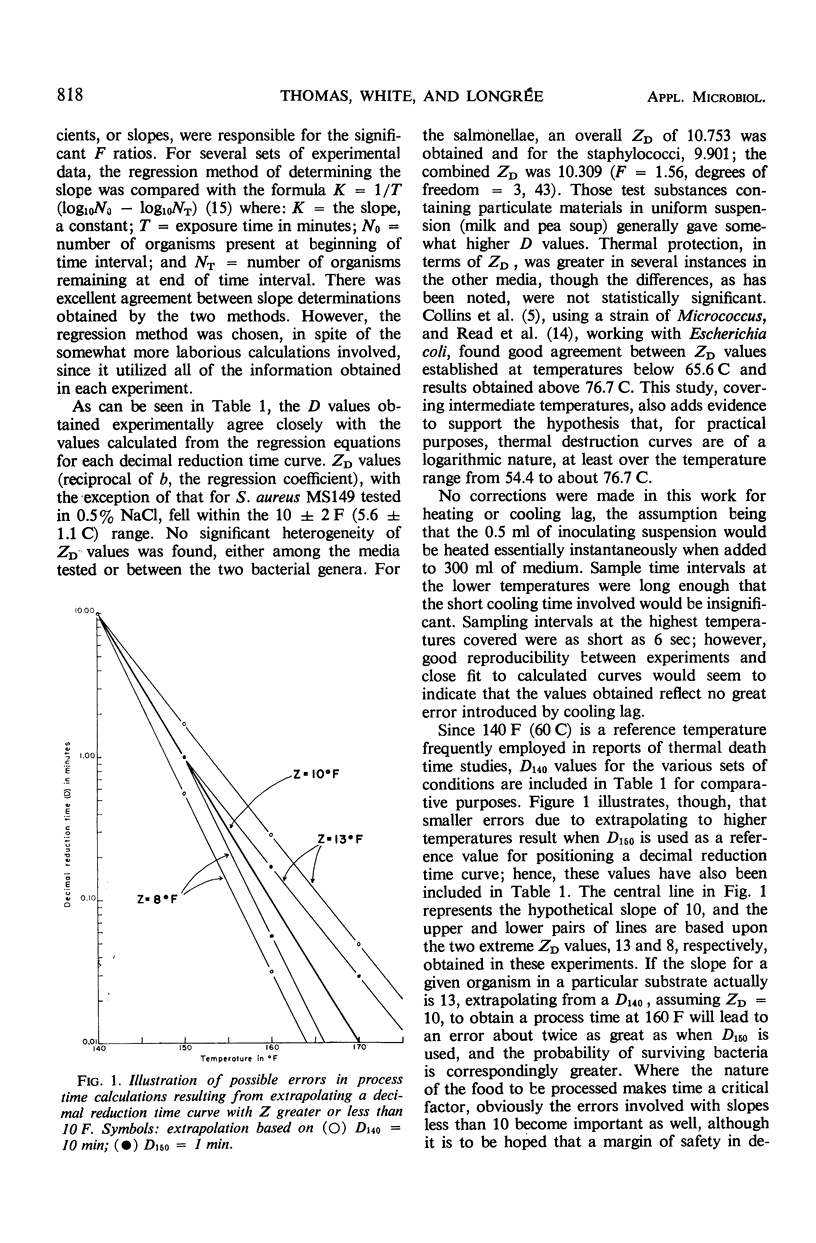
Abstract
The heat-resistant Salmonella senftenberg 775W and two strains of Staphylococcus aureus were tested at temperatures up to 68.3 C (71.1 C for S. senftenberg) in four different media. From the survival data, decimal reduction times (D values) were calculated for each set of conditions, and decimal reduction time curves were constructed for each bacterial strain in each medium. Slopes of decimal reduction time curves (ZD) ranged from 4.52 to 6.38 C with a single exception. There was no statistical heterogeneity among the remaining values. Results were in close agreement with published results of similar studies conducted at somewhat lower temperatures and support the practice of using a slope value (ZD) of 5.56 C for establishing time-temperature relationships for food processing. It is recommended that such a decimal reduction time curve not be extrapolated to temperatures more than 5.56 C higher than those actually tested.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ANGELOTTI R., FOTER M. J., LEWIS K. H. Time-temperature effects on Salmonellae and Staphylococci in foods. III. Thermal death time studies. Appl Microbiol. 1961 Jul;9:308–315. doi: 10.1128/am.9.4.308-315.1961. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BUSTA F. F., JEZESKI J. J. EFFECT OF SODIUM CHLORIDE CONCENTRATION IN AN AGAR MEDIUM ON GROWTH OF HEAT-SHOCKED STAPHYLOCOCCUS AUREUS. Appl Microbiol. 1963 Sep;11:404–407. doi: 10.1128/am.11.5.404-407.1963. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COLLINS E. B., DUNKLEY W. L., PERRY R. L., EDMONDSON L. F. Thermal destruction of Micrococcus freudenreichii and Streptococcus thermophilus with particular reference to pasteurization without holding. Appl Microbiol. 1956 May;4(3):133–140. doi: 10.1128/am.4.3.133-140.1956. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elliker P. R., Frazier W. C. Influence of Time and Temperature of Incubation on Heat Resistance of Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1938 Jul;36(1):83–98. doi: 10.1128/jb.36.1.83-98.1938. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HUMPHREY A. E., NICKERSON J. T. Testing thermal death data for significant nonlograithmic behavior. Appl Microbiol. 1961 Jul;9:282–286. doi: 10.1128/am.9.4.282-286.1961. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KAPLAN A. M., LICHTENSTEIN H., REYNOLDS H. The initial deviation from linearity of the thermal death rate curve of a putrefactive anaerobe. J Bacteriol. 1953 Aug;66(2):245–246. doi: 10.1128/jb.66.2.245-246.1953. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NIVEN C. F., Jr, BUETTNER L. G., EVANS J. B. Thermal tolerance studies on the heterofermentative lactobacilli that cause greening of cured meat products. Appl Microbiol. 1954 Jan;2(1):26–29. doi: 10.1128/am.2.1.26-29.1954. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- READ R. B., Jr, SCHWARTZ C., LITSKY W. Studies on thermal destruction of Escherichia coli in milk and milk products. Appl Microbiol. 1961 Sep;9:415–418. doi: 10.1128/am.9.5.415-418.1961. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rahn O. PHYSICAL METHODS OF STERILIZATION OF MICROORGANISMS. Bacteriol Rev. 1945 Mar;9(1):1–47. doi: 10.1128/br.9.1.1-47.1945_1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WANG D. I., SCHARER J., HUMPHREY A. E. KINETICS OF DEATH OF BACTERIAL SPORES AT ELEVATED TEMPERATURES. Appl Microbiol. 1964 Sep;12:451–454. doi: 10.1128/am.12.5.451-454.1964. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


