Abstract
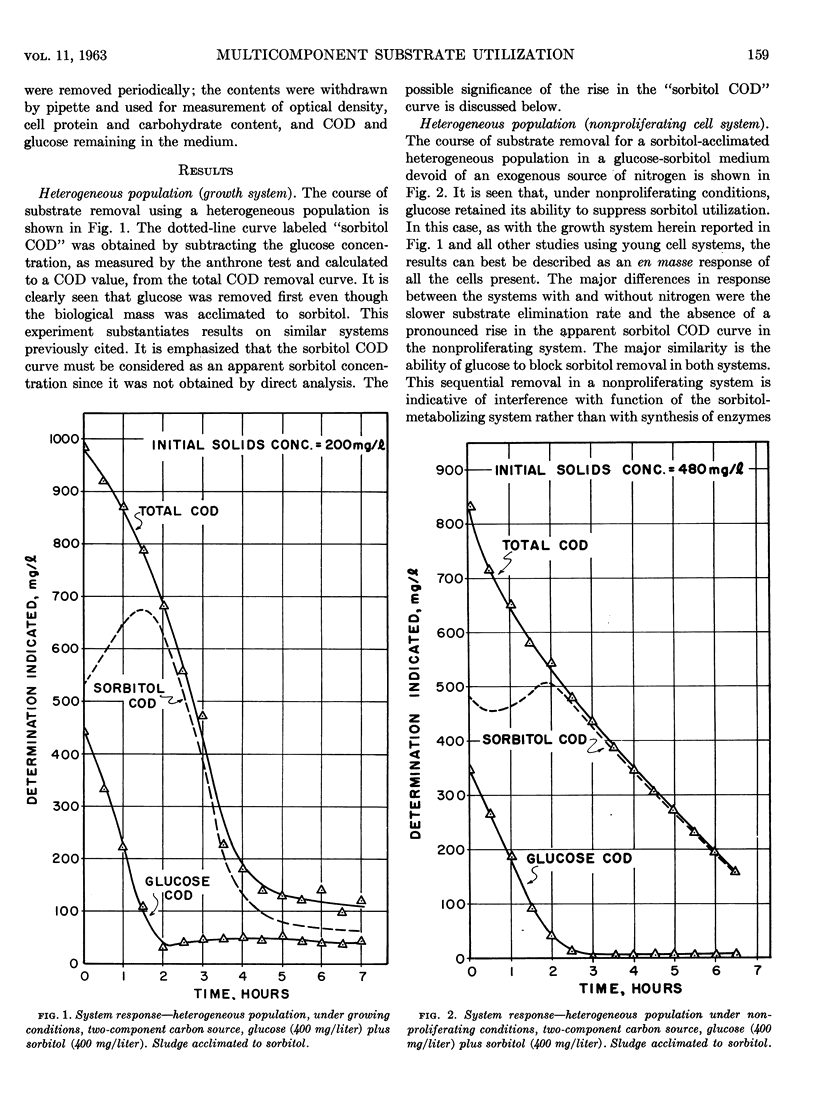
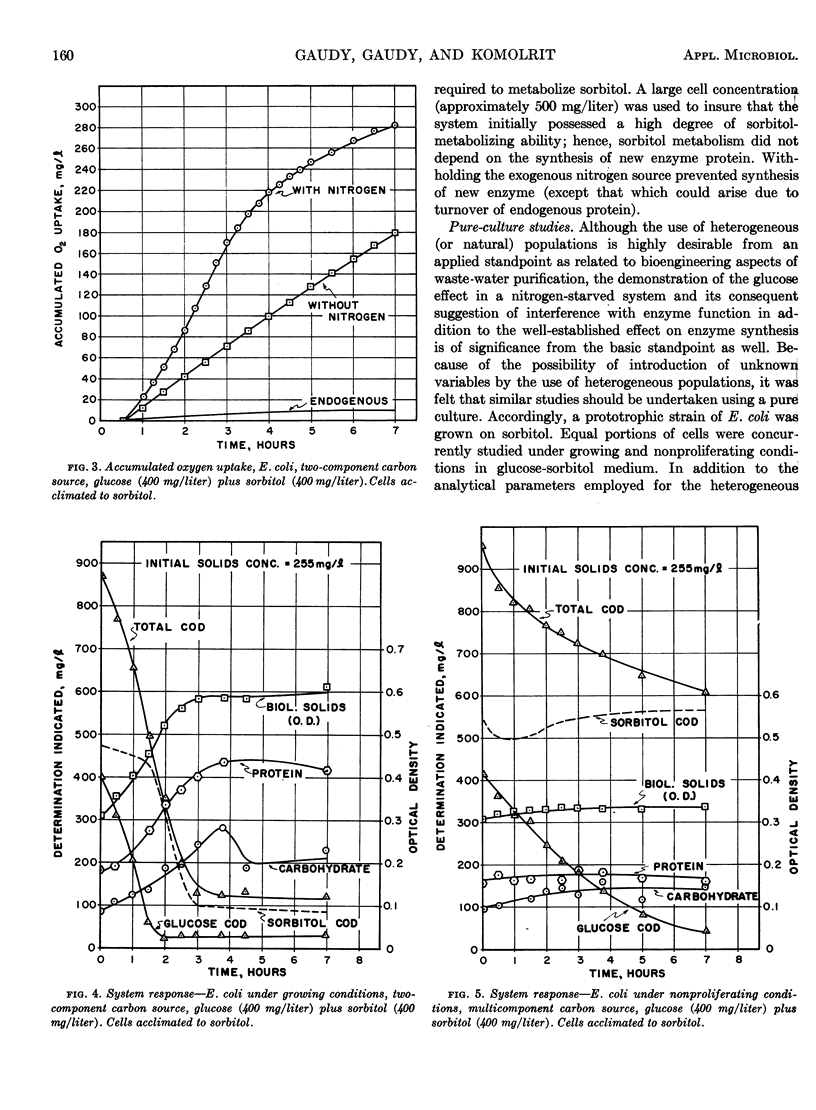
A heterogeneous population, typical of activated sludge, and a prototrophic strain of Escherichia coli were used to test for sequential substrate removal in a glucose-sorbitol medium. Each culture was preacclimated to sorbitol and was studied in the two-component medium under growing and nonproliferating conditions. In all four systems, glucose blocked sorbitol removal. Since large initial inocula were used, the suppression of sorbitol metabolism could not be totally due to repression of enzyme synthesis. The results indicate that glucose may affect the functioning of an existing enzyme system in addition to its established effect on enzyme synthesis. From an applied standpoint, the results indicate that an activated sludge may be completely and immediately prevented from eliminating a waste constituent to which it is acclimated.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Gaudy A. F. Studies on Induction and Repression in Activated Sludge Systems. Appl Microbiol. 1962 May;10(3):264–271. doi: 10.1128/am.10.3.264-271.1962. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MAGASANIK B. Catabolite repression. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1961;26:249–256. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1961.026.01.031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morris D. L. Quantitative Determination of Carbohydrates With Dreywood's Anthrone Reagent. Science. 1948 Mar 5;107(2775):254–255. doi: 10.1126/science.107.2775.254. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stephenson M., Gale E. F. Factors influencing bacterial deamination: The deamination of glycine, dl-alanine and l-glutamic acid by Bacterium coli. Biochem J. 1937 Aug;31(8):1316–1322.1. doi: 10.1042/bj0311316. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


