Abstract
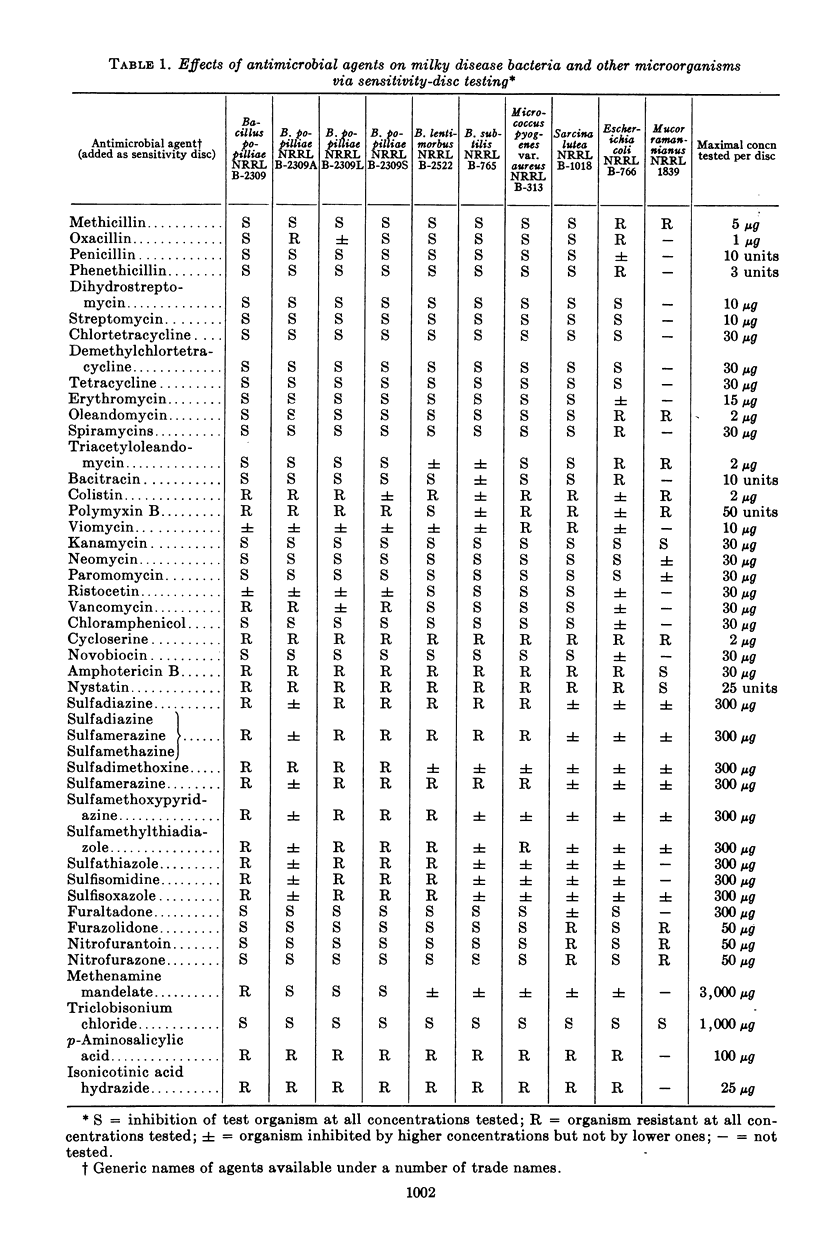
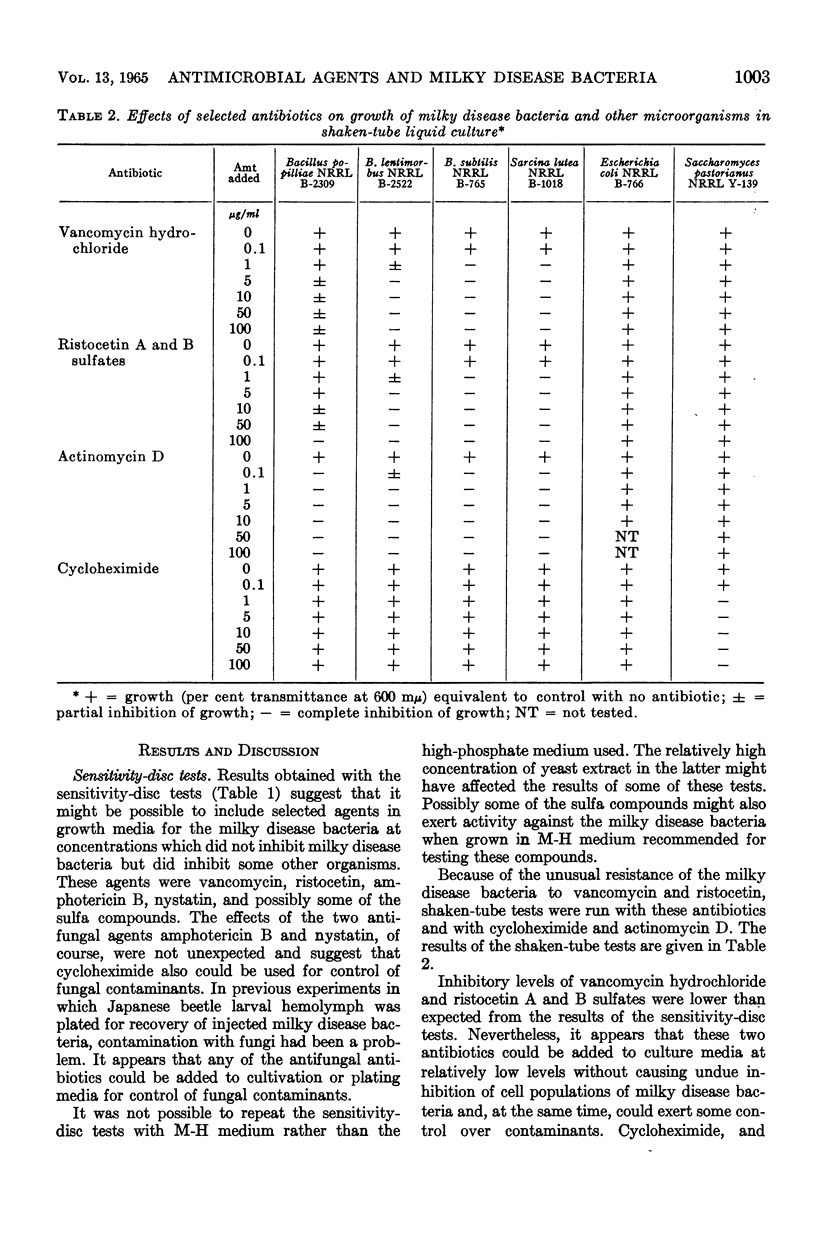
The effects of antibiotics, sulfonamides, and other antimicrobial agents on vegetative cultures of five strains of milky disease bacteria were compared with those on Bacillus subtilis Cohn emend. Prazmowski, Staphylococcus aureus Rosenbach, Sarcina lutea Schroeter, Escherichia coli (Migula) Castellani and Chalmers, Saccharomyces pastorianus Hansen, and Mucor ramannianus Moel. Similar numbers of viable cells of each organism were exposed to the test materials by use of an antibiotic-sensitivity disc method adapted from techniques recommended by the Food and Drug Administration in the Federal Register. The results suggest that vancomycin or ristocetin, as well as a few other materials, might be useful in controlling contamination either during culture of the fastidious milky disease bacteria or in large populations of vegetative cells undergoing treatment to induce sporulation. Inhibitory concentrations of vancomycin and ristocetin in shaken-tube tests were much lower than expected in comparison with results of sensitivity-disc tests on the milky disease bacteria. Sublethal concentrations of the two antibiotics elicited some morphological change in the bacteria.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- LYONS A. J., Jr, PRIDHAM T. G. COLORIMETRIC DETERMINATION OF COLOR OF AERIAL MYCELIUM OF STREPTOMYCETES. J Bacteriol. 1965 Jan;89:159–169. doi: 10.1128/jb.89.1.159-169.1965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindenfelser L. A., Shotwell O. L., Bachler M. J., Shannon G. M., Pridham T. G. Antibiotics Against Plant Disease: VIII. Screening for Nonpolyenic Antifungal Antibiotics Produced by Streptomycetes. Appl Microbiol. 1964 Nov;12(6):508–512. doi: 10.1128/am.12.6.508-512.1964. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RUSSELL A. D. MODE OF ACTION OF VANCOMYCIN. J Pharm Pharmacol. 1964 Sep;16:637–637. doi: 10.1111/j.2042-7158.1964.tb07528.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


