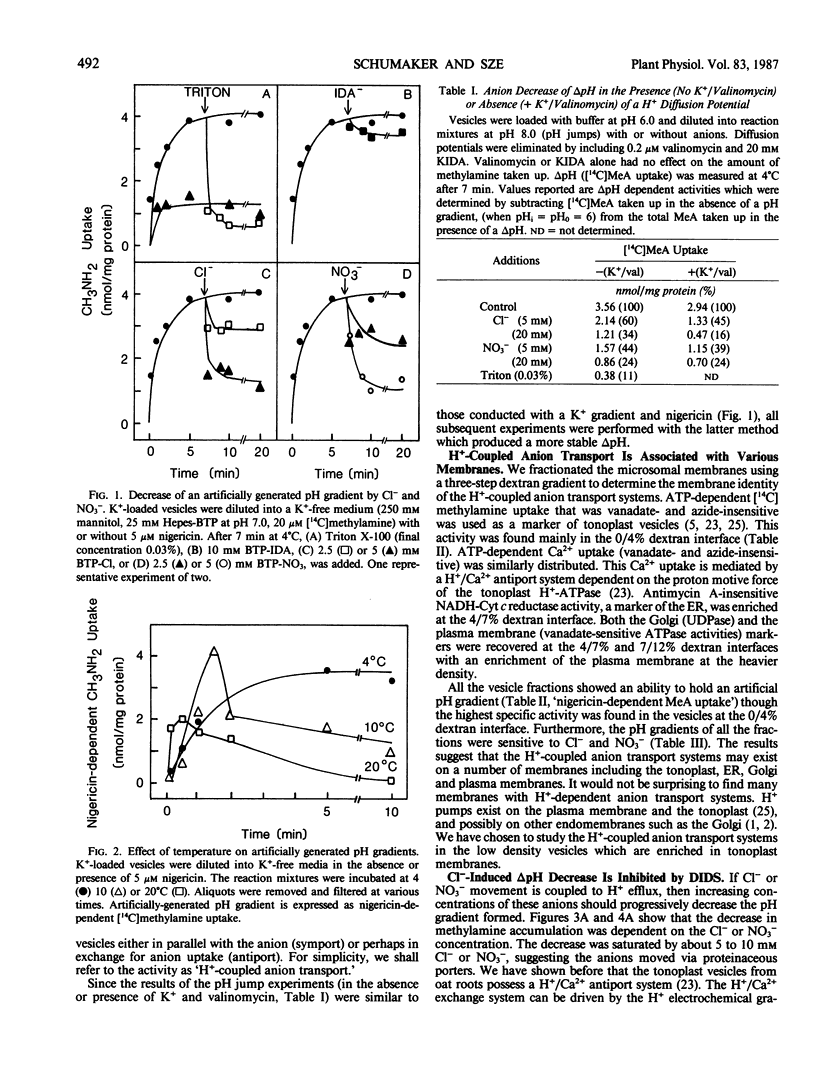
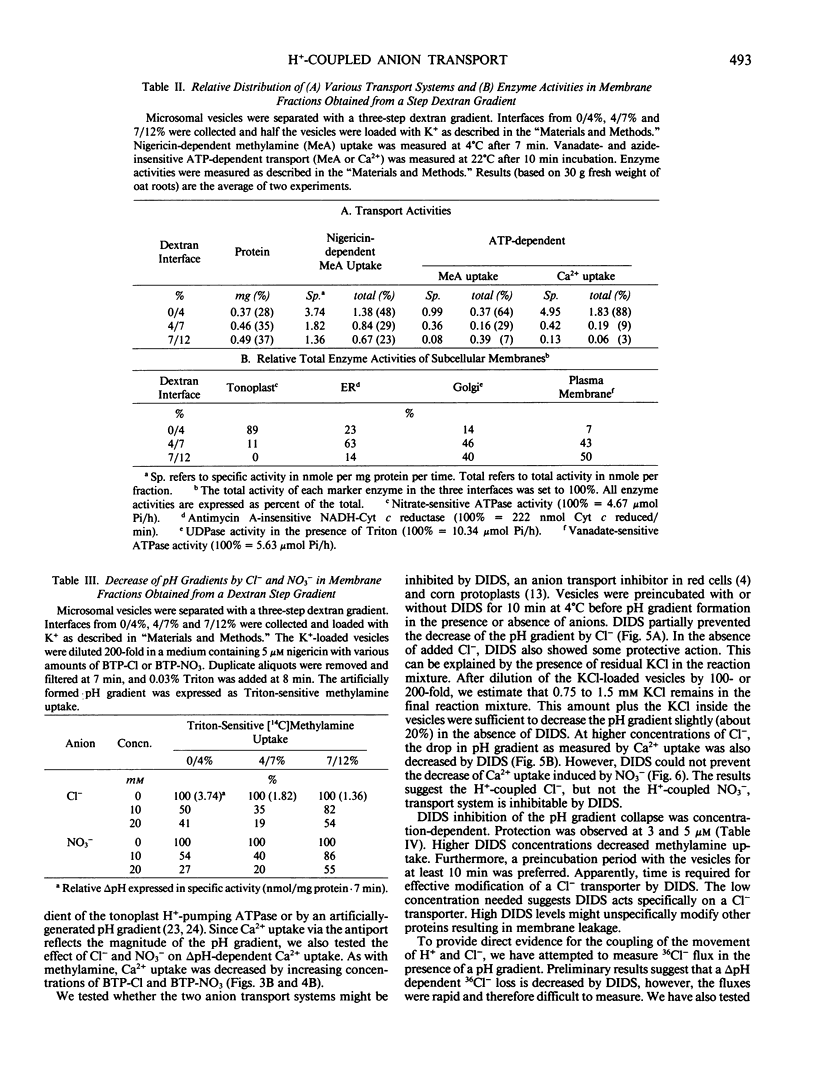
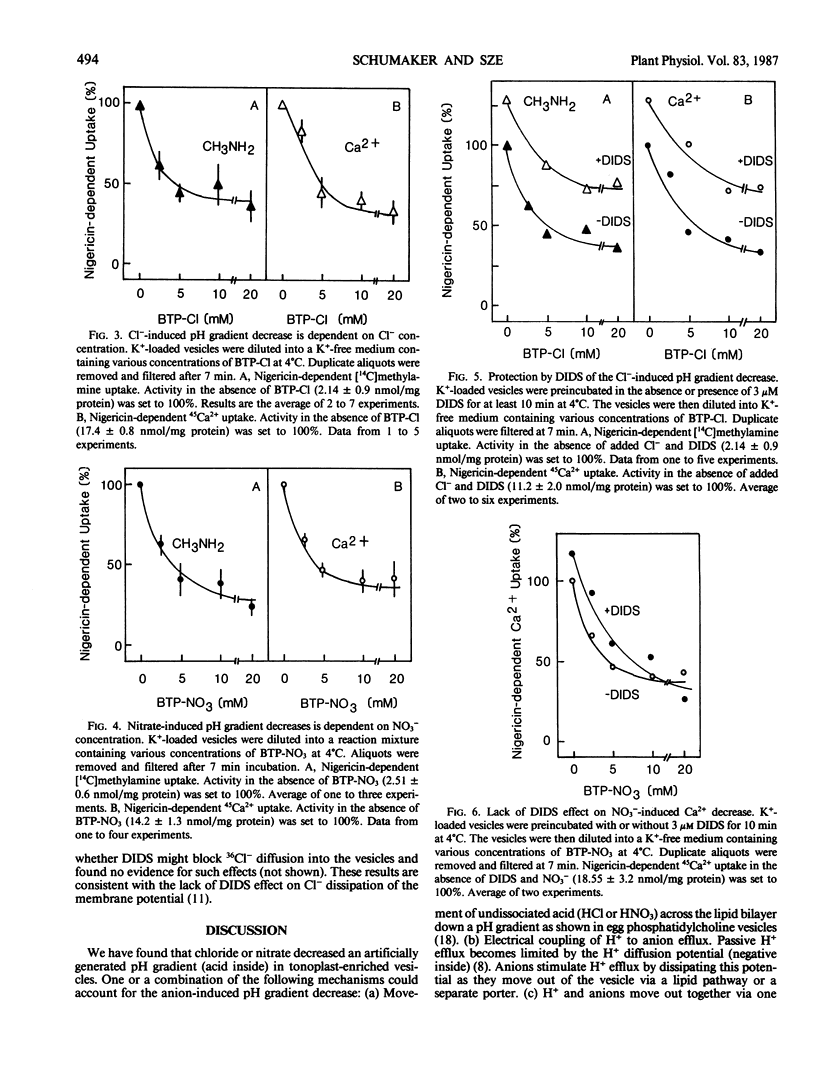
Chloride or nitrate decreased a pH gradient (measured as [14C]methylamine accumulation) in tonoplast-enriched vesicles. The ΔpH decrease was dependent on the anion concentration. These effects are independent of the anion-sensitive H+-ATPase of the tonoplast, since the pH gradient (acid inside) was imposed artificially using a pH jump or a K+ gradient and nigericin. 4,4′-Diisothiocyano-2,2′-stilbene disulfonic acid partially prevented the decrease in pH gradient induced by Cl−. Two possible models to account for this anion-dependent decrease of ΔpH are: (a) H+ loss is accompanied by Cl− or NO3− efflux from the vesicles via H+/anion symport systems on the tonoplast and (b) H+ loss is accompanied by Cl− or NO3− uptake into the vesicles via H+/anion antiport systems. Depending on the requirements and conditions of the cell, these two systems would serve to either mobilize Cl− and NO3− stored in the vacuole for use in the cytoplasm or to drive anions into the vacuole. Chloride or nitrate also decreased a pH gradient in fractions containing plasma membrane and Golgi, implying that these membranes may have similar H+-coupled anion transport systems.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ali M. S., Akazawa T. Association of H-Translocating ATPase in the Golgi Membrane System from Suspension-Cultured Cells of Sycamore (Acer pseudoplatanus L.). Plant Physiol. 1986 May;81(1):222–227. doi: 10.1104/pp.81.1.222. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Binari L. L., Racusen R. H. Membrane-associated ATPases in isolated secretory vesicles. Plant Physiol. 1983 Mar;71(3):594–597. doi: 10.1104/pp.71.3.594. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blumwald E., Poole R. J. Nitrate storage and retrieval in Beta vulgaris: Effects of nitrate and chloride on proton gradients in tonoplast vesicles. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jun;82(11):3683–3687. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.11.3683. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cabantchik Z. I., Knauf P. A., Rothstein A. The anion transport system of the red blood cell. The role of membrane protein evaluated by the use of 'probes'. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1978 Sep 29;515(3):239–302. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(78)90016-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Churchill K. A., Holaway B., Sze H. Separation of two types of electrogenic h-pumping ATPases from oat roots. Plant Physiol. 1983 Dec;73(4):921–928. doi: 10.1104/pp.73.4.921. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Churchill K. A., Sze H. Anion-Sensitive, H-Pumping ATPase of Oat Roots : Direct Effects of Cl, NO(3), and a Disulfonic Stilbene. Plant Physiol. 1984 Oct;76(2):490–497. doi: 10.1104/pp.76.2.490. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deamer D. W., Nichols J. W. Proton-hydroxide permeability of liposomes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jan;80(1):165–168. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.1.165. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hodges T. K., Leonard R. T. Purification of a plasma membrane-bound adenosine triphosphatase from plant roots. Methods Enzymol. 1974;32:392–406. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(74)32039-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaestner K. H., Sze H. Potential-dependent anion transport in tonoplast vesicles from oat roots. Plant Physiol. 1987 Mar;83(3):483–489. doi: 10.1104/pp.83.3.483. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacRobbie E. A. The active transport of ions in plant cells. Q Rev Biophys. 1970 Aug;3(3):251–294. doi: 10.1017/s0033583500004741. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nozaki Y., Tanford C. Proton and hydroxide ion permeability of phospholipid vesicles. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jul;78(7):4324–4328. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.7.4324. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pierce W. S., Higinbotham N. Compartments and Fluxes of K, NA, and CL in Avena Coleoptile Cells. Plant Physiol. 1970 Nov;46(5):666–673. doi: 10.1104/pp.46.5.666. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rea P. A., Poole R. J. Proton-Translocating Inorganic Pyrophosphatase in Red Beet (Beta vulgaris L.) Tonoplast Vesicles. Plant Physiol. 1985 Jan;77(1):46–52. doi: 10.1104/pp.77.1.46. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schumaker K. S., Sze H. A Ca/H Antiport System Driven by the Proton Electrochemical Gradient of a Tonoplast H-ATPase from Oat Roots. Plant Physiol. 1985 Dec;79(4):1111–1117. doi: 10.1104/pp.79.4.1111. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schumaker K. S., Sze H. Calcium transport into the vacuole of oat roots. Characterization of H+/Ca2+ exchange activity. J Biol Chem. 1986 Sep 15;261(26):12172–12178. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ullrich-Eberius C. I., Novacky A., Fischer E., Lüttge U. Relationship between Energy-dependent Phosphate Uptake and the Electrical Membrane Potential in Lemna gibba G1. Plant Physiol. 1981 Apr;67(4):797–801. doi: 10.1104/pp.67.4.797. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang Y., Leigh R. A., Kaestner K. H., Sze H. Electrogenic h-pumping pyrophosphatase in tonoplast vesicles of oat roots. Plant Physiol. 1986 Jun;81(2):497–502. doi: 10.1104/pp.81.2.497. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang Y., Sze H. Similarities and differences between the tonoplast-type and the mitochondrial H+-ATPases of oat roots. J Biol Chem. 1985 Sep 5;260(19):10434–10443. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- West I. C. Energy coupling in secondary active transport. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1980 May 27;604(1):91–126. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(80)90586-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


