Abstract
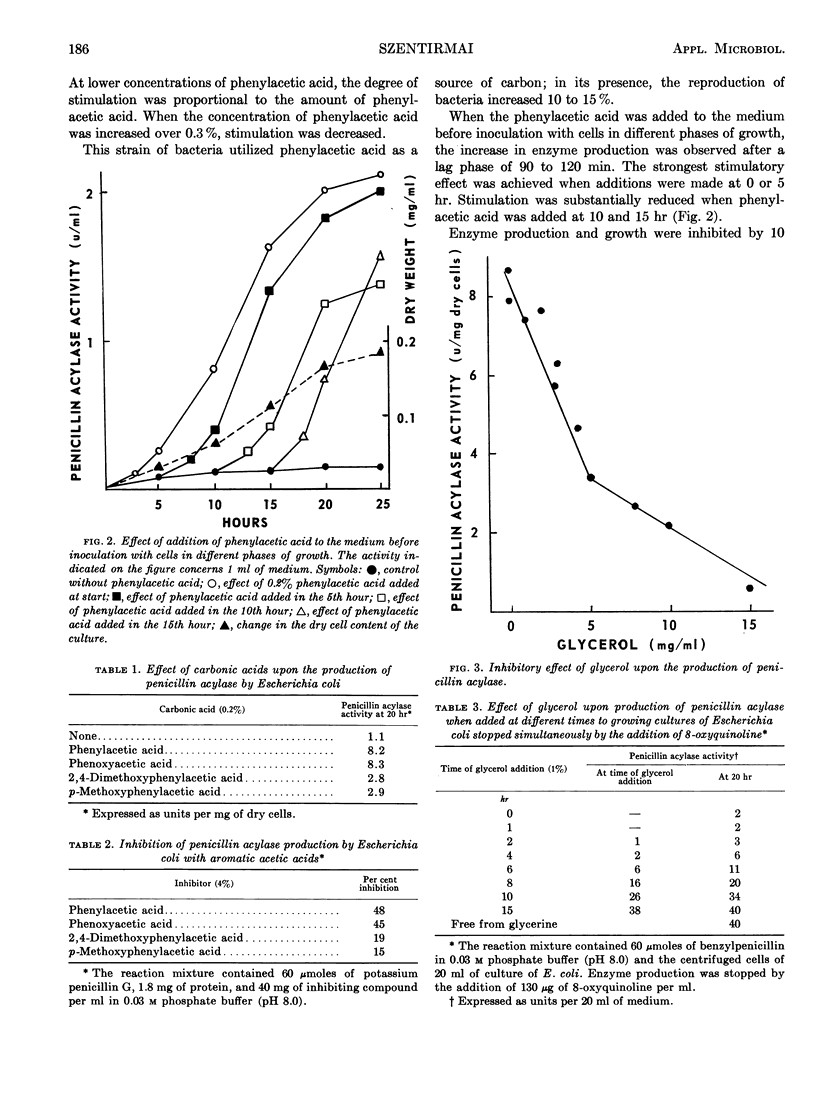
The production of penicillin acylase by Escherichia coli Ny.I/3-67 has been increased by phenylacetic acid and phenoxyacetic acid, which themselves strongly inhibit the function of this specific enzyme. Other carbonic acids also increased penicillin acylase production, but to a lesser degree; they also weakly inhibited enzyme function. The production of this enzyme was effectively repressed with metabolic carbohydrates and polyalcohols. Because enzyme production is dependent upon temperature, an increase in the temperature of incubation (above 31 C) decreased production of the enzyme, and increased the repressive effect of carbohydrates and polyalcohols.
Full text
PDF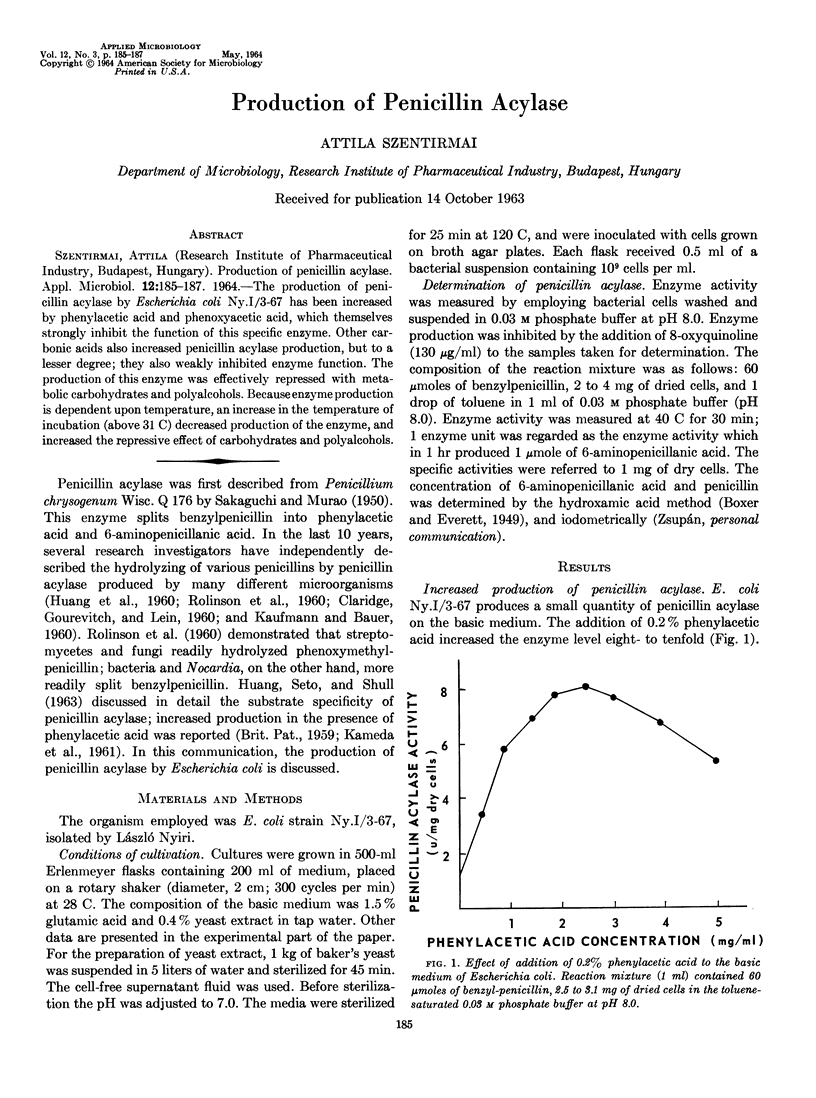

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- CLARIDGE C. A., GOUREVITCH A., LEIN J. Bacterial penicillin amidase. Nature. 1960 Jul 16;187:237–238. doi: 10.1038/187237a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HALPERN Y. S. Induction and repression of glutamic acid decarboxylase in Escherichia coli. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1962 Dec 31;61:953–962. doi: 10.1016/0926-6550(62)90011-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HUANG H. T., SETO T. A., SHULL G. M. Distribution and substrate specificity of benzylpenicillin acylase. Appl Microbiol. 1963 Jan;11:1–6. doi: 10.1128/am.11.1.1-6.1963. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KAMEDA Y., KIMURA Y., TOYOURA E., OMORI T. A method for isolating bacteria capable of producing 6-aminopenicillanic acid from benzylpenillin. Nature. 1961 Sep 9;191:1122–1123. doi: 10.1038/1911122a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NG H., INGRAHAM J. L., MARR A. G. Damage and derepression in Escherichia coli resulting from growth at low temperatures. J Bacteriol. 1962 Aug;84:331–339. doi: 10.1128/jb.84.2.331-339.1962. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROLINSON G. N., BATCHELOR F. R., BUTTERWORTH D., CAMERON-WOOD J., COLE M., EUSTACE G. C., HART M. V., RICHARDS M., CHAIN E. B. Formation of 6-aminopenicillanic acid from penicillin by enzymatic hydrolysis. Nature. 1960 Jul 16;187:236–237. doi: 10.1038/187236a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


