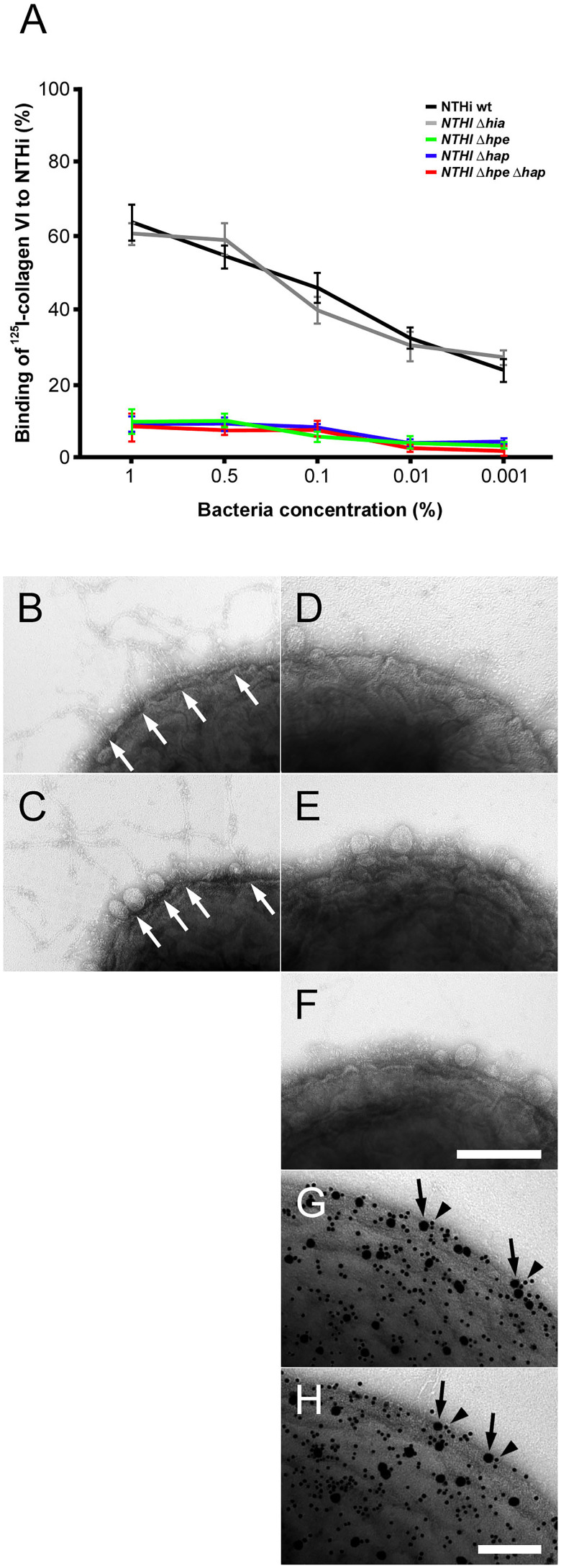
In the published article, there was an error in Figure 3 as published. Panel 3D does not show the correct bacterial specimen. The corrected Figure 3 and its caption “Targeting of NTHi surface adhesins PE and Hap by collagen VI VWA domains. (A) Titration of bacterial solutions with radiolabeled collagen VI microfibrils. Serial dilutions of bacteria were used: 1% (2 × 109 cfu/ml), 0.5% (1 × 109 cfu/ml), 0.1% (2 × 108 cfu/ml), 0.01% (2 × 107 cfu/ml), and 0.001% (2 × 106 cfu/ml). Wild type bacteria are compared to isogenic mutants as indicated. (B–F) negative staining and transmission electron microscopy of collagen VI networks bound to the bacterial surface. Wild type (B) and Δhia (C) bacteria interact with collagen VI (arrows) as opposed to Δhpe (D), Δhap (E), and ΔhpeΔhap (F). PE (G) and Hap (H) are frequently colocalized with collagen VI on the bacterial surface as visualized by antibodies conjugated with 5 nm (PE and Hap, arrowheads) and 10 nm (collagen VI, arrows) colloidal gold, respectively. The scale bars represent 200 nm (B–F) and 100 nm (G, H).” appear below.
Figure 3.
Targeting of NTHi surface adhesins PE and Hap by collagen VI VWA domains. (A) Titration of bacterial solutions with radiolabeled collagen VI microfibrils. Serial dilutions of bacteria were used: 1% (2 × 109 cfu/ml), 0.5% (1 × 109 cfu/ml), 0.1% (2 × 108 cfu/ml), 0.01% (2 × 107 cfu/ml), and 0.001% (2 × 106 cfu/ml). Wild type bacteria are compared to isogenic mutants as indicated. (B–F) negative staining and transmission electron microscopy of collagen VI networks bound to the bacterial surface. Wild type (B) and Δhia (C) bacteria interact with collagen VI (arrows) as opposed to Δhpe (D), Δhap (E), and ΔhpeΔhap (F). PE (G) and Hap (H) are frequently colocalized with collagen VI on the bacterial surface as visualized by antibodies conjugated with 5 nm (PE and Hap, arrowheads) and 10 nm (collagen VI, arrows) colloidal gold, respectively. The scale bars represent 200 nm (B–F) and 100 nm (G, H).
The authors apologize for this error and state that this does not change the scientific conclusions of the article in any way. The original article has been updated.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.