Figure 2.
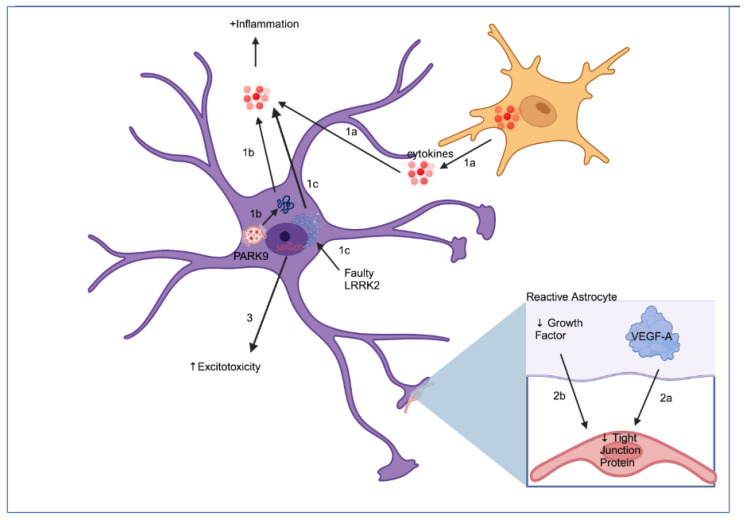
Various factors lead to astrocyte reactivity, which causes neurodegenerative properties in astrocytes. (1a) Microglia secrete various inflammatory cytokines that stimulate the expression of pro-inflammatory cytokines in astrocytes and turn them into a reactive phenotype. (1b) The loss-of-function mutation of PARK9 protein leads to an inability to neutralize αS, causing an accumulation of αS that induces astrocyte-mediated inflammation. (1c) LRRK2 mutation leads to ER stress-induced secretion of inflammatory cytokines through dyshomeostasis of calcium ions. (2a) Reactive astrocytes express VEGF-A, a protein that reduces BBB integrity by downregulating the expression of tight junction proteins, claudin-5 and occludin. (2b) Reactive astrocytes produce fewer growth factors, molecules implicated in tight junction expression, and thus BBB integrity. (3) Various genetic mutations found in PD such as LRRK2 and DJ-1 impair glutamate metabolism, which induces excitotoxicity in neurons. Figure created with biorender.com. Accessed on 13 August 2023.