Abstract
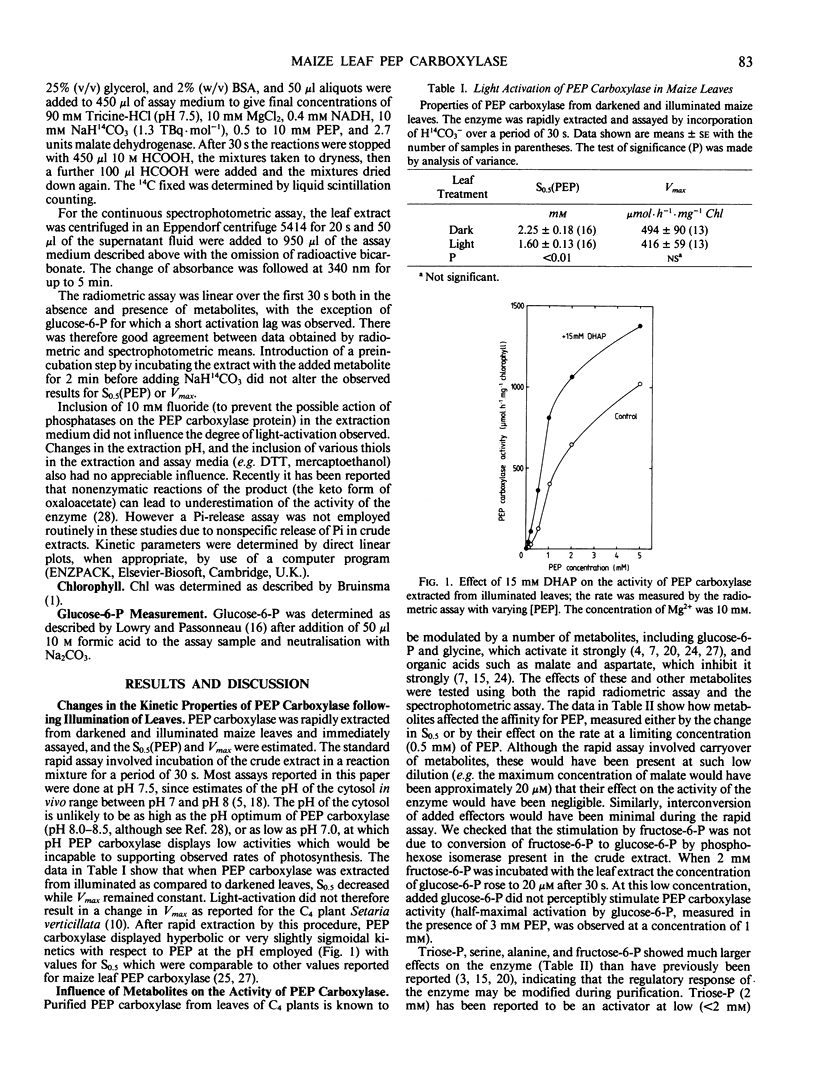
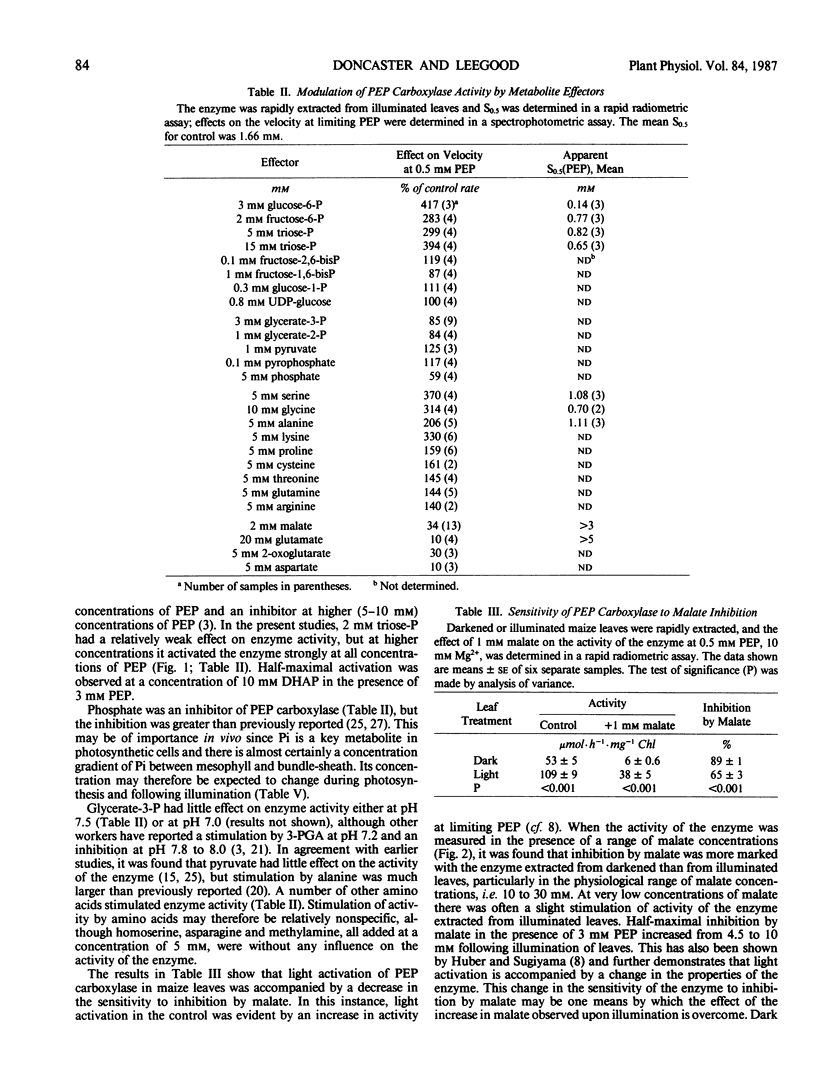
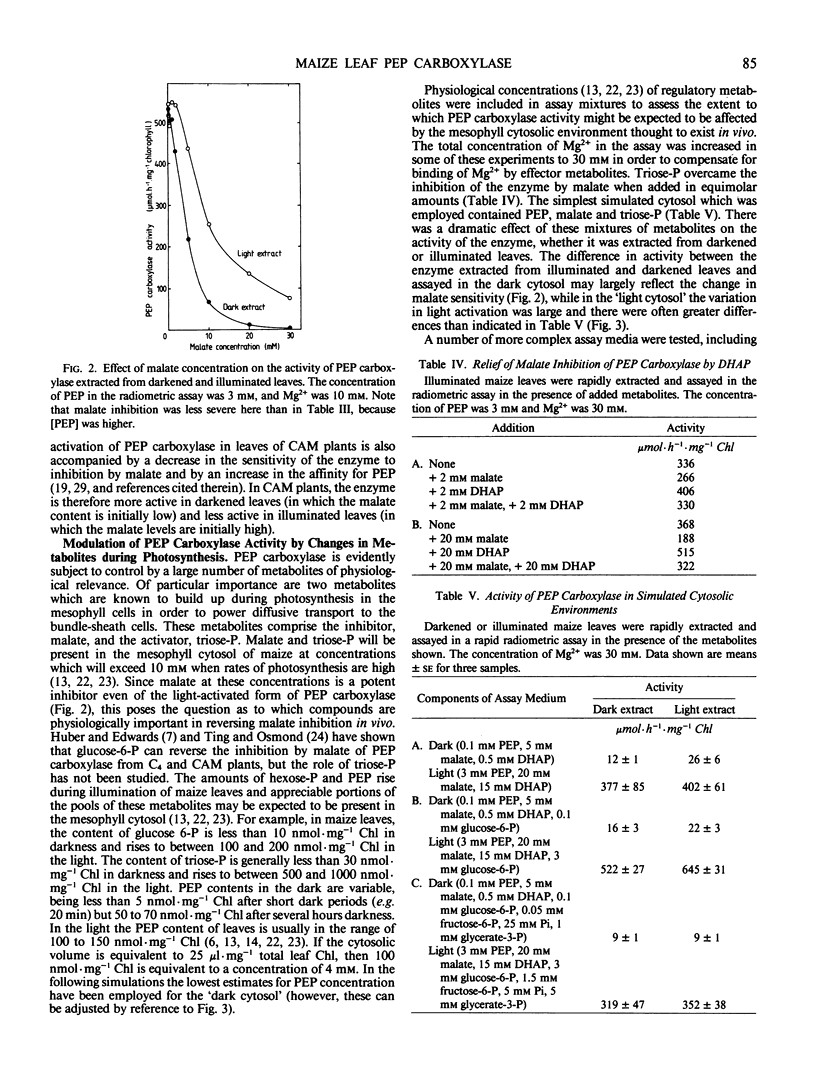
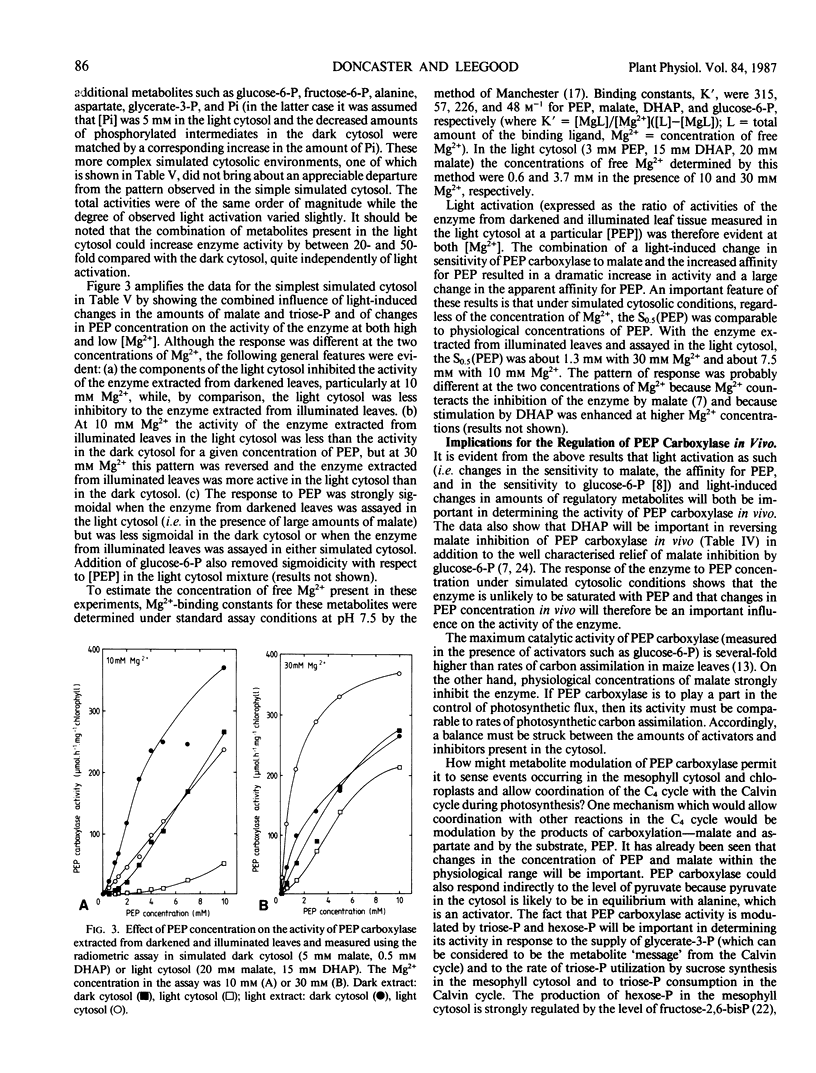
The aim of this work was to investigate how light regulates the activity of phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase in vivo in C4 plants. The properties of phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase were investigated in extracts which were rapidly prepared (in less than 30 seconds) from darkened and illuminated leaves of Zea mays. Illumination resulted in a significant decrease in the S0.5(phosphoenolpyruvate) but there was no change in Vmax. The form of the enzyme from illuminated leaves was less sensitive to malate inhibition than was the form from darkened leaves. At low concentrations of phosphoenolpyruvate, the activity of the enzyme was strongly stimulated by glucose-6-phosphate, fructose-6-phosphate, triose-phosphate, alanine, serine, and glycine and was inhibited by organic acids. The enzyme was assayed in mixtures of metabolites at concentrations believed to be present in the mesophyll cytosol in the light and in the dark. It displayed low activity in a simulated `dark' cytosol and high activity in a simulated `light' cytosol, but activities were different for the enzyme from darkened compared to illuminated leaves.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BRUINSMA J. A comment on the spectrophotometric determination of chlorophyll. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1961 Sep 30;52:576–578. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(61)90418-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Budde R. J., Chollet R. In vitro phosphorylation of maize leaf phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase. Plant Physiol. 1986 Dec;82(4):1107–1114. doi: 10.1104/pp.82.4.1107. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huber S. C., Sugiyama T. Changes in Sensitivity to Effectors of Maize Leaf Phosphoenolypyruvate Carboxylase during Light/Dark Transitions. Plant Physiol. 1986 Jun;81(2):674–677. doi: 10.1104/pp.81.2.674. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karabourniotis G., Manetas Y., Gavalas N. A. Detecting Photoactivation of Phosphoenolpyruvate Carboxylase in C(4) Plants : An Effect of pH. Plant Physiol. 1985 Feb;77(2):300–302. doi: 10.1104/pp.77.2.300. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karabourniotis G., Manetas Y., Gavalas N. A. Photoregulation of Phosphoenolpyruvate Carboxylase in Salsola soda L. and Other C(4) Plants. Plant Physiol. 1983 Nov;73(3):735–739. doi: 10.1104/pp.73.3.735. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lowe J., Slack C. R. Inhibition of maize leaf phosphopyruvate carboxylase by oxaloacetate. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1971 Apr 14;235(1):207–209. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(71)90048-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manchester K. L. Determination of magnesium and potassium binding constants to phosphoenolpyruvate, 2- and 3-phosphoglycerate and a number of other anions. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1980 Jun 19;630(2):225–231. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(80)90425-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nimmo G. A., Nimmo H. G., Hamilton I. D., Fewson C. A., Wilkins M. B. Purification of the phosphorylated night form and dephosphorylated day form of phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase from Bryophyllum fedtschenkoi. Biochem J. 1986 Oct 1;239(1):213–220. doi: 10.1042/bj2390213. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishikido T., Takanashi H. Glycine activation of PEP carboxylase from monocotyledoneous C4 plants. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1973 Jul 2;53(1):126–133. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(73)91410-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ting I. P., Osmond C. B. Multiple forms of plant phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase associated with different metabolic pathways. Plant Physiol. 1973 Mar;51(3):448–453. doi: 10.1104/pp.51.3.448. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ting I. P., Osmond C. B. Photosynthetic phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylases: characteristics of alloenzymes from leaves of c(3) and c(1) plants. Plant Physiol. 1973 Mar;51(3):439–447. doi: 10.1104/pp.51.3.439. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uedan K., Sugiyama T. Purification and characterization of phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase from maize leaves. Plant Physiol. 1976 Jun;57(6):906–910. doi: 10.1104/pp.57.6.906. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker G. H., Ku M. S., Edwards G. E. Activity of maize leaf phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase in relation to tautomerization and nonenzymatic decarboxylation of oxaloacetate. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1986 Aug 1;248(2):489–501. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(86)90502-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu M. X., Wedding R. T. Regulation of phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase from Crassula by interconversion of oligomeric forms. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1985 Aug 1;240(2):655–662. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(85)90073-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


