Abstract
A new strain, Streptomyces rimosus LS-T hybrid, characterized by a lower level of foaming and higher antibiotic activity as compared to the other active strains of S. rimosus, is obtained as a result of selection among prototrophic recombinant forms of strains LS-T293 and BS-21. The studies on strain LS-T hybrid show the possibilities of combining properties of different strains of S. rimosus in the hybrid forms. The occurrence of new properties in the hybrid forms is detected.
Full text
PDF
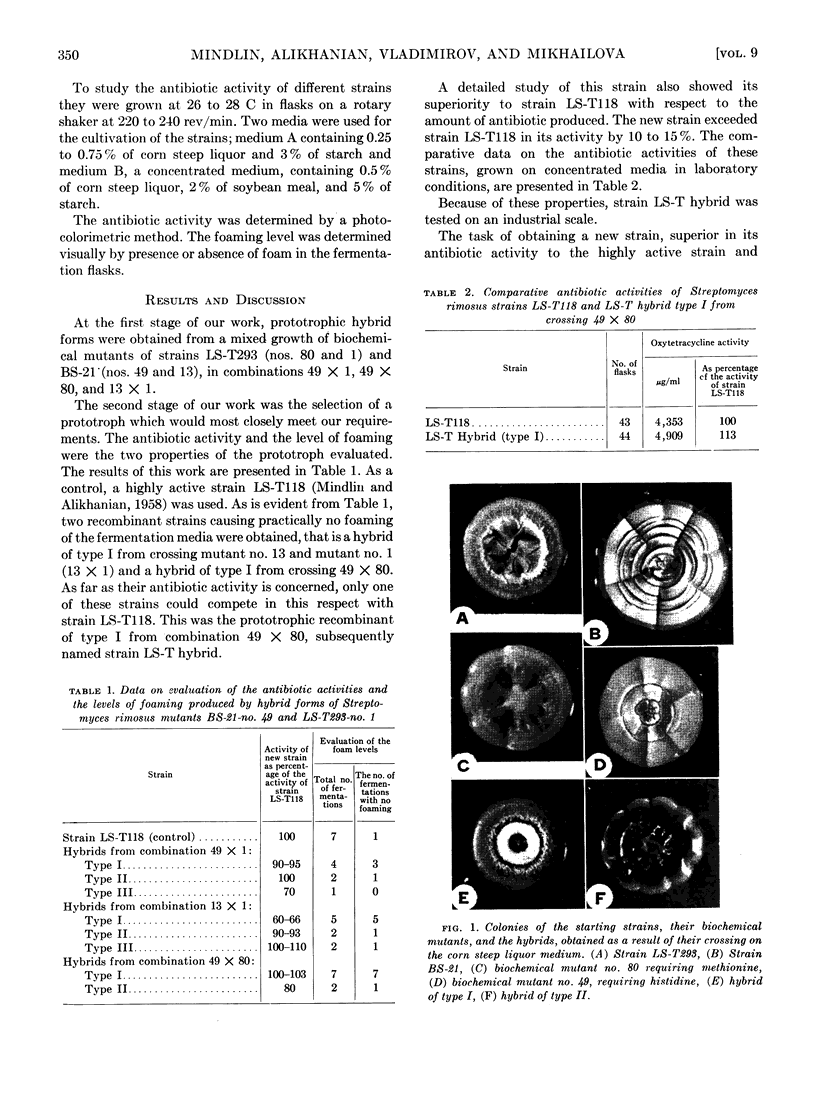
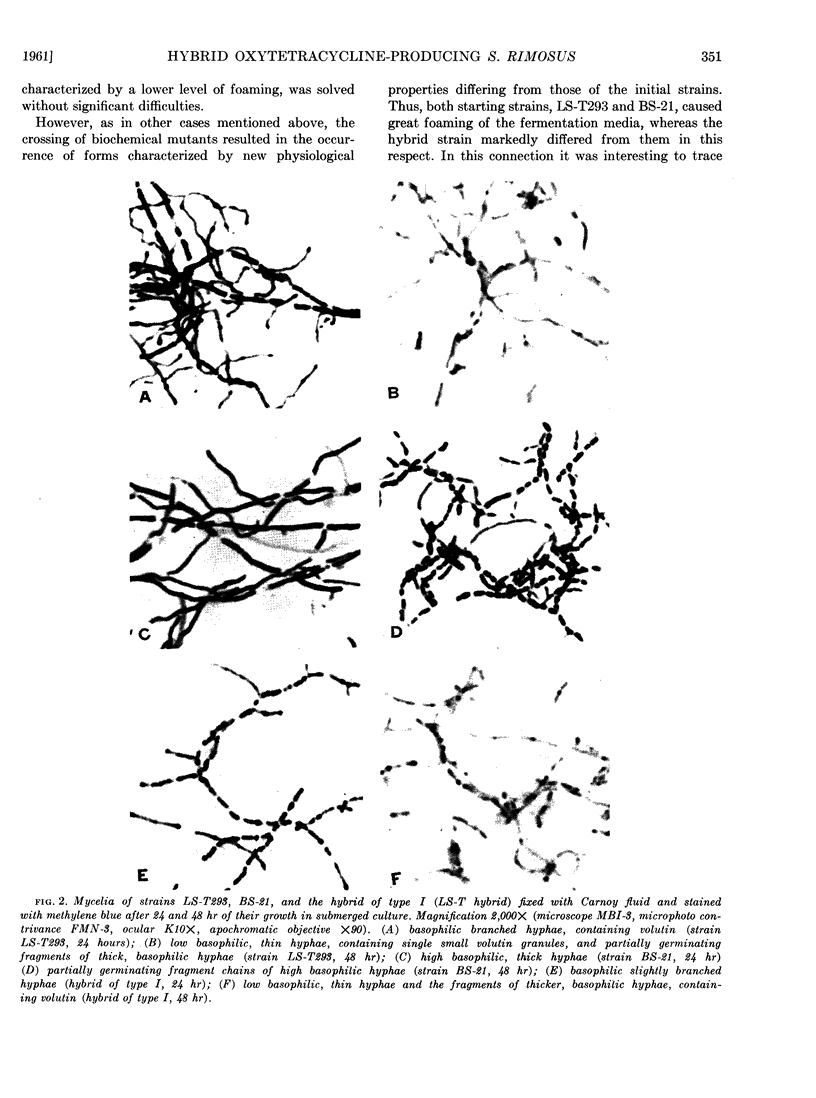

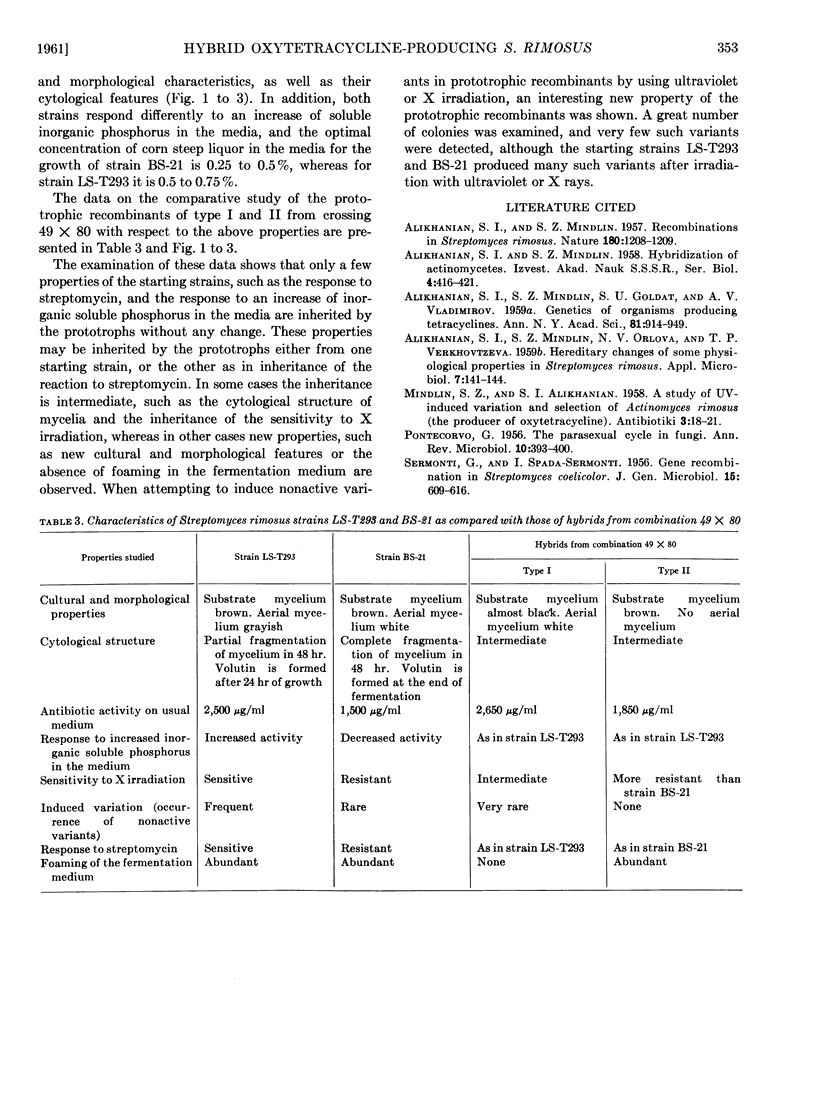
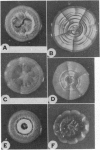
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ALIKHANIAN S. I., MINDLIN S. Z., GOLDAT S. U., VLADIMIZOV A. V. Genetics of organisms producing tetracyclines. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1959 Sep 30;81:914–949. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1959.tb49379.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ALIKHANIAN S. I., MINDLIN S. Z., ORLOVA N. V., VERKHOVTZEVA T. P. Hereditary changes of some physiological properties in Streptomyces rimosus. Appl Microbiol. 1959 May;7(3):141–144. doi: 10.1128/am.7.3.141-144.1959. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ALIKHANIAN S. I., MINDLIN S. Z. Recombinations in Streptomyces rimosus. Nature. 1957 Nov 30;180(4596):1208–1209. doi: 10.1038/1801208a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PONTECORVO G. The parasexual cycle in fungi. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1956;10:393–400. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.10.100156.002141. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SERMONTI G., SPADA-SERMONTI I. Gene recombination in Streptomyces coelicolor. J Gen Microbiol. 1956 Dec;15(3):609–616. doi: 10.1099/00221287-15-3-609. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]