Abstract
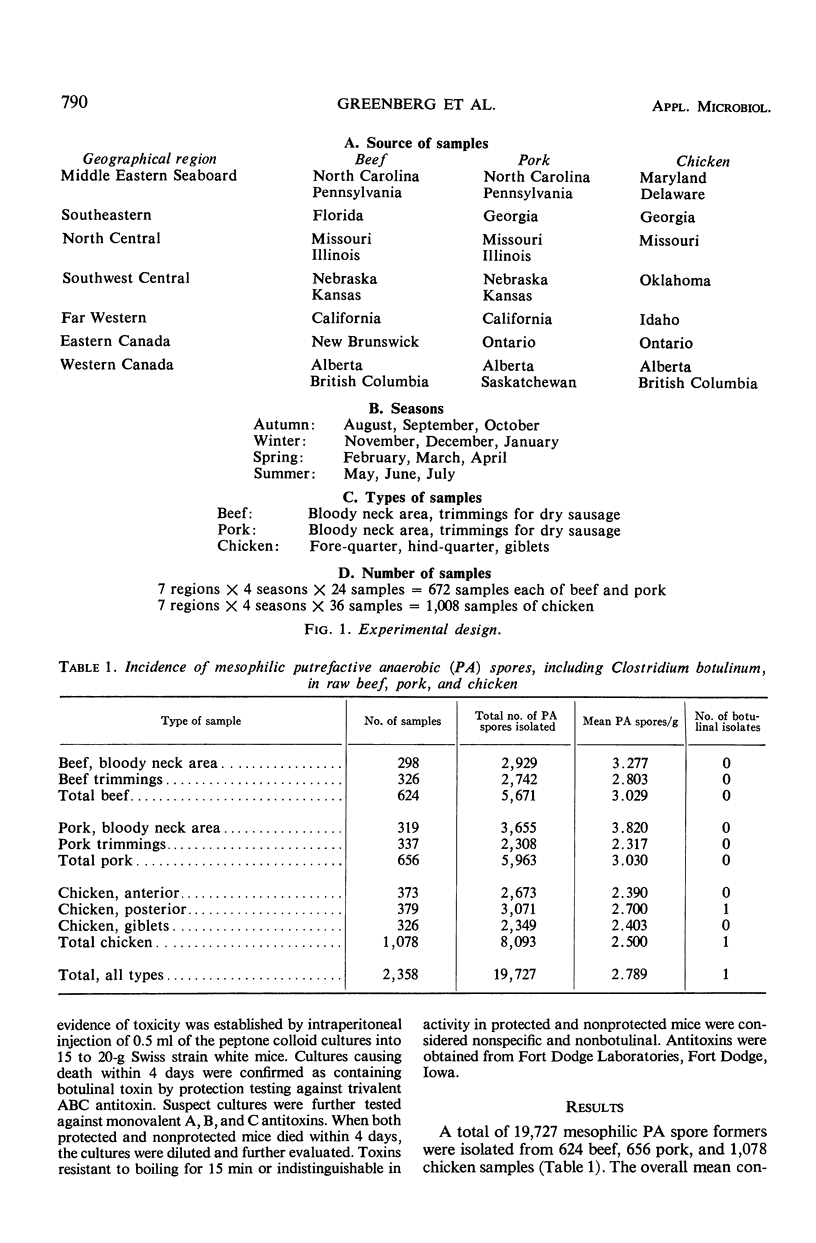
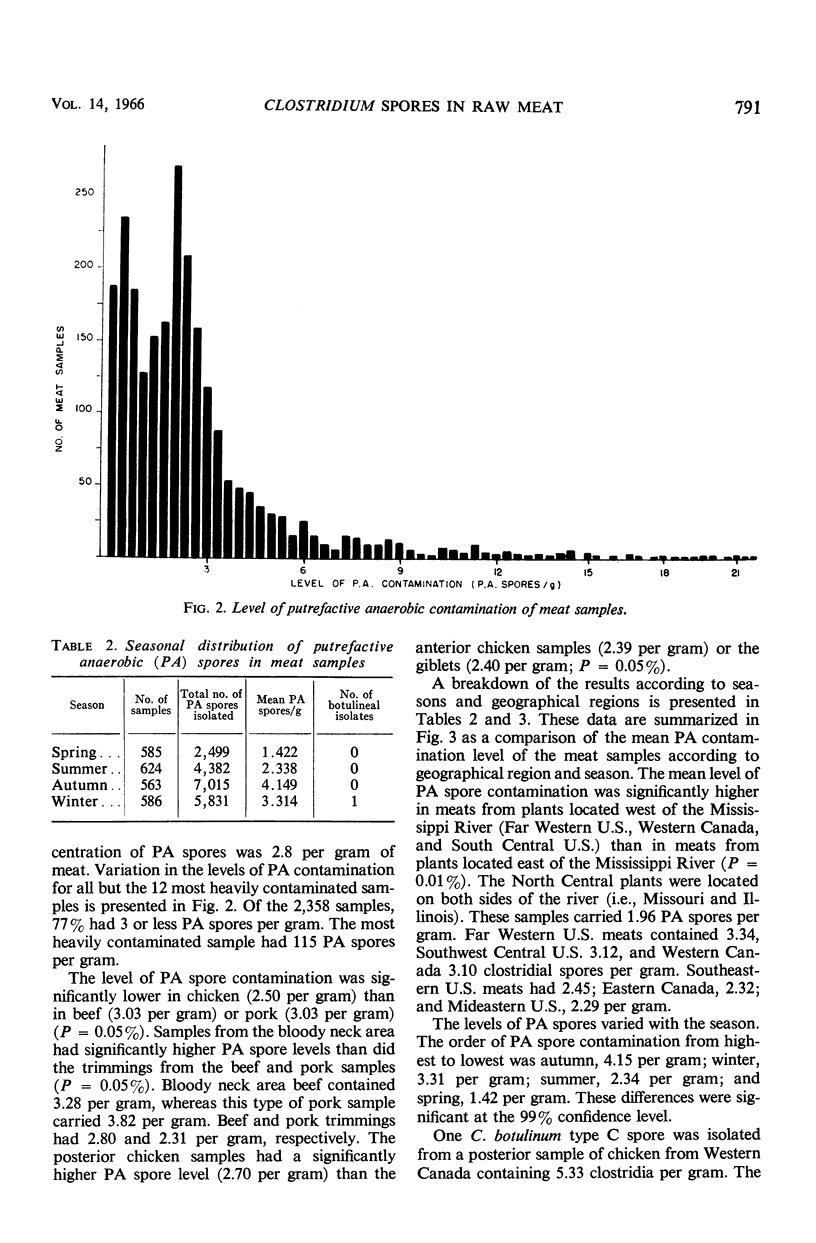
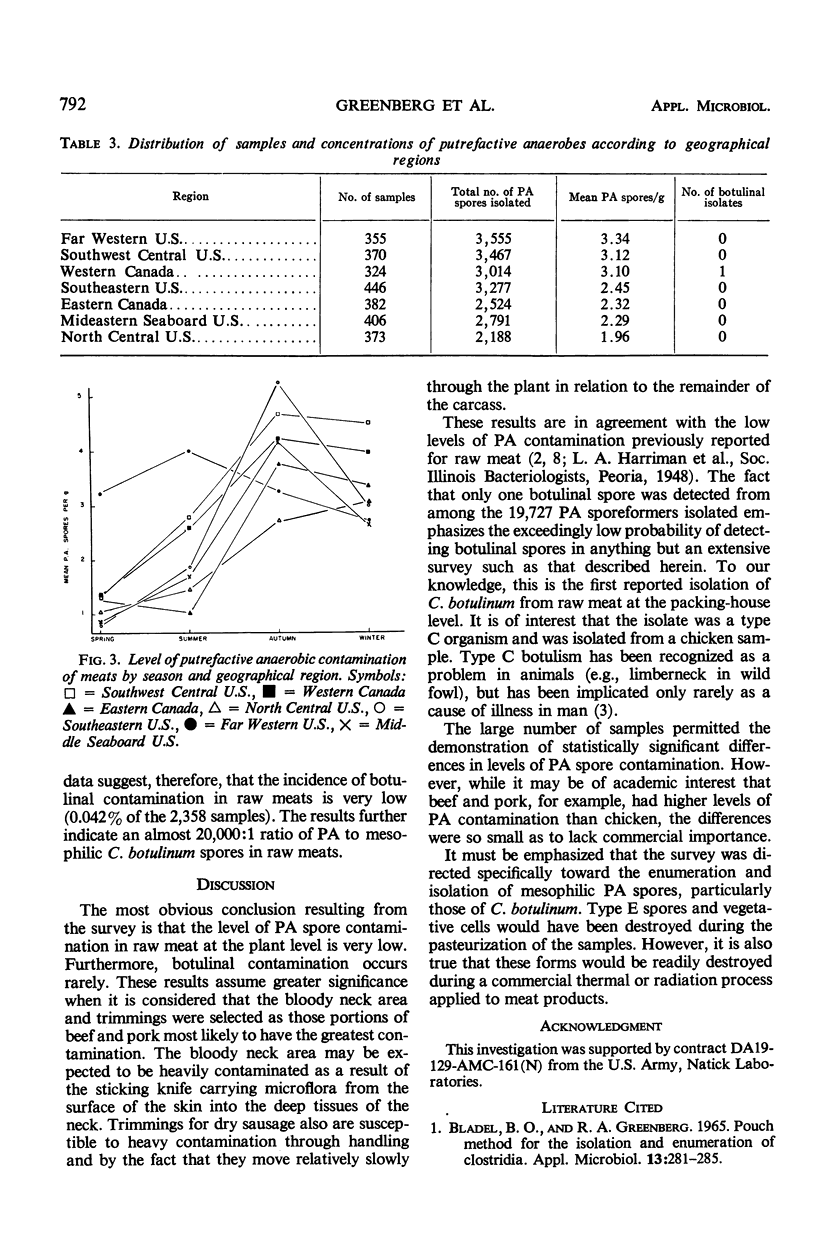
The anaerobic film pouch technique was used to quantitate and isolate clostridial spores in 2,358 samples of raw meat (1,078 of chicken, 624 of beef, 656 of pork). Of 19,727 putrefactive anaerobic (PA) sporeformers isolated, 1 was confirmed by mouse protection testing to be Clostridium botulinum type C. This isolate was obtained from a Western Canada chicken sample which contained 5.33 clostridia per gram. These data indicate a very low incidence of botulinal contamination in raw meats at the packing-plant level (0.042% of 2,358 samples) and an almost 20,000:1 ratio of nonbotulinal PA sporeformers to mesophilic C. botulinum spores. The mean level of PA contamination was 2.8 PA sporeformers per gram of meat; 77% of the samples contained three or less PA sporeformers per gram. Small but statistically significant differences in the incidence of clostridial spores were noted for season, geographical region, and type of meat.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BLADEL B. O., GREENBERG R. A. POUCH METHOD FOR THE ISOLATION AND ENUMERATION OF CLOSTRIDIA. Appl Microbiol. 1965 Mar;13:281–285. doi: 10.1128/am.13.2.281-285.1965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenberg R. A., Bladel B. O., Zingelmann W. J. Use of the anaerobic pouch in isolating Clostridium botulinum spores from fresh meats. Appl Microbiol. 1966 Mar;14(2):223–228. doi: 10.1128/am.14.2.223-228.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


