Abstract
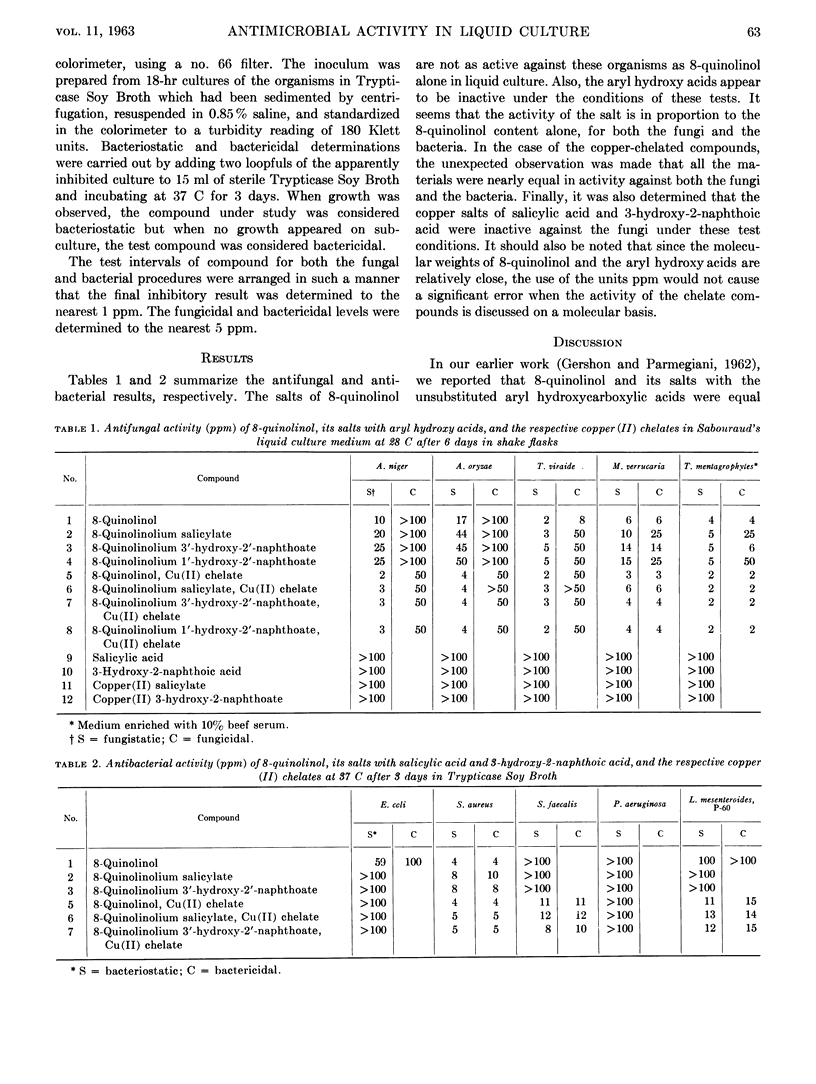
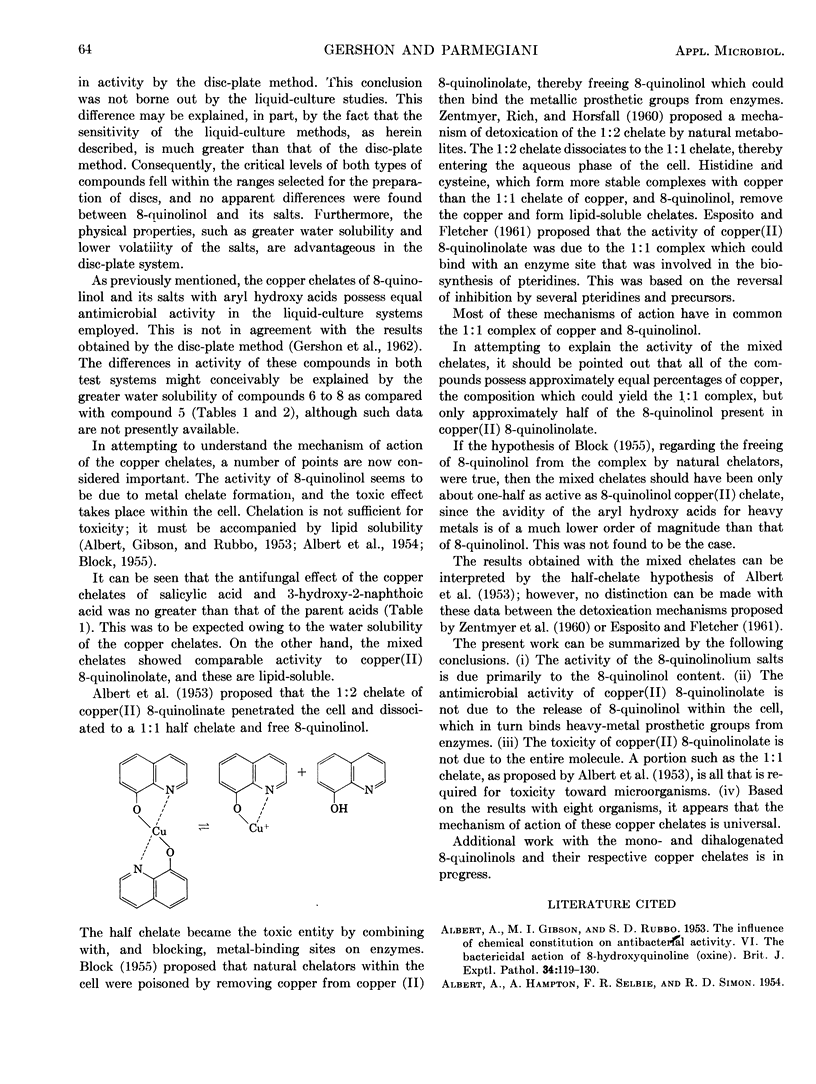
A study was made of the antimicrobial activities of 8-quinolinol and its salts with salicylic acid and 3-hydroxy-2-naphthoic acid in liquid culture. Comparisons of results were made with those obtained by the discplate method. The mechanism of action of copper chelates was discussed.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ALBERT A., GIBSON M. I., RUBBO S. D. The influence of chemical constitution on antibacterial activity. VI. The bactericidal action of 8-hydroxyquinoline (oxine). Br J Exp Pathol. 1953 Apr;34(2):119–130. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ALBERT A., HAMPTON A., SELBIE F. R., SIMON R. D. The influence of chemical constitution on anti-bacterial activity. VII. The site of action of 8-hydroxy-quinoline (oxine). Br J Exp Pathol. 1954 Feb;35(1):75–84. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ESPOSITO R. G., FLETCHER A. M. The relationship of pteridine biosynthesis to the action of copper 8-hydroxyquinolate on fungal spores. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1961 May;93:369–376. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(61)90280-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GERSHON H., PARMEGIANI R. Antimicrobial activity of 8-quinolinols, salicylic acids, hydroxynaphthoic acids, and salts of selected quinolinols with selected hydroxy-acids. Appl Microbiol. 1962 Jul;10:348–353. doi: 10.1128/am.10.4.348-353.1962. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GERSHON H., PARMEGIANIR, NICKERSON W. J. Antimicrobial activity of metal chelates of salts of 8-quinolinols with aromatic hydroxycarboxylic acids. Appl Microbiol. 1962 Nov;10:556–560. doi: 10.1128/am.10.6.556-560.1962. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


