Abstract
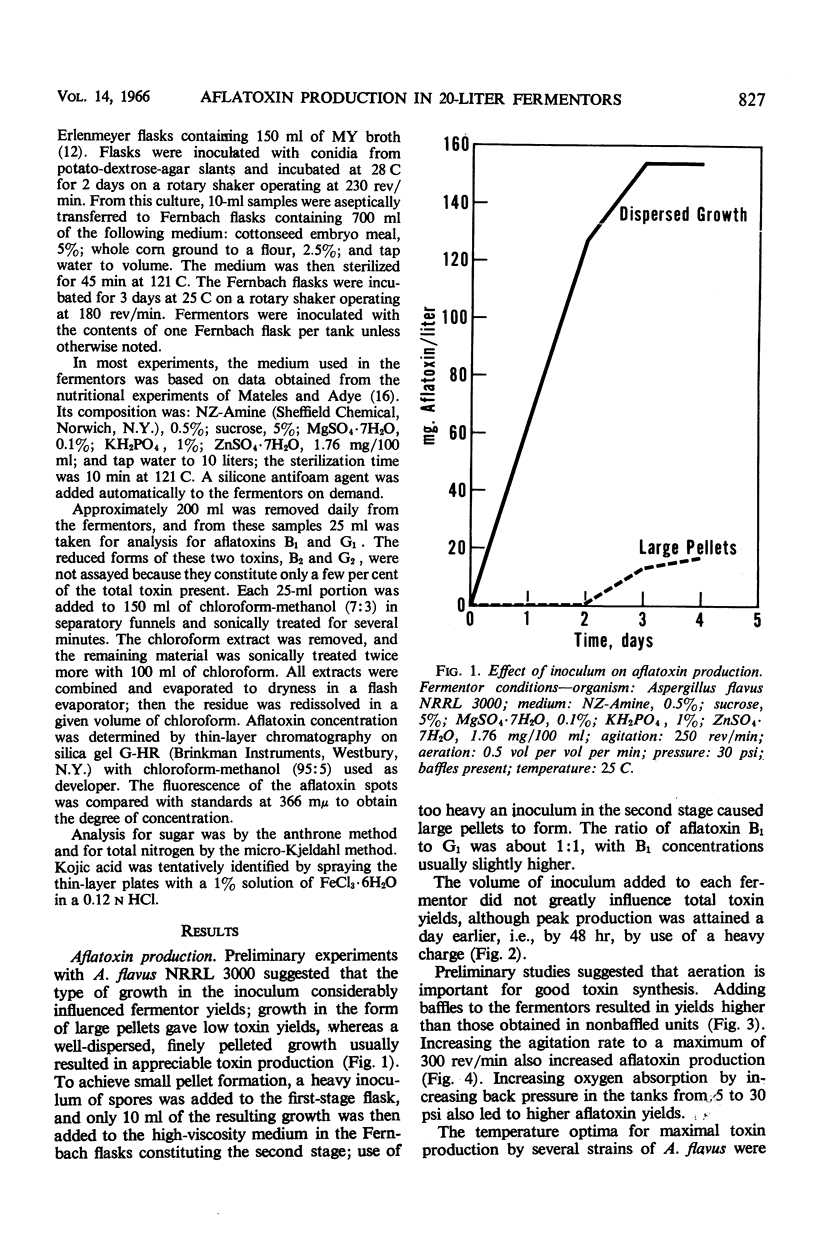
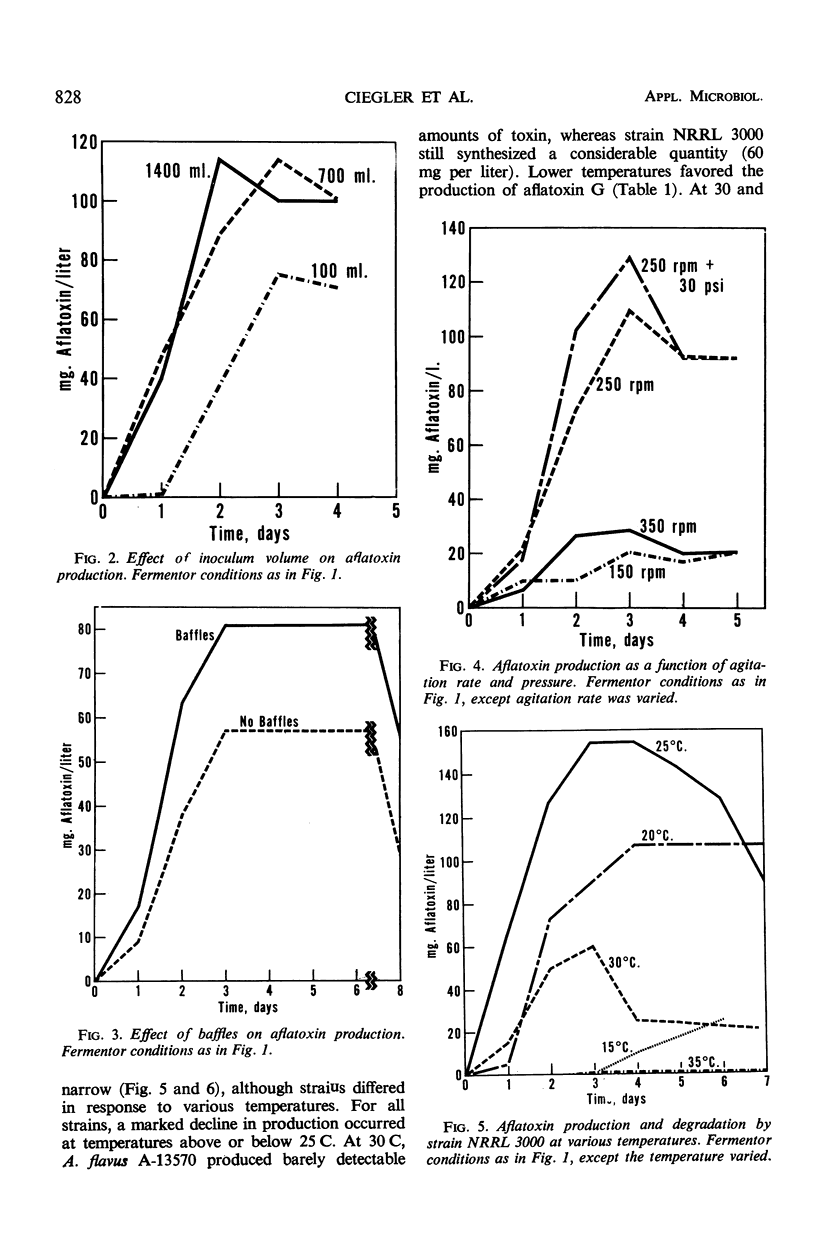
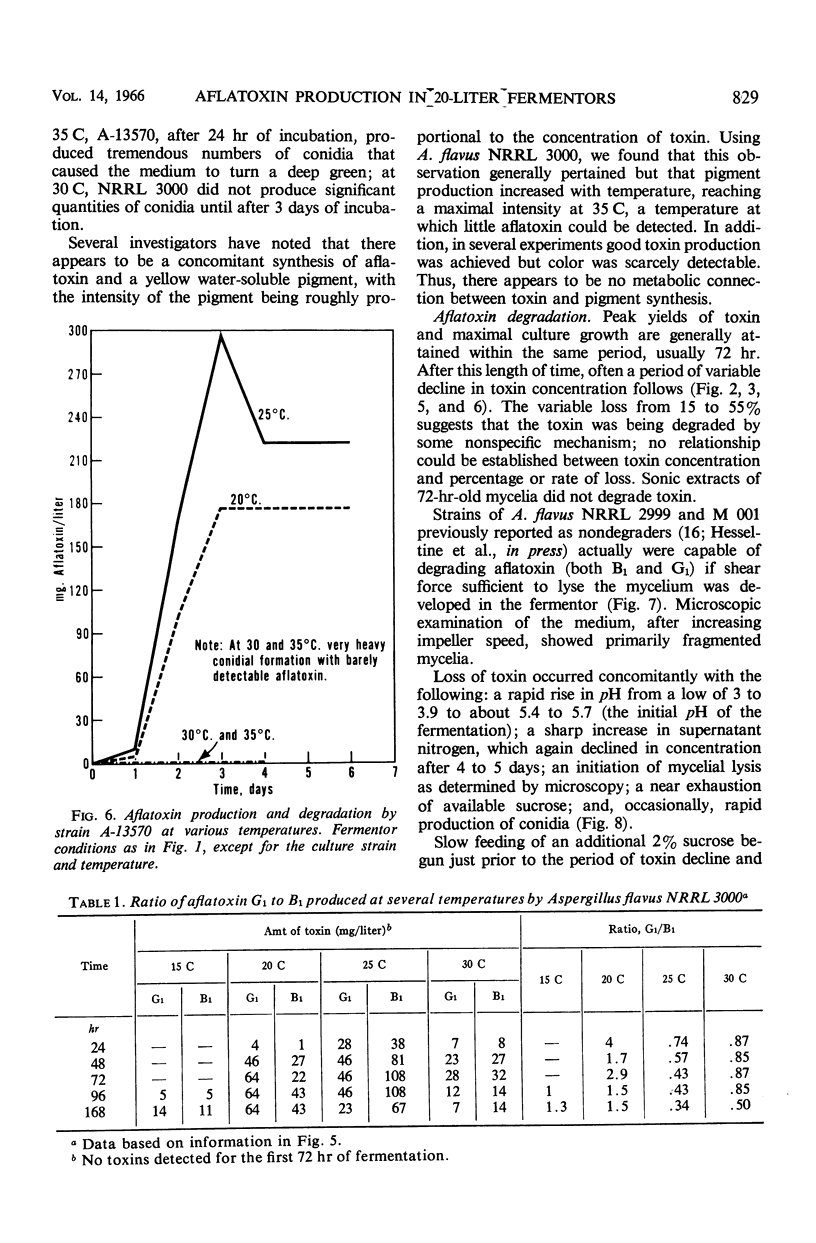
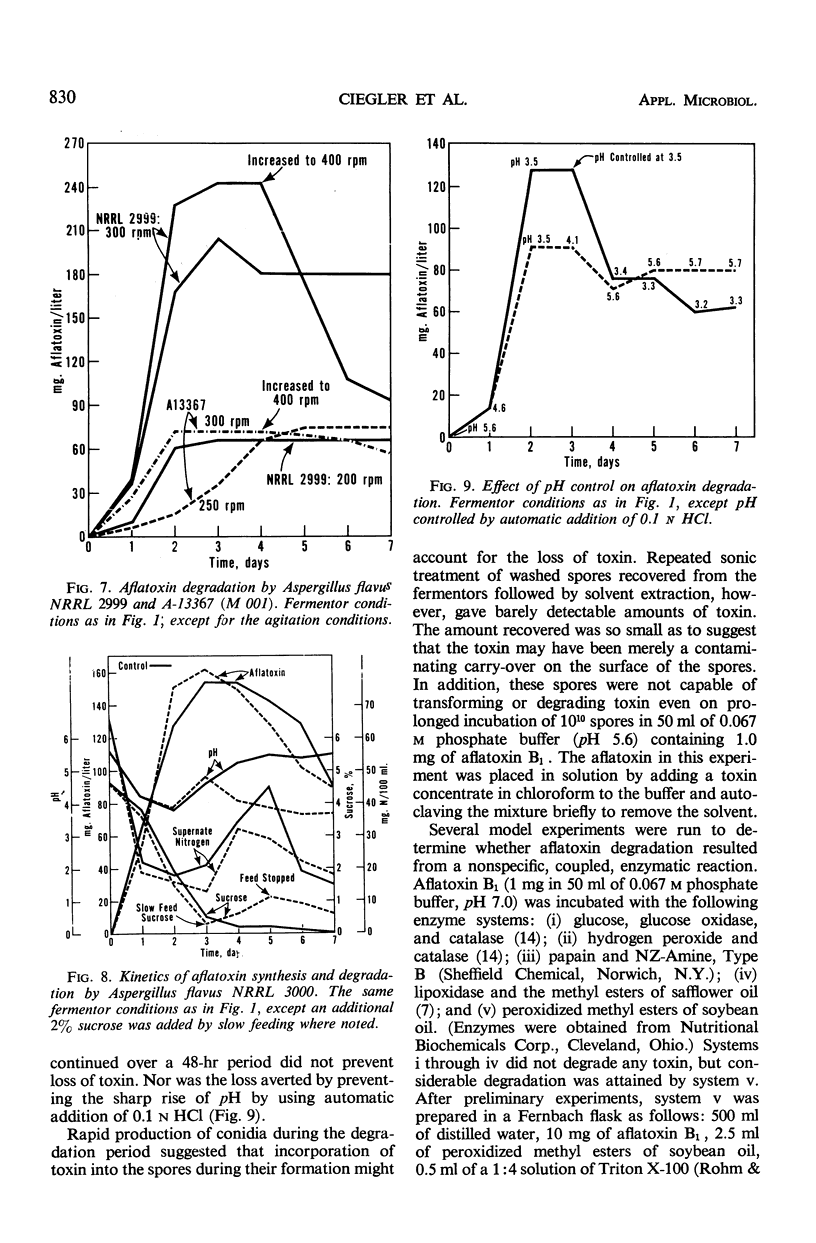
Yields of from 200 to 300 mg per liter of aflatoxins B1 and G1 were produced by two strains of Aspergillus flavus in 20-liter fermentors under proper conditions of inoculum (well-dispersed growth) and aeration (0.5 volume per volume per min of air, 300 rev/min, 30 psi back pressure, baffles). Peak yields were usually attained in 72 hr, after which the aflatoxin concentration declined rapidly. Degradation of aflatoxin depended primarily on mycelial lysis and high-aeration conditions. Cultures previously reported not to degrade aflatoxin could be induced to do so under these conditions. The percentage and rate of toxin degradation were independent of toxin concentration, and appeared to be nonenzymatic and nonspecific. Degradation simulating that occurring in the fermentor was achieved by reacting aflatoxin with peroxidized methyl esters of vegetable oil; initial degradation was rapid and appeared to involve a complex series of reactions.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ADYE J., MATELES R. I. INCORPORATION OF LABELLED COMPOUNDS INTO AFLATOXINS. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1964 May 11;86:418–420. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(64)90077-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ashworth L. J., Jr, Schroeder H. W., Langley B. C. Aflatoxins: Environmental Factors Governing Occurrence in Spanish Peanuts. Science. 1965 May 28;148(3674):1228–1229. doi: 10.1126/science.148.3674.1228. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Butler W. H., Clifford J. I. Extraction of aflatoxin from rat liver. Nature. 1965 Jun 5;206(988):1045–1046. doi: 10.1038/2061045a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CHANG S. B., ABDEL-KADER M. M., WICK E. L., WOGAN G. N. AFLATOXIN B2: CHEMICAL IDENTITY AND BIOLOGICAL ACTIVITY. Science. 1963 Nov 29;142(3596):1191–1192. doi: 10.1126/science.142.3596.1191. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DE IONGH H., VLES R. O., VAN PELTJ MILK OF MAMMALS FED AN AFLATOXIN-CONTAINING DIET. Nature. 1964 May 2;202:466–467. doi: 10.1038/202466a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DESAI I. D., TAPPEL A. L. DAMAGE TO PROTEINS BY PEROXIDIZED LIPIDS. J Lipid Res. 1963 Apr;4:204–207. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DICKENS F. CARCINOGENIC LACTONES AND RELATED SUBSTANCES. Br Med Bull. 1964 May;20:96–101. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.bmb.a070324. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DICKENS F., JONES H. E. Carcinogenic activity of a series of reactive lactones and related substances. Br J Cancer. 1961 Mar;15:85–100. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1961.10. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DWORSCHACK R. G., LAGODA A. A., JACKSON R. W. Fermentor for small-scale submerged fermentations. Appl Microbiol. 1954 Jul;2(4):190–197. doi: 10.1128/am.2.4.190-197.1954. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HAYNES W. C., WICKERHAM L. J., HESSELTINE C. W. Maintenance of cultures of industrially important microorganisms. Appl Microbiol. 1955 Nov;3(6):361–368. doi: 10.1128/am.3.6.361-368.1955. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HODGES F. A., ZUST J. R., SMITH H. R., NELSON A. A., ARMBRECHT B. H., CAMPBELL A. D. MYCOTOXINS: AFLATOXIN ISOLATED FROM PENICILLIUM PUBERULUM. Science. 1964 Sep 25;145(3639):1439–1439. doi: 10.1126/science.145.3639.1439. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hauschka T., Toennies G., Swain A. P. THE MECHANISM OF GROWTH INHIBITION BY HEXENOLACTONE. Science. 1945 Apr 13;101(2624):383–385. doi: 10.1126/science.101.2624.383-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keilin D., Hartree E. F. Properties of catalase. Catalysis of coupled oxidation of alcohols. Biochem J. 1945;39(4):293–301. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Legator M. S., Zuffante S. M., Harp A. R. Aflatoxin: effect on cultured heteroploid human embryonic lung cells. Nature. 1965 Oct 23;208(5008):345–347. doi: 10.1038/208345a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MATELES R. I., ADYE J. C. PRODUCTION OF AFLATOXINS IN SUBMERGED CULTURE. Appl Microbiol. 1965 Mar;13:208–211. doi: 10.1128/am.13.2.208-211.1965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schroeder H. W. Effect of corn steep liquor on mycelial growth and aflatoxin production in Aspergillus parasiticus. Appl Microbiol. 1966 May;14(3):381–385. doi: 10.1128/am.14.3.381-385.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


