Extended Data Fig. 6 |. Inter-monomer interactions, biochemical characterization, and TnsC heptamer formation.
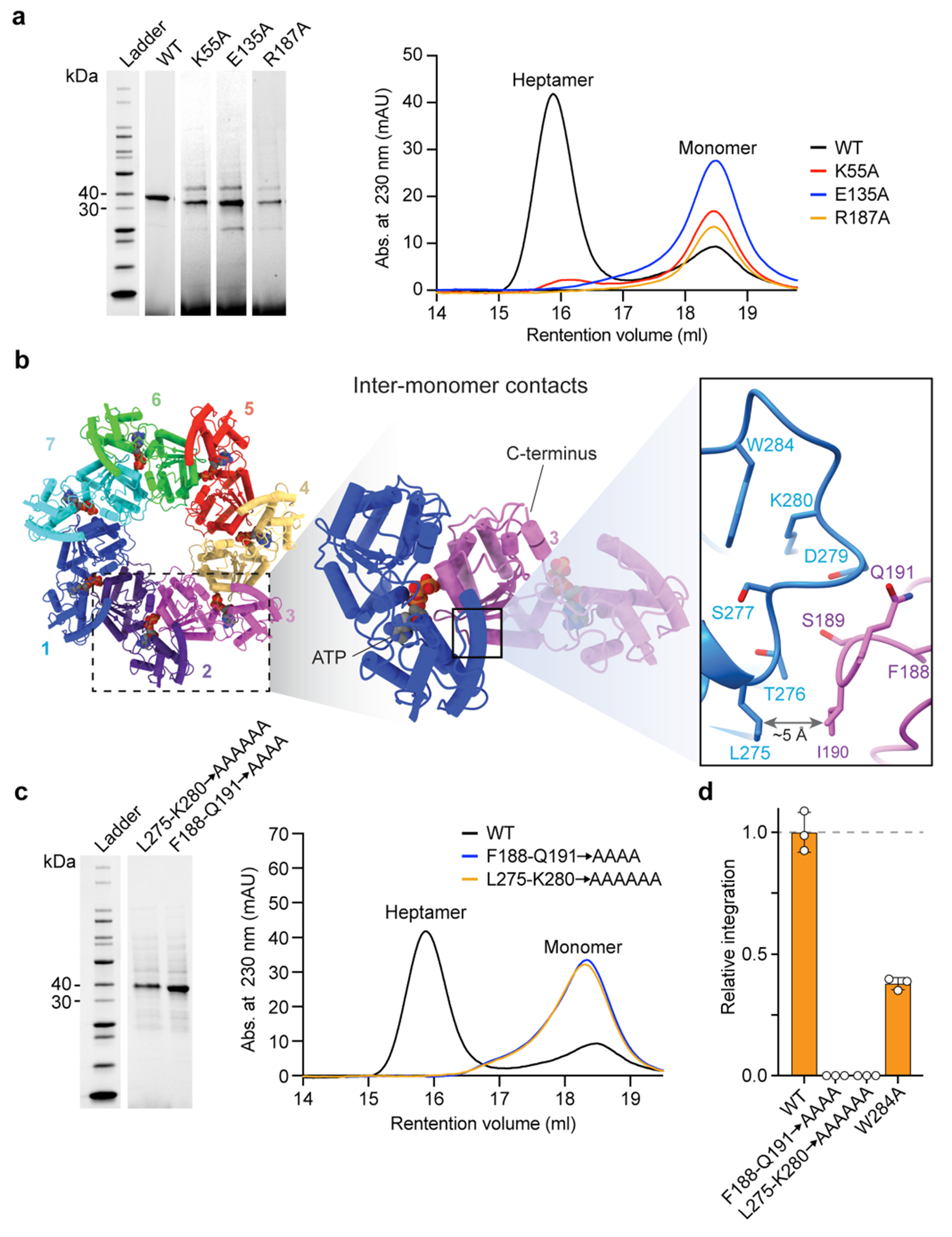
a, Purification and heptamer assembly experiments with ATPase mutants of TnsC. SDS–PAGE analysis (left) and SEC chromatograms (right) are shown for the indicated mutants, with TnsC monomer and heptamer peaks indicated. Mutations in the Walker A (K55A), Walker B (E135A), and arginine finger (R187A) motifs prevent formation of stable heptamers. b, Adjacent TnsC monomers interact via two proximal loops, in which residues 275–280 from one monomer engage residues 188–191 from the neighbouring monomer (inset on the right) c, Purification and heptamer assembly experiments with interface and pore loop mutants of TnsC, shown as in a. Mutations at the monomer-monomer interface are unable to form stable heptamers in the presence of ATP. For gel source data, see Supplementary Fig. 1. d, CRISPR RNA-guided transposition assays for the indicated loop mutants, as measured by qPCR. Data are normalized relative to WT. Data in d are shown as mean ± s.d. for n = 3 independent biological replicates.
