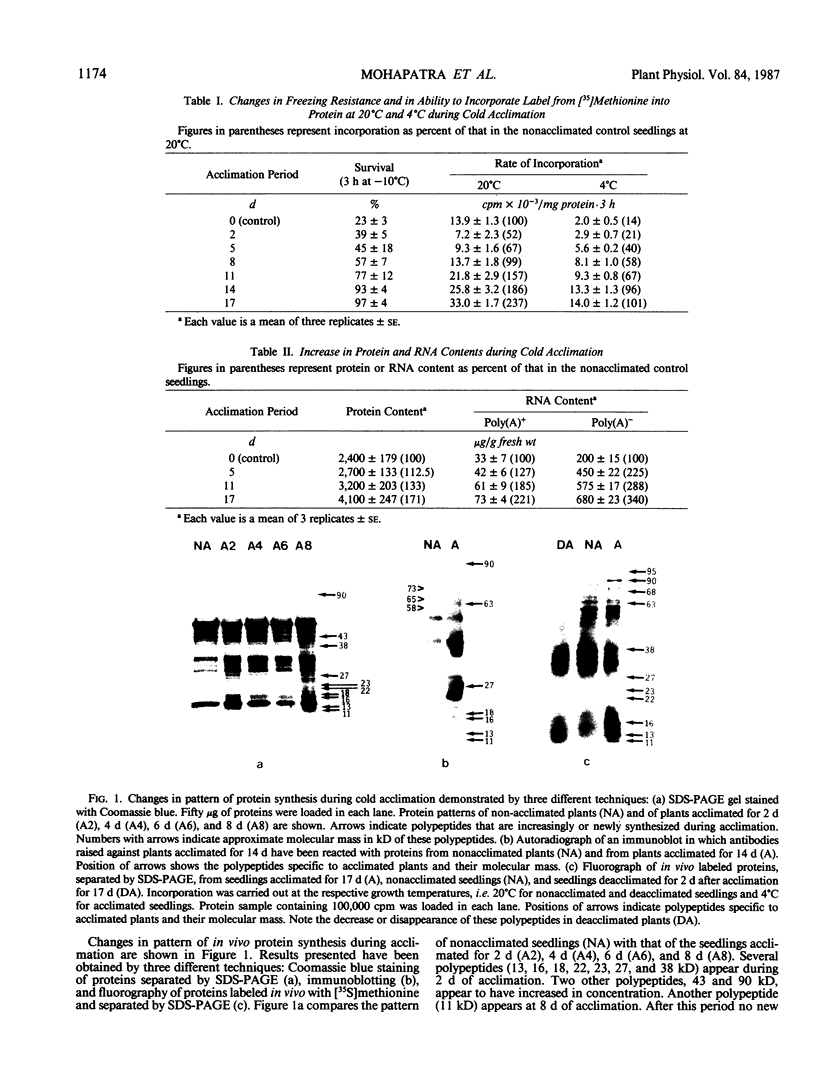
Abstract
Changes in the rate and pattern of protein synthesis and in translatable mRNA population during cold acclimation of alfalfa (Medicago falcata cv Anik) seedlings have been examined. There appears to be a positive correlation between the increase in ability to synthesize proteins at 4°C and the increase in freezing resistance (survival at −10°C). Results obtained with three different approaches using sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis pattern visualized by (a) staining, (b) immunoblotting and autoradiography, and (c) fluorography of in vivo labeled proteins, show that at least eight polypeptides are newly synthesized during cold acclimation. Results of analysis of in vitro translation products of mRNA from nonacclimated and acclimated seedlings show the appearance of new translatable mRNAs. It is concluded that changes in gene expression occur during cold acclimation, most probably at the transcriptional level.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coleman E. A., Bula R. J., Davis R. L. Electrophoretic and Immunological Comparisons of Soluble Root Proteins of Medicago sativa L. Genotypes in the Cold Hardened and Non-Hardened Condition. Plant Physiol. 1966 Dec;41(10):1681–1685. doi: 10.1104/pp.41.10.1681. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Faw W. F., Jung G. A. Electrophoretic protein patterns in relation to low temperature tolerance and growth regulation of alfalfa. Cryobiology. 1972 Dec;9(6):548–555. doi: 10.1016/0011-2240(72)90177-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerloff E. D., Stahmann M. A., Smith D. Soluble proteins in alfalfa roots as related to cold hardiness. Plant Physiol. 1967 Jul;42(7):895–899. doi: 10.1104/pp.42.7.895. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guy C. L., Niemi K. J., Brambl R. Altered gene expression during cold acclimation of spinach. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jun;82(11):3673–3677. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.11.3673. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sarhan F., Chevrier N. Regulation of RNA Synthesis by DNA-Dependent RNA Polymerases and RNases during Cold Acclimation in Winter and Spring Wheat. Plant Physiol. 1985 Jun;78(2):250–255. doi: 10.1104/pp.78.2.250. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiser C. J. Cold Resistance and Injury in Woody Plants: Knowledge of hardy plant adaptations to freezing stress may help us to reduce winter damage. Science. 1970 Sep 25;169(3952):1269–1278. doi: 10.1126/science.169.3952.1269. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]




