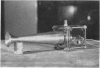
Abstract
The lethal effects of high-intensity airborne sonic (9.9 kc/sec) and ultrasonic waves (30.4 kc/sec) on spores of Bacillus subtilis var. niger ATCC 9372 were determined. The spores, which were deposited on filter-paper strips, were exposed to sound waves for periods varying from 1 to 8 hr, at a temperature of 40 C and a relative humidity of 40%. Significant reductions in the viable counts of spores exposed to airborne sonic or ultrasonic irradiations were obtained. The antibacterial activity of airborne sound waves varied with the sound intensity level, the period of irradiation, and the distance of the sample from the sound source. At similar intensity levels, the amplitude of motion of the sound waves appeared to be a factor in acoustic sterilization.
Full text
PDF
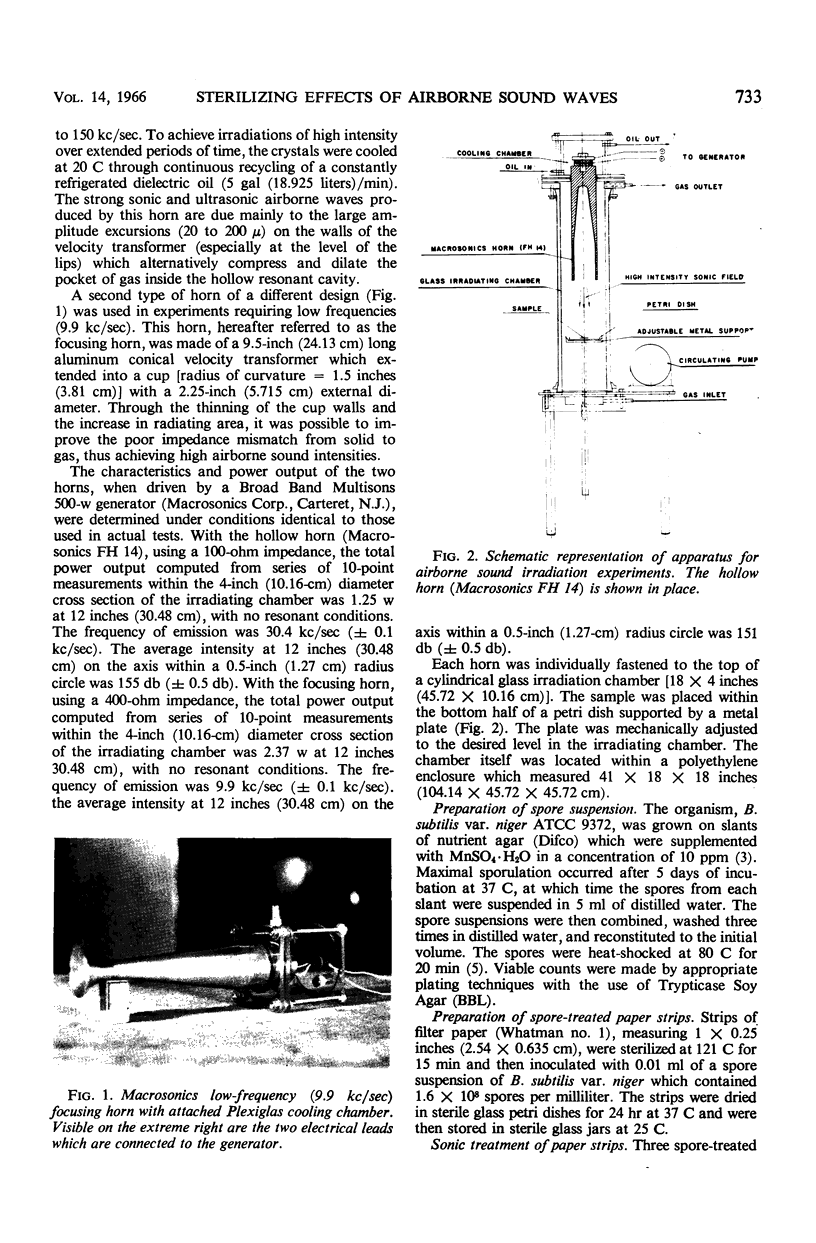

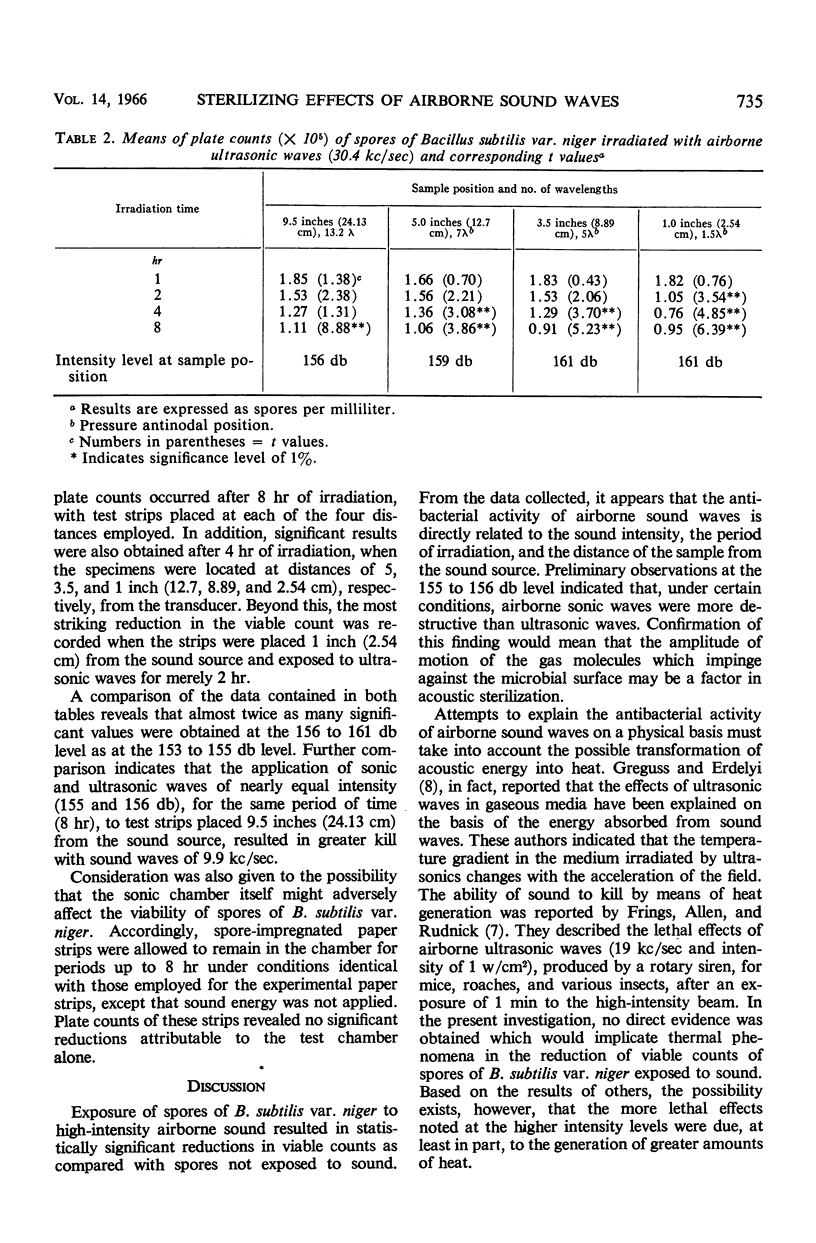

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- CHURCH B. D., HALVORSON H., HARTMAN R. S., RAMSEY D. S. Population heterogeneity in the resistance of aerobic spores to ethylene oxide. J Bacteriol. 1956 Aug;72(2):242–247. doi: 10.1128/jb.72.2.242-247.1956. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DEMAIN A. L. Minimal media for quantitative studies with Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1958 May;75(5):517–522. doi: 10.1128/jb.75.5.517-522.1958. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Opfell J. B., Miller C. E. Cold sterilization techniques. Adv Appl Microbiol. 1965;7:81–102. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2164(08)70384-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROSS K. F., BILLING E. The water and solid content of living bacterial spores and vegetative cells as indicated by refractive index measurements. J Gen Microbiol. 1957 Apr;16(2):418–425. doi: 10.1099/00221287-16-2-418. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WALDHAM D. G., HALVORSON H. O. Studies on the relationship between equilibrium vapor pressure and moisture content of bacterial endospores. Appl Microbiol. 1954 Nov;2(6):333–338. doi: 10.1128/am.2.6.333-338.1954. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]