Abstract
A major triticale (X Triticosecale Wittmack) endosperm acid phosphatase (EC 3.1.2.2) (APase) from sib-lines producing plump and shriveled seed was purified 140- and 230-fold to a specific activity of 94 and 153 micromoles per minute per milligram protein respectively, by ammonium sulfate fractionation, ion-exchange chromatography, chromatofocusing, affinity column chromatography, and gel filtration. The purified enzyme from both materials is a monomeric glycoprotein with an apparent molecular weight of 45,700 ± 500 containing 12% carbohydrate and an apparent isoelectric point of pH 5.9. It hydrolyzes tri- and di-phosphate of nucleosides as well as phosphate esters and exhibits characteristics of ATP-hydrolase and phosphatase. About 2-fold more of the APase was isolated from shriveled seeds, and the purified enzyme exhibited 3- and 5-fold higher Vmax for p-nitrophenyl phosphate and ATP, respectively, than that of plump seed. The I50 for Pi concentration was 5.5-fold higher in APase of shriveled seed than the plump one. These varied quantitative and kinetic properties substantiate the role of APase in lines with shriveled seeds being reduction of starch accumulation by depleting substrates and energy supply in the cytosol.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ching T. M., Poklemba C. J., Metzger R. J. Starch synthesis in shriveled and plump triticale seeds. Plant Physiol. 1983 Nov;73(3):652–657. doi: 10.1104/pp.73.3.652. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
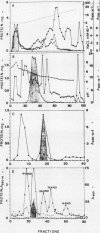
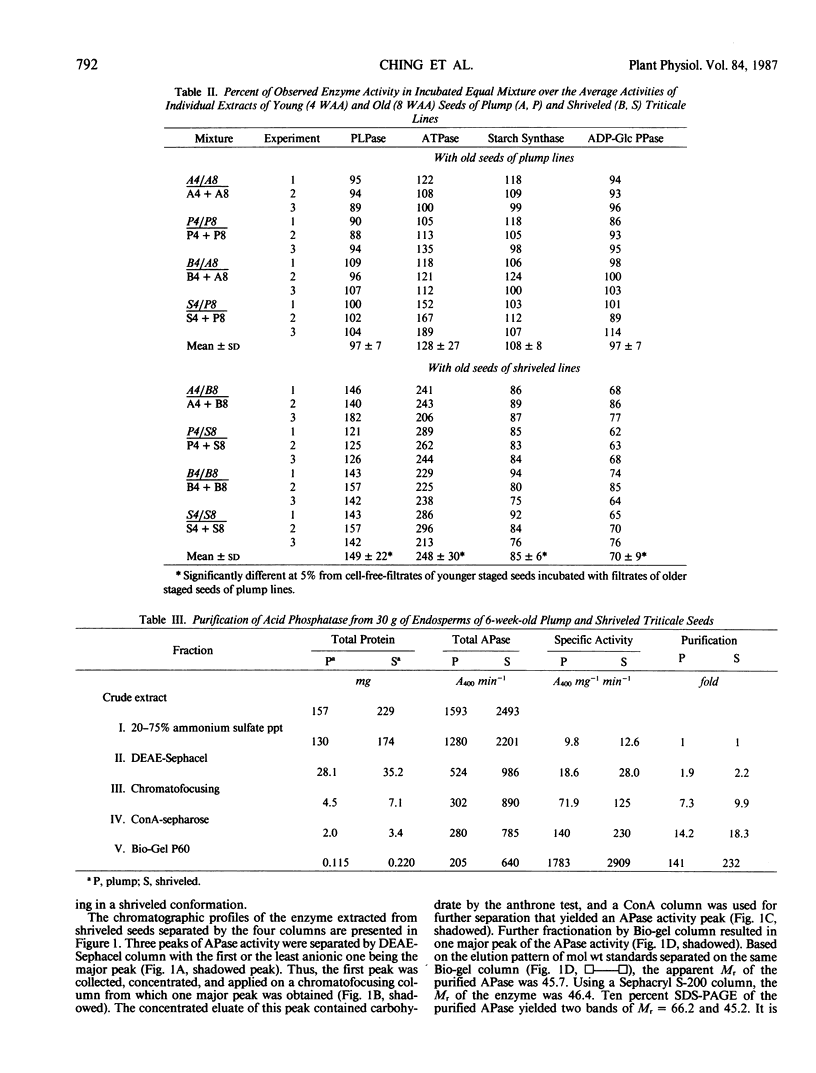
- Ching T. M., Thompson D. M., Metzger R. J. Acid phosphatases and seed shriveling in triticale. Plant Physiol. 1984 Oct;76(2):478–482. doi: 10.1104/pp.76.2.478. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Choe B. K., Pontes E. J., McDonald I., Rose N. R. Purification and characterization of human prostatic acid phosphatase. Prep Biochem. 1978;8(1):73–89. doi: 10.1080/00327487808068219. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dibenedetto G., Mura U. Some kinetic aspects of the mechanism of hydrolysis of phosphoric acid esters by nonspecific acid phosphatase from Schizosaccharomyces pombe. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1978 Jan 12;522(1):122–129. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(78)90328-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fedoroff N., Mauvais J., Chaleff D. Molecular studies on mutations at the Shrunken locus in maize caused by the controlling element Ds. J Mol Appl Genet. 1983;2(1):11–29. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hannah L. C., Tuschall D. M., Mans R. J. Multiple forms of maize endosperm adp-glucose pyrophosphorylase and their control by shrunken-2 and brittle-2. Genetics. 1980 Aug;95(4):961–970. doi: 10.1093/genetics/95.4.961. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JOYCE B. K., GRISOLIA S. Purification and properties of a nonspecific acid phosphatase from wheat germ. J Biol Chem. 1960 Aug;235:2278–2281. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee L., Tsai C. Y. Effect of RNase on Zein Synthesis in Endosperms of brittle-2opaque-2 Maize Double Mutant. Plant Physiol. 1984 Sep;76(1):79–83. doi: 10.1104/pp.76.1.79. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakabayashi T., Ikezawa H. Acid adenosine triphosphatase from chicken liver lysosomes. I. Partial purification and some properties. J Biochem. 1980 Jun;87(6):1669–1680. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a132911. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishimura M., Beevers H. Hydrolases in vacuoles from castor bean endosperm. Plant Physiol. 1978 Jul;62(1):44–48. doi: 10.1104/pp.62.1.44. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plaxton W. C., Preiss J. Purification and Properties of Nonproteolytic Degraded ADPglucose Pyrophosphorylase from Maize Endosperm. Plant Physiol. 1987 Jan;83(1):105–112. doi: 10.1104/pp.83.1.105. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saini M. S., Van Etten R. L. A homogeneous isoenzyme of human liver acid phosphatase. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1978 Dec;191(2):613–624. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(78)90399-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]