SUMMARY
Cells can irreversibly exit the cell cycle and become senescent to safeguard against uncontrolled proliferation. While the p53-p21 and p16-Rb pathways are thought to mediate senescence, they also mediate reversible cell cycle arrest (quiescence), raising the question of whether senescence is actually reversible or whether alternative mechanisms underly the irreversibility associated with senescence. Here, we show that senescence is irreversible and that commitment to and maintenance of senescence are mediated by irreversible MYC degradation. Senescent cells start dividing when a non-degradable MYC mutant is expressed, and quiescent cells convert to senescence when MYC is knocked down. In early oral carcinogenesis, epithelial cells exhibit MYC loss and become senescent as a safeguard against malignant transformation. Later stages of oral premalignant lesions exhibit elevated MYC levels and cellular dysplasia. Thus, irreversible cell cycle exit associated with senescence is mediated by constitutive MYC degradation, but bypassing this degradation may allow tumor cells to escape during cancer initiation.
In brief
Afifi et al. use time-lapse imaging, high-throughput single-cell analyses, and quantitative measurements to investigate the irreversibility of cellular senescence. Senescent cells enter and maintain senescence by constitutive MYC degradation. These findings provide a new framework for understanding the role of MYC in mediating senescence in vitro and in vivo.
Graphical Abstract
INTRODUCTION
In response to stress, such as DNA damage,1,2 telomere shortening,3,4 or oncogenic stress,5 human cells permanently exit the cell cycle to a state of cellular senescence. Senescent cells stay metabolically active, secrete an array of cytokines and growth factors known as the senescence-associated secretory phenotype (SASP),6 display increased cell and nuclear size,7 heterochromatin foci,8 and increased senescence associated beta-galactosidase (SA-β Gal) activity.9 Although these distinct phenotypes, which manifest over the course of days, can often distinguish senescent from proliferative and terminally differentiated cells, irreversible cell cycle exit remains the consensus definition of senescence under normal conditions.10,11 However, this concept has been challenged in recent years, especially in the context of tumor cells.11
The ability of human cells to irreversibly exit the cell cycle to a state of senescence plays numerous roles in human health and disease. Senescence is implicated as a driver of aging,12,13 tissue remodeling during embryonic development,14–16 and wound healing.14 Senescence is one of the first defense mechanisms against tumor promotion during carcinogenesis, where tumor suppression pathways offset the pro-proliferative effects of oncogenic stimuli by forcing cells to become senescent (oncogene-induced senescence [OIS]), triggering an immune response, and preventing the expansion of otherwise pre-cancerous cells.17–22 In cancer treatment, senescence is often a therapeutic endpoint of many chemotherapeutic drugs or radiation therapy resulting from treatment-induced DNA damage.17,21,23
Mechanistically, the irreversible cell cycle exit associated with senescence is thought to be mediated by two major tumor suppressor pathways: p53/p21 and p16INK4a/Rb.8,24,25 However, activation of these pathways can also induce entry into a reversible cell cycle arrest, either at checkpoints or in a cell cycle phase referred to as quiescence,26–28 suggesting either that activation of p53/p21 or p16INK4a/Rb alone cannot account for the irreversible nature of cell cycle exit that is uniquely associated with senescence or that senescence is actually reversible as some have suggested.9,10,29,30
To investigate the irreversibility of senescence, we used a combination of the MEK inhibitor (MEKi) trametinib and the CDK4/6 inhibitor (CDK4/6i) palbociclib, which were recently shown to induce senescence in KRAS mutant lung cancer cells.31 Using live-cell imaging, automated single-cell tracking, and high-throughput single-cell analyses, we tracked the long-term fate of cells treated with these inhibitors as they exited the cell cycle and entered a senescence state. Given that senescence is a multifaceted phenomenon, we developed a quantitative single-cell assay to measure key features associated with cellular senescence. We found that cells remained senescent even when the drugs were washed off and downstream signaling recovered, demonstrating that senescence is indeed irreversible. We found that the timing at which cells enter and commit to senescence is variable depending on the duration of the perturbation. Mechanistically, cells irreversibly exit the cell cycle and enter senescence after losing cyclin-dependent kinase 2 (CDK2) activity via c-MYC (MYC) degradation. This loss of MYC protein is both necessary and sufficient to maintain the irreversible cell cycle exit that defines senescence. Consistent with this, we found that cells escaped senescence by expressing either a non-degradable MYC mutant or treating senescent cells with a GSK3β inhibitor, which prevents MYC degradation. Conversely, cancer cells treated with the CDK4/6i could be converted from a transient quiescent state to an irreversible senescent state by knocking down MYC. We found that constitutive MYC degradation was necessary to maintain senescence induced by a variety of methods including therapy-induced, DNA damage-induced, oncogene-induced, and replicative senescence. Spatial proteomic analysis, immunohistochemistry, and an unbiased digital quantitative approach in human oral premalignant lesions showed mild dysplastic lesions were enriched with MYC negative senescent cells, while conversely, carcinoma in situ was enriched with MYC positive dysplastic cells. Thus, our data suggests that cells can escape senescence in vitro or in vivo if they overexpress MYC or acquire specific mutations that interfere with the constitutive degradation of MYC. Therefore, we propose that MYC degradation underlies the switch from the proliferative and quiescent states to the senescent state.
RESULTS
A combination of MEKi and CDK4/6i induces senescence in transformed and non-transformed cells
Recently, a combination of the MEKi trametinib and the CDK4/6i palbociclib was shown to induce senescence in KRAS mutant lung cancer cells.31 To determine if the combination of MEKi and CDK4/6i could induce cellular senescence in non-KRAS mutant cells, we treated MCF7 cells, a human breast cancer cell line, and MCF10A cells, a non-transformed breast epithelial cell line, with increasing doses of both MEKi and CDK4/6i. We measured the proliferation markers phospho-ERK (pERK), phospho-retinoblastoma (pRb), and Ki-67 as well as SA-β Gal activity in single-cells and selected the dose combination that maximized the percent of Ki-67 low and SA-β Gal high cells. In MCF7 cells, 500 nM CDK4/6i and 100 nM MEKi were the minimum doses that yielded the maximum amount of cellular senescence, while 500 nM CDK4/6i and 30 nM MEKi were the optimal dose combination in MCF10A cells (Figures S1A–S1D).
We then compared the ability of this drug combination to induce SA-β Gal activity to that of γ-irradiation (γ-IR), a treatment that is well known to induce senescence,32–34 as a positive control. MCF7 cells treated with the drug combination accumulated high SA-β Gal activity at the same rate as γ-IR-treated cells (Figures 1A and 1B), but without inducing DNA damage (Figure S1E).
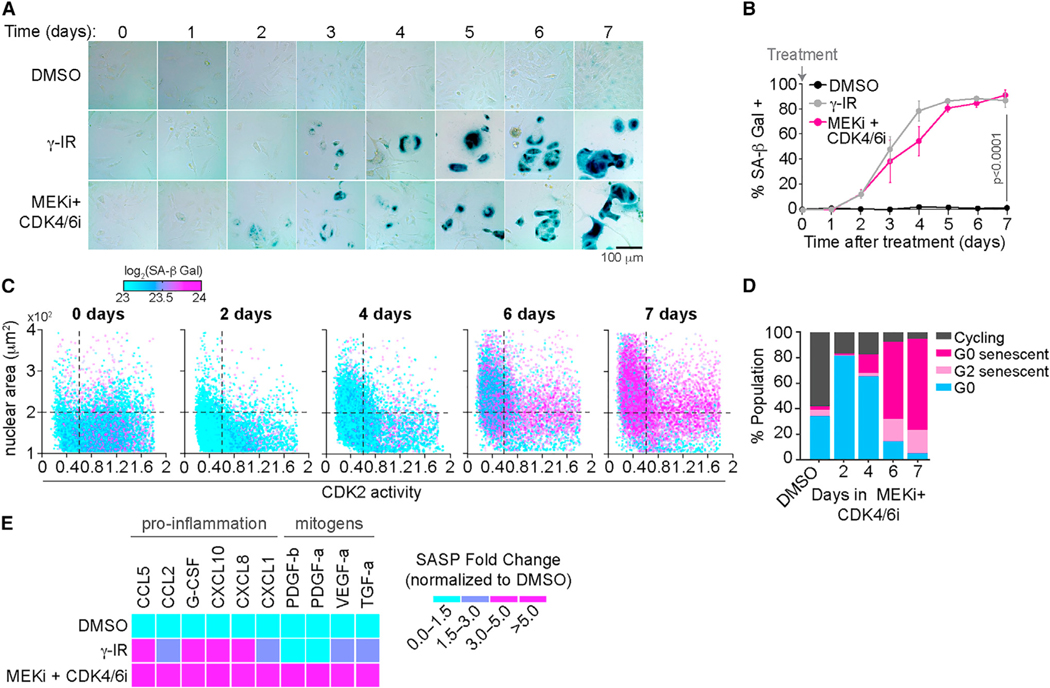
Figure 1. A combination of MEKi and CDK4/6i induces senescence in transformed and non-transformed cells.
(A) Representative images of MCF7 cells treated with DMSO, 10 Gy γ-IR, or 100 nM MEKi and 500 nM CDK4/6i and stained for SA-β Gal activity every day for 7 days. Scale bar, 100 μm.
(B) Percentage of SA-β Gal-positive cells treated with the indicated conditions as a function of time after treatment. Data are represented as mean ± SD from three independent experiments. p values were obtained from one-way ANOVA with multiple-comparison test. ns, not significant.
(C) Scatterplot of CDK2 activity versus nuclear area (NA) of single cells. Color represents SA-β Gal activity in each cell. MCF7 cells were treated with 100 nM MEKi and 500 nM CDK4/6i for 2, 4, 6, and 7 days. Vertical line represents the 0.6 threshold, below which cells were considered to have low CDK2 activity. Horizontal line indicates the 200 μm2 threshold above which nuclei were considered large.
(D) Quantification of cells (from C) that were either cycling (CDK2 > 0.6, NA < 200 μm2, log2[SA-β Gal] < 23.5), G0 senescent (CDK2 < 0.6, NA > 200 μm2, log2[SA-β Gal] > 23.5), G2 senescent (CDK2 > 0.6, NA > 200 μm2, log2[SA-β Gal] > 23.5), or G0/quiescent cells (CDK2 < 0.6, NA < 200 μm2, log2[SA-β Gal] < 23.5). N > 1,500 cells per condition.
(E) Heatmap of SASP released by cells treated with DMSO, 10 Gy γ-IR, or 100 nM MEKi and 500 nM CDK4/6i at day 7 of treatment. Conditioned media were collected at day 7 and analyzed by multiplex immunoassays. Data are fold change normalized to the DMSO-treated condition.
As senescence is a multifaceted phenomenon, we wanted to validate that the drug combination could induce other key features of cellular senescence in addition to SA-β Gal activity. We developed a quantitative single-cell assay to measure multiple parameters associated with cellular senescence. MCF7 cells stably expressing a fluorescently tagged CDK2 activity reporter (Figure S1F)28 were treated with either DMSO, γ-IR, or the drug combination for 7 days followed by cell fixation and staining with a fluorescent SA-β Gal kit (Figure S1G). Using an automated image analysis pipeline (Figures S1H and S1I), we quantified SA-β Gal levels and nuclear area in the same single cells and used a receiver operating characteristic (ROC) analysis to identify threshold levels for each parameter that best discriminated cycling from senescent cells, using γ-IR-treated cells as a truth set (Figures S1J and S1K). Consistent with cellular senescence, we found that MCF7 cells treated with the drug combination exhibited all the traits of senescent cells including elevated SA-β Gal activity, enlarged nuclear area, and low CDK2 activity (Figures 1C and 1D). Furthermore, given that SASP is an integral effector program associated with senescence, we also quantified SASP levels in MCF7 cells treated with the drug combination for 7 days and observed an increased SASP activity profile similar to γ-IR-treated cells (Figure 1E). Together, our data show that combination treatment with MEKi and CDK4/6i results in high SA-β Gal activity, large nuclear area, low CDK2 activity, and increased SASP in a DNA damage-independent manner, indicating cellular senescence and is similar to previous findings in KRAS mutant cancer cells.31
Cells maintain senescence after withdrawal of MEKi and CDK4/6i combination
Given that the key hallmark of senescence is the irreversibility of cell cycle exit10 we sought to investigate whether cells treated with the drug combination for 7 days remained non-proliferative after the drug combination was removed. To achieve this, we treated MCF7 cells with a MEKi and/or CDK4/6i for 7 days, washed off the drugs, and measured cell confluence for up to 20 days using time-lapse microscopy (Figure 2A). We observed no increase in cell confluence of the MEKi and CDK4/6i combination treated cells after drug removal, even though control experiments showed that the drug wash-off restored ERK and Rb phosphorylation (Figures S2A–S2D). Furthermore, MCF7 cells remained SA-β Gal positive and exhibited high SASP levels at days 10 and 17 (Figures 2B–2E). This effect was not unique to MCF7 cells, as we observed similar results in primary human lung fibroblasts and MCF10A cells (Figures S2E–S2G).
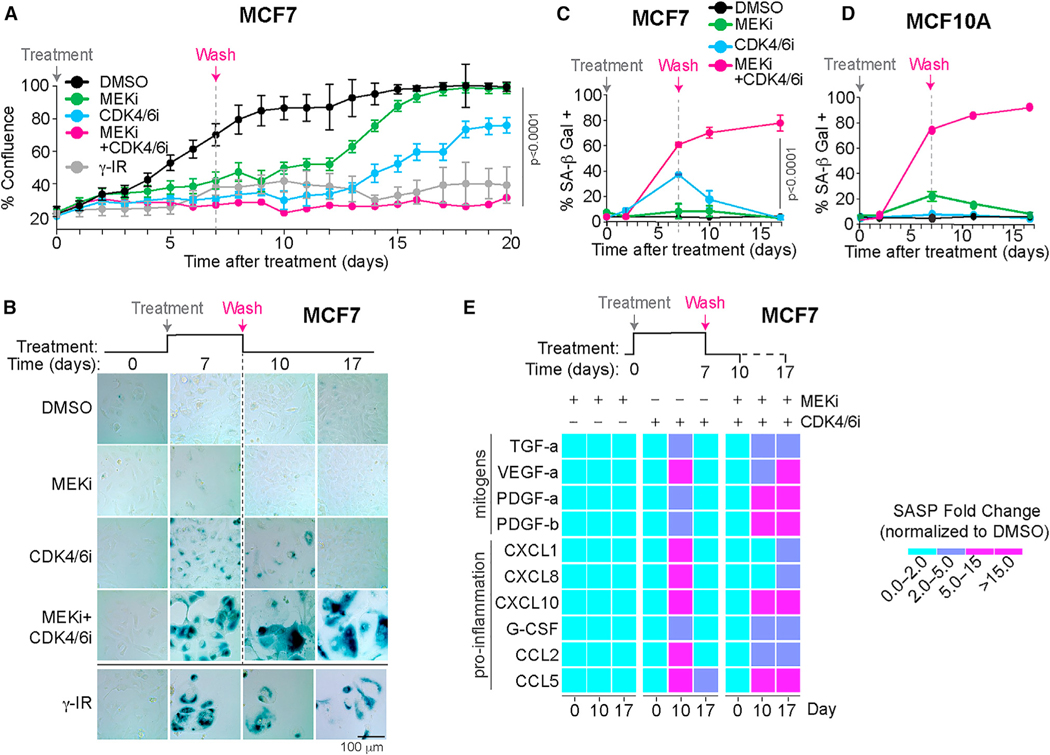
Figure 2. Cells maintain senescence after withdrawal of MEKi and CDK4/6i combination.
(A) Percentage confluence of cells treated with the indicated conditions as a function of time after treatment. Data are represented as mean ± SD from three independent experiments. p values were obtained from one-way ANOVA with multiple-comparison test. Vertical line denotes time at which drugs were washed off. 10 Gy γ-IR-treated cells were used as a positive control.
(B) Representative images of MCF7 cells treated with DMSO, 100 nM MEKi, 500 nM CDK4/6i, or a combination of MEKi and CDK4/6i for 7 days after which thetreatments were washed off and the cells were grown in complete culture medium until day 17. Cells were stained for SA-β Gal activity at days 10 and 17. Cells exposed to 10 Gy γ-IR at day 0 were used as a positive control. Scale bar, 100 μm.
(C and D) Quantification of SA-β Gal-positive MCF7 (C) or MCF10A (D) cells treated with the indicated conditions as a function of time after treatment. Data are represented as mean ± SD from three independent experiments. p values were obtained from ANOVA with multiple-comparison test.
(E) Heatmap of SASP factors released by cells treated with DMSO, 100 nM MEKi, 500 nM CDK4/6i, or a combination of MEKi and CDK4/6i. All treatments were washed off at day 7 and the cells were allowed to grow in complete medium until day 17. Conditioned media was collected at days 10 and 17 and analyzed by multiplex immunoassays. Data are SASP fold change normalized to DMSO-treated condition.
Notably, we found that almost 40% of MCF7 cells treated with CDK4/6i alone exhibited high SA-β Gal activity by day 7, which returned to baseline levels after washing the drug off (Figures 2A and 2B). Similarly, MCF10A cells treated with MEKi alone (Figure 2C) accumulated SA-β Gal activity by day 7, and following the wash, declined back to baseline by day 15. Thus, single-agent treatment with MEKi or CDK4/6i alone can induce a quiescent state that is reversible, confirmed by the fact that washing out the single drug treatments restored cell proliferation and low SASP levels by day 17 (Figures 2A–2E). These results indicate that MEKi and CDK4/6i combination treatment induces a truly irreversible senescent state after at least 7 days of treatment that is maintained following drug withdrawal, while single-agent treatments induce a reversible quiescent state.
Probability of cells irreversibly committing to senescence increases with treatment duration
Having established that a combination of MEKi and CDK4/6i can induce irreversible exit from the cell cycle to senescence, we next sought to establish when cells commit to senescence. To achieve this, we treated MCF7 cells with the drug combination for increasing durations before washing it off and quantifying SA-β Gal activity at day 17 (Figure 3A). We found that a small population of cells was able to enter and maintain senescence with as little as 48 h of treatment (Figures 3B and 3C). However, most cells (>60%) required longer drug combination exposure to enter and maintain senescence, suggesting that cells typically need between 3 and 6 days to irreversibly commit to senescence. We obtained similar results in MCF10A and U2OS cells (Figures S3A and S3B).
Figure 3. Probability of cells irreversibly committing to senescence increases with treatment duration.
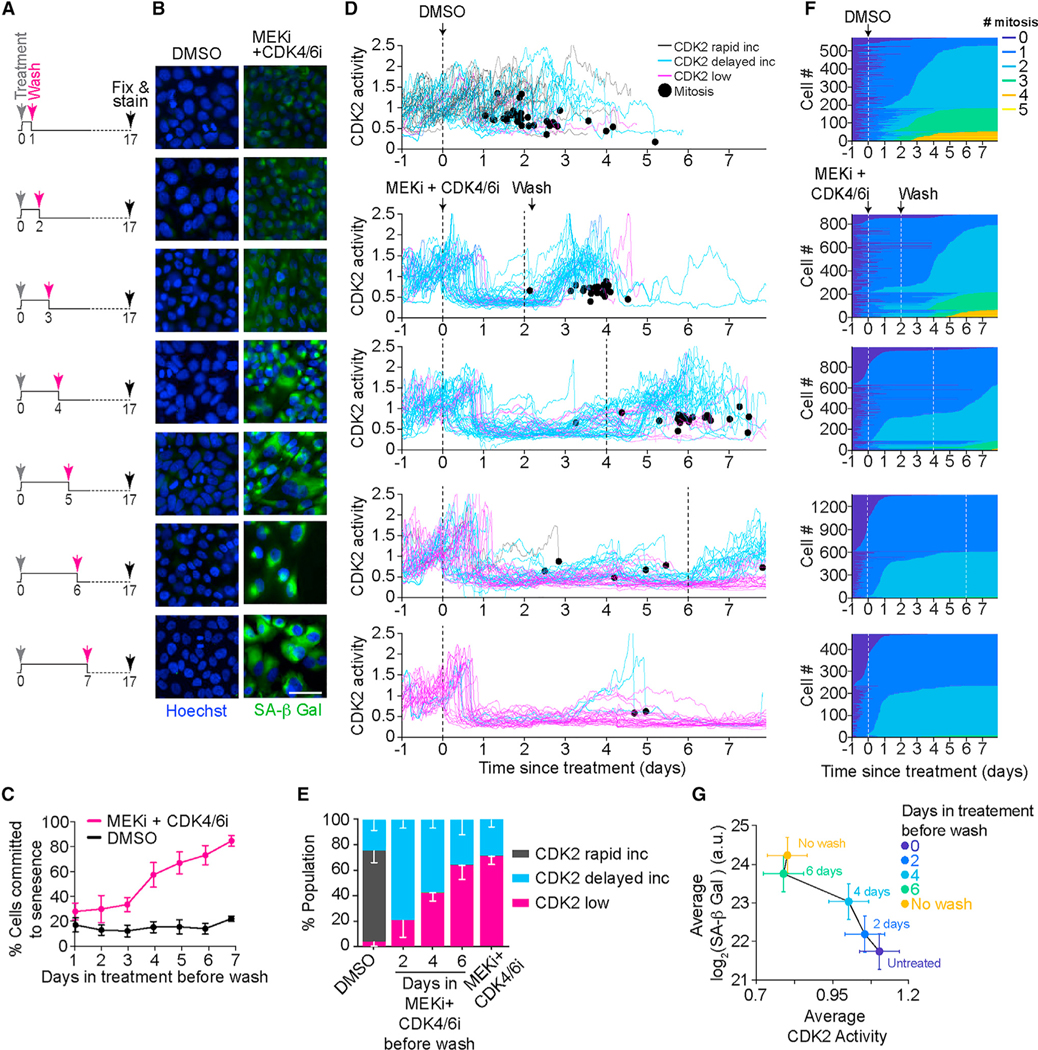
(A) Experimental scheme showing that MCF7 cells were treated with DMSO or a combination of 100 nM MEKi and 500 nM CDK4/6i for increasing durations 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, and 7 days before washing off the drugs. Cells were then grown in complete medium until day 17, when cells were fixed and stained for SA-β Gal activity.
(B) Representative images of MCF7 cells treated as described in (A). Cells were fixed and stained for SA-β Gal activity using SPIDR-IF-SA-β Gal assay (green). Nuclei were stained with Hoechst (blue). Scale bar, 10 μm.
(C) Quantification of SA-β Gal-positive cells from (B) plotted as a function of time exposed to treatment before washing off the drugs. Data are represented as mean ± SD from three independent experiments.
(D) Single-cell CDK2 activity traces from MCF7 cells treated with DMSO or 100 nM MEKi and 500 nM CDK4/6i while in S/G2 phase (defined as CDK2 activitygreater than 1 and APC/C activity less than 0.3 at the time of treatment). Vertical black lines indicate when drugs were added (solid) and washed off (dashed). Trace color denotes long-term fate of each cell: black, immediately built up CDK2 activity after mitosis (CDK2 rapid increase); cyan, variable time spent in a CDK2-low state following mitosis before eventually building up CDK2 activity (CDK2 delayed increase); pink, remained in CDK2-low state for the entire imaging period (CDK2 low). Black dot denotes when a cell went through mitosis.
(E) Percentage of CDK2 rapid increase, CDK2 delayed increase, and CDK2-low cells from (D). Data are mean ± SD from three biological replicates.
(F) Heatmaps indicating when each cell went through mitosis following the indicated treatment conditions. Vertical white lines denote times at which drugs were added (solid) and washed (dashed).
(G) Phase plane diagram of the mean CDK2 activity versus the mean of SA-β Gal activity in cells treated as shown in (B). Data are mean ± SD from a representative experiment.
Given that CDK2 activity is both a marker for cell cycle exit and a downstream effector of both MEK and CDK4/6 signaling (Figures S3C–S3G), we measured CDK2 activity in MCF7 cells treated with the drug combination for increasing duration before washing it off. We observed that upon treatment, all cells lost CDK2 activity after the first mitosis following the addition of the drugs, indicating that all cells initially underwent cell cycle arrest (Figure 3D). However, when the drugs were washed off 48 h later, 80% of cells recovered and went on to build up high CDK2 activity and divide, suggesting that these cells were transiently arrested in a quiescent and not senescent state (Figures 3D–3F and S3H). Notably, cells that were incubated with the drugs for 4–6 days before being washed were more likely to permanently lose CDK2 activity, fail to go through another mitosis, and exhibit elevated SA-β Gal activity (Figures 3D–3G). Together, these data suggest that cells irreversibly commit to senescence after 3 to 6 days of treatment and that the proportion of cells within the population that irreversibly commit to senescence is correlated to the treatment duration.
Senescence entry and maintenance are associated with MYC loss
We next sought to understand the molecular mechanism underlying the irreversible loss of CDK2 activity we observed during combination treatment-induced senescence. We first investigated the possible role of the cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitors (CKIs) p16, p21, and p27 and their upstream activator p53,35 which inhibit CDK2 activity and are known to play a role in cell cycle exit during senescence.36–38 Interestingly, MCF7 cells lack p1639,40 and CDK2 activity remained low following treatment with the combination of MEKi and CDK4/6i even after knocking down the CKIs p21 or p27, as well as their upstream activator p53 (Figures S4A and S4B). Therefore, senescence entry is not mediated by these canonical CKIs. We next tested several transcription factors that are downstream of MEK and upstream of CDK4/6 including the pro-proliferative activator protein-1 (AP-1)41 proteins c-JUN and c-FOS as well as MYC, and the anti-proliferative CCAAT/enhancer binding protein alpha (C/EBPα)42,43 (Figure 4A). Interestingly, c-JUN and c-FOS mRNA levels increased, while C/EBPα mRNA and protein levels slightly decreased over time after treatment with the combination of MEKi and CDK4/6i (Figures 4B and 4C). The direction of these changes was opposite to what one might expect if they were to mediate a loss of CDK2 activity. As a result, we ruled out c-JUN, c-FOS, and C/EBPα as potential mediators of CDK2 loss during senescence. Only MYC mRNA and protein levels (Figures 4B and 4C) were downregulated within 2 days following treatment with the drug combination, corroborating previous results showing MYC loss during senescence,44,45 and the timing of the loss of MYC protein was correlated with the detection of SA-β Gal activity (Figures 4C–4E). Interestingly, MYC protein was irreversibly lost after 4 days of treatment with the drug combination, as we did not observe a recovery in MYC protein levels despite washing off the drugs and waiting 3 days (Figures 4F and 4G). The timing of the irreversible loss of MYC protein levels was correlated with our earlier observations of irreversible loss of CDK2 activity and irreversible increase in SA-β Gal activity (see Figure 3).
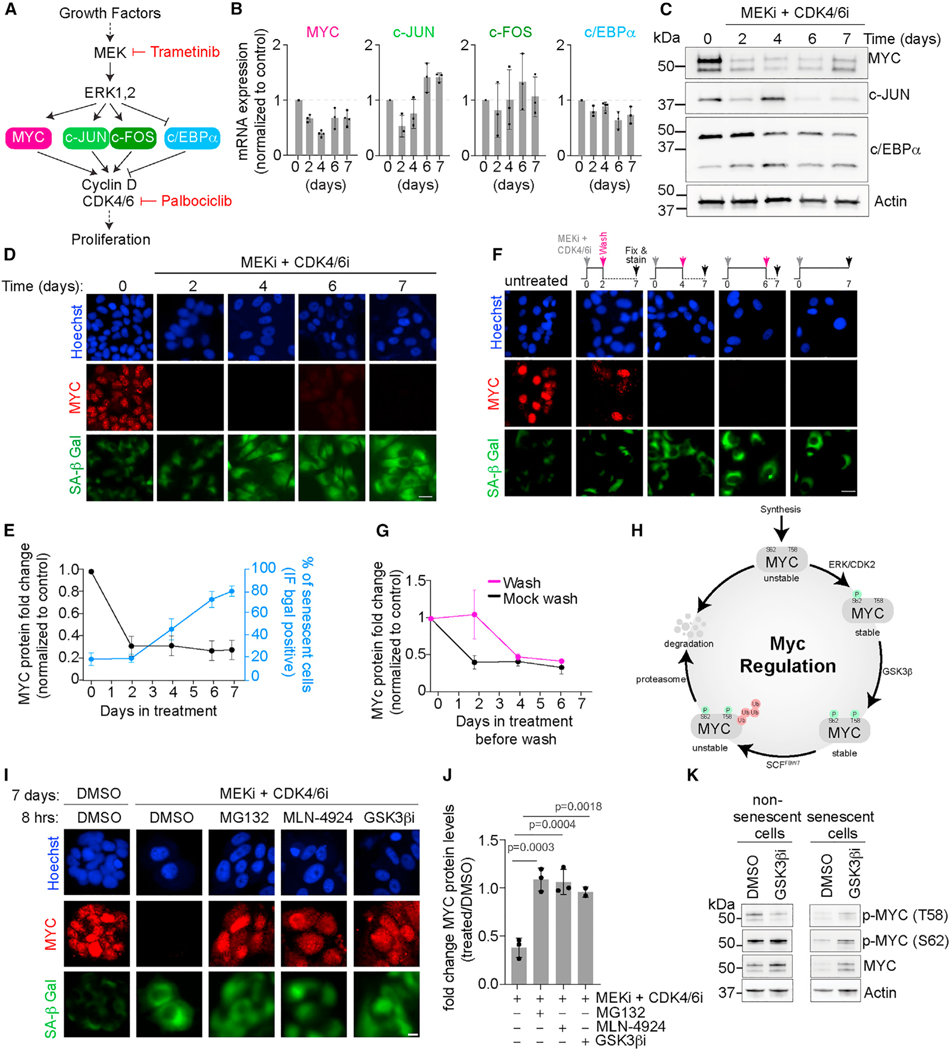
Figure 4. Senescence entry and maintenance are associated with irreversible MYC loss.
(A) Signaling diagram showing major transcription factors as possible proteins mediating entry and commitment to cellular senescence.
(B) Quantification of MYC, c-JUN, c-FOS, and c/EBPα mRNA levels normalized to control at different time points after adding MEKi + CDK4/6i. Data are represented as mean ± SD from three independent experiments.
(C) Immunoblotting of MYC, c-Jun, and c/EBPα at days 0, 2, 4, 6, and 7 post-treatment. Actin was used as the loading control. Representative blot from three independent experiments.
(D) Representative images of MCF7 cells treated with MEKi + CDK4/6i for the indicated number of days. Cells were fixed and stained for MYC protein (red) and SA-β Gal activity (green). Nuclei were stained with Hoechst (blue). Scale bar, 10 μm.
(E) Quantification of MYC and SA-β Gal-positive cells from (D) plotted as a function of time exposed to treatment. Data are represented as mean ± SD from three independent experiments.
(F) Representative images of MCF7 cells treated with DMSO, or MEKi + CDK4/6i for 2, 4, or 6 days before washing off the drugs. Cells were fixed and stained at day 7 for MYC protein (red) and SA-β Gal activity (green). Nuclei were stained with Hoechst (blue).
(G) Quantification of MYC and SA-β Gal-positive cells from (F) plotted as a function of time exposed to treatment before wash. Data are represented as mean ± SD from three independent experiments.
(H) Signaling diagram showing post-translational modifications mediating MYC stability and degradation.
(I) Representative images of MCF7 cells treated with MEKi + CDK4/6i for 7 days, then treated with DMSO, MG132 (10 μM), MLN-4924 (3 μM), or GSK3β inhibitor (1 μM) for 8 h before fixation. Scale bar, 10 μm.
(J) Quantification of the fold change in MYC protein levels after treatment with the indicated drugs (treated/DMSO) from (I). Data are represented as mean ± SD from three independent experiments. p values were obtained from one-way ANOVA with multiple comparison test.
(K) Immunoblotting of MYC, p-MYC (T58), and p-MYC (S62) in control cells (left) and cells initially treated with MEKi + CDK4/6i for 4 days to induce senescence(right), followed by treatment with DMSO, MG132 (10 μM), MLN-4924 (3 μM), or GSK3β inhibitor (1 μM) for 8 h before collection of cell lysates. Actin was used as the loading control.
MYC is a transcriptional amplifier that is activated by growth factor signaling and functions to promote cellular proliferation.46,47 MYC protein levels are largely regulated via phosphorylation of serine 62 (S62) and threonine 58 (T58).48 A number of kinases including ERK and CDK2 have been shown to phosphorylate S62 co-translationally, stabilizing MYC, while GSK3β phosphorylates T58,49,50 targeting MYC for ubiquitination. The dually phosphorylated MYC is recognized by the ubiquitin ligase SCFFBW7 which ubiquitinates MYC and targets it for proteasomal degradation (Figure 4H).51,52 We observed that the loss of MYC protein levels following 7 days of treatment with the combination of MEKi and CDK4/6i could be rescued by treatment with either MG132, a proteasome inhibitor, or MLN-4924, a cullin neddylation inhibitor which inactivates cullin-based ubiquitin ligases (Figures 4I, 4J, and S4C), suggesting that the irreversible loss of MYC protein levels we observed was largely due to SCF- and proteasomal-mediated degradation. Furthermore, we observed an increase in T58 phosphorylation in senescent cells treated with MG132 or MLN-4924, suggesting that GSK3β is responsible for maintaining MYC degradation during senescence entry (Figure S4C). In support of this hypothesis, inhibiting GSK3β in senescent cells reduced the T58 phosphorylation of MYC which led to an increase in MYC protein levels (Figures 4I–4K). Concomitant with this, GSK3β inhibition also led to an accumulation of MYCS62 phosphorylation compared with the DMSO-treated control (Figure 4K) thus stabilizing MYC protein. Therefore, in cells treated with the combination of MEKi and CDK4/6i, GSK3β mediates constitutive MYCT58 phosphorylation and subsequent ubiquitin-mediated degradation, even after the combination treatment is washed off the cells.
Cells enter and maintain senescence by constitutive degradation of MYC
To determine if loss of MYC protein is necessary for senescence entry, we established an MCF7 cell line to inducibly express either wild-type MYC (teton-MYCWT) or mutated MYC that cannot be phosphorylated at T58 (teton-MYCT58A) (Figures S5A–S5C). As expected, DMSO-treated cells exhibited low SA-β Gal activity and hyper-phosphorylated Rb, indicative of proliferating cells, while cells treated with a combination of MEKi and CDK4/6i for 7 days exhibited high SA-β Gal activity, hypo-phosphorylated Rb, markers of cellular senescence and cell cycle exit, respectively (Figure S5D). Induction of MYCWT using doxycycline (Dox) greatly reduced the percentage of SA-β Gal-positive cells but failed to increase the percentage of hyper-phosphorylated Rb cells (Figures 5A and S5D), indicating the ability of these cells to divide was partially rescued. Conversely, induction of MYCT58A was able to both reduce the percentage of SA-β Gal-positive cells and increase the percentage of hyper-phosphorylated Rb to similar levels as the untreated control (Figures 5B and S5E), indicating GSK3β-mediated MYC degradation is necessary for senescence entry.
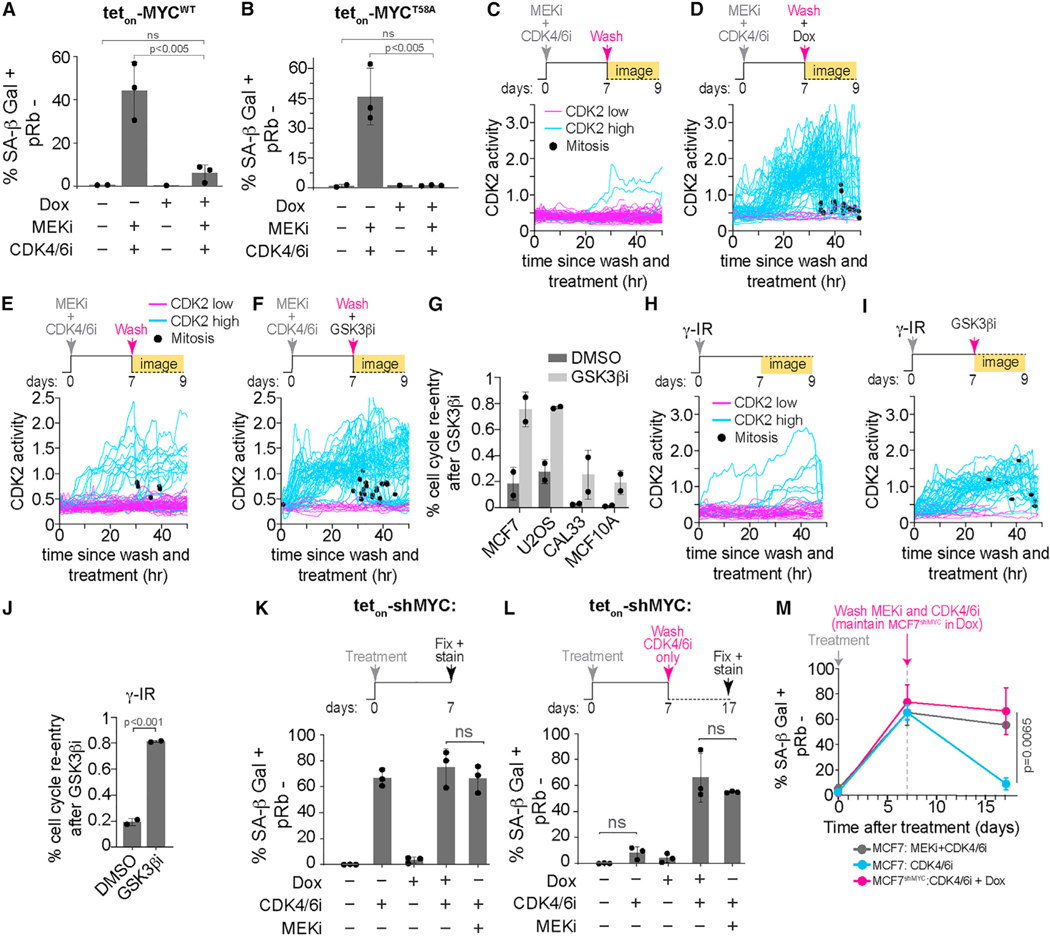
Figure 5. Cells enter and maintain senescence by irreversible degradation of MYC.
(A and B) Quantification of SA-β Gal-positive and pRb-negative cells from Figures S5D and S5E treated with the indicated conditions. Data are represented as mean ± SD from three independent experiments. p values were obtained from one-way ANOVA with multiple-comparison test. ns, not significant.
(C and D) Single-cell CDK2 activity traces from MCF7 cells transduced with teton-MYCT58A treated with 100 nM MEKi and 500 nM CDK4/6i for 7 days. At day 7, cells were washed to remove drugs and were treated with either DMSO (C) or 1 μM doxycycline (Dox) (D) when time-lapse imaging was started. Trace color denotes the long-term fate of each cell: cyan, started in the CDK2-low state before eventually building up CDK2 activity (CDK2 high); pink, remained in CDK2-low state for the entire imaging period (CDK2 low). Black dot denotes when a cell went through mitosis.
(E and F) Single-cell CDK2 activity traces from MCF7 cells treated with 100 nM MEKi and 500 nM CDK4/6i for 7 days. At day 7, cells were washed to remove drugs and were treated with either DMSO (E) or 1 μM GSK3βi (F) when time-lapse imaging was started.
(G) Bar graph depicting the percent of senescent cells that activated CDK2 activity and re-entered the cell cycle after treatment with a GSK3βi as described in (F). Data are represented as mean ± SD from two independent experiments. Example single-cell CDK2 traces can be found in Figure S5G.
(H and I) Single-cell CDK2 activity traces from MCF7 cells exposed to 10 Gy γ-IR. At day 7, cells were treated with either DMSO (H) or 1 μM GSK3βi (I) when time-lapse imaging was started.
(J) Bar graph depicting the percent of senescent cells that activated CDK2 activity and re-entered the cell cycle after treatment with a GSK3βi as described in (I). Data are mean ± SD from two biological replicates. p value was obtained from Student’s t test. Example single-cell CDK2 traces can be found in (H) and (I).
(K) Quantification of SA-β Gal-positive and pRb-negative cells from Figure S6A treated with the indicated conditions. Data are represented as mean ± SD from three independent experiments. p values were obtained from one-way ANOVA with multiple-comparison test. ns, not statistically significant.
(L) Quantification of SA-β Gal-positive and pRb-negative cells from Figure S6B treated with the indicated conditions. Data are represented as mean ± SD from three independent experiments.
p values were obtained from one-way ANOVA with multiple-comparison test. ns, not significant.
(M) Quantification of SA-β Gal-positive and pRb-negative cells from (K) and (L) treated with the indicated conditions as a function of time after treatment. Vertical line denotes time at which MEKi plus CDK4/6i or CDK4/6i alone were washed off. Cells continued to grow in media containing Dox (1 mM) for the shMYC+CDK4/6i treated cells until fixation. Data are represented as mean ± SD from three independent experiments. p values were obtained from one-way ANOVA with multiple-comparison test.
To determine if GSK3β-dependent MYC degradation is necessary to maintain cells in the senescent state, we first treated MCF7 cells with the combination of MEKi and CDK4/6i for 7 days to render them senescent, washed off the drugs, and then either induced the expression of MYCT58A or treated the cells with a GSK3β inhibitor. Strikingly, we observed after either MYCT58A induction or GSK3β inhibition most cells turned on CDK2 activity, re-entered the cell cycle, and eventually went through mitosis where the daughter cells exhibited normal nuclear area compared with both senescent cells and the mother cells, indicating that they were no longer senescent (Figures 5C–5F and S5F). In the long term, we observed increased proliferation in cells expressing MYCT58A or treated with a GSK3β inhibitor compared with the untreated, senescent control (Figures S5G and S5H). We observed similar findings in U2OS, an osteosarcoma cell line, CAL33, an oral squamous cell carcinoma (OSCC) cell line, and MCF10A, indicating a cell line-independent phenomenon (Figures 5G and S5I). Furthermore, these results were not limited to senescence induced by the combination of MEKi and CDK4/6i. We found that treatment with a GSK3β inhibitor caused cell cycle re-entry in senescent cells induced by γ-IR, treatment with the DNA damaging drug doxorubicin, or with hydrogen peroxide (Figures 5H–5J, S5J, and S5K). Thus, MYC degradation is necessary to both enter and maintain therapy-induced and DNA damage-induced cellular senescence.
We next sought to ask whether MYC degradation underlies the transition from a reversible quiescent arrest to an irreversible cell cycle exit and senescence. To test this hypothesis, we treated cells with a CDK4/6i, which induces a reversible cell cycle arrest as previously mentioned, and asked if knocking down MYC in combination would convert these cells to an irreversible senescent state. We observed an increase in SA-β Gal-positive cells in both Rb hyper- and hypo-phosphorylated cells after treatment with CDK4/6i (Figures 5K and S6A). However, as we demonstrated earlier, these cells recovered to an SA-β Gal-negative state after washing off the CDK4/6i (Figures 2B, 2E, 5L, 5M, and S6B), demonstrating that these cells were reversibly arrested in quiescence. Consistent with our model, knocking down MYC in combination with the CDK4/6i greatly increased the percentage of SA-β Gal-positive and Rb hypo-phosphorylated cells (Figure 5K, S6A, S6C and S6D), and this population of senescent cells was maintained even after washing off the CDK4/6i (Figures 5L, 5M, and S6B). Thus, MYC knockdown in combination with CDK4/6 inhibition is sufficient for senescence entry, and once senescent, MYC knockdown alone is sufficient to maintain senescence irreversibly.
MYC loss is necessary to maintain replicative and OIS
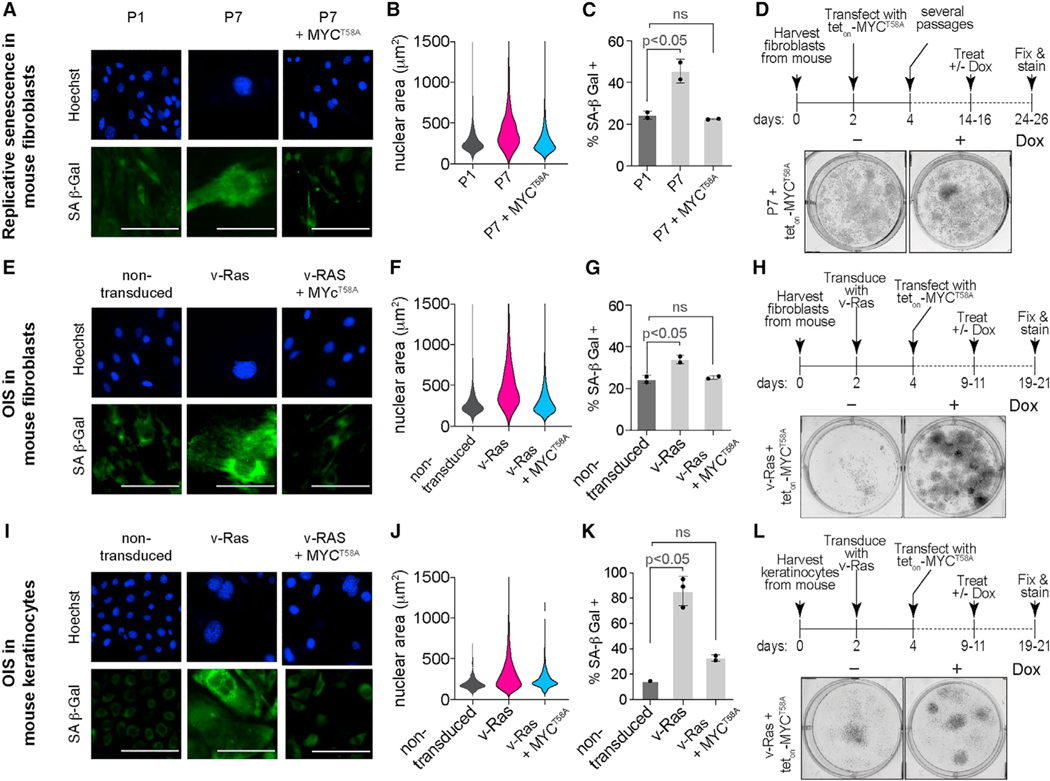
Having demonstrated that expressing a non-degradable MYC mutant can make therapy-induced and DNA damage-induced senescent cells start to proliferate again, we next tested our model in replicative and oncogene-induced senescent cells. We used primary mouse fibroblasts from early (P1) and late (P7) passages to model replicative senescence (Figures S7A–S7C), observing a high percentage of SA-β Gal-positive cells and large nuclear area in late-passage cells. We transfected early passage fibroblasts with teton-MYCT58A, which allowed us to induce MYCT58A once cells were deemed senescent in later passages (Figure S7D). Induction of MYCT58A in late-passage cells reversed these phenotypes; cells exhibited a low percentage of SA-β Gal-positive cells and lower nuclear areas comparable with early-passage cells (Figures 6A–6C). In the long term, we observed increased proliferation in cells expressing MYCT58A compared with the untreated, late-passage senescent cells (Figure 6D). To model OIS, we transduced primary mouse fibroblasts with the oncogene v-RasHa, observing a high percentage of SA-β Gal-positive cells and large nuclear area in Ras-transduced cells compared with the non-transduced controls (Figures S7A–S7C). Induction of MYCT58A in the Ras-transduced cells (Figure S7E) again reversed these phenotypes; cells exhibited a low percentage of SA-β Gal-positive cells and lower nuclear areas comparable with non-transduced cells (Figures 6E–6G). In the long term, we observed increased proliferation in cells expressing MYCT58A compared with the untreated, Ras-transduced senescent cells (Figure 6H). We further validated these findings using mouse keratinocytes and show that they enter OIS (Figures S7F–S7H) but inducing MYCT58A (Figure S7I) again reversed the senescent phenotypes (Figures 6I–6K) and restored their proliferation (Figure 6L). These data demonstrate that MYC degradation is necessary to maintain the senescent state not only in therapy- and DNA damage-induced senescence but also in replicative and OIS.
Figure 6. MYC loss is necessary to maintain replicative and oncogene-induced senescence.
(A) Representative images of early-passage (P1) and late-passage (P7) primary mouse fibroblasts and late-passage fibroblasts treated with doxycycline (Dox) (2 μM) to induce MYCT58A (P7+MYCT58A). Cells were fixed and stained at the indicated times for SA-β Gal activity (green). Nuclei were stained with Hoechst (blue). Scale bar, 50 μm.
(B) Violin plots of nuclear area (μm2) in the indicated conditions from (A).
(C) Quantification of SA-β Gal-positive cells from (A). Data are represented as mean ± SD from two independent experiments. p values were obtained from one-way ANOVA with multiple-comparison test. ns, not significant.
(D) Experimental setup (top) and representative images (bottom) of survival assay showing timeline starting with harvesting and culturing mouse fibroblasts fromC57 mice, then transfection with teton-MYCT58A construct, followed by several passages to induce replicative senescence (P7). Finally, doxycycline (Dox, 2 μM) was added to induce teton-MYCT58A expression. Cells were fixed and stained with crystal violet 10 days after Dox treatment.
(E) Representative images of primary mouse fibroblasts, untreated (non-transduced), transduced with oncogenic RAS (v-RasHa), and oncogene-induced senescent fibroblasts treated with Dox (2 μM) to induce MYCT58A expression (v-RAS+ MYCT58A). Cells were fixed and stained at the indicated times for SA-β Gal activity (green). Nuclei were stained with Hoechst (blue). Scale bar, 50 μm.
(F) Violin plots of nuclear area (μm2) in the indicated conditions from (E).
(G) Quantification of SA-β Gal-positive cells from (E). Data are represented as mean ± SD from two independent experiments. p values were obtained from one-way ANOVA with multiple-comparison test. ns, not significant.
(H) Experimental setup and representative images of survival assay showing timeline starting with harvesting and culturing mouse fibroblasts from C57 mice, then transduction with oncogenic RAS (v-RAS) to induce OIS and transfection with teton-MYCT58A construct. Finally, Dox (2 μM) was added to induce MYCT58A expression. Cells were fixed and stained with crystal violet 10 days after Dox treatment.
(I) Representative images of primary mouse keratinocytes, untreated (non-transduced), transduced with oncogenic RAS (v-RAS), and oncogene-induced senescent keratinocytes treated with Dox (2 μM) to induce MYCT58A expression (v-RAS+ MYCT58A). Cells were fixed and stained at the indicated times for SA-β Gal activity (green). Nuclei were stained with Hoechst (blue). Scale bar, 50 μm.
(J) Violin plots of nuclear area (μm2) in the indicated conditions from (I).
(K) Quantification of SA-β Gal-positive cells from (I). Data are represented as mean ± SD from two independent experiments. p values were obtained from one-way ANOVA with multiple-comparison test. ns, not significant.
(L) Experimental setup and representative images of a survival assay showing timeline starting with harvesting and culturing mouse keratinocytes from C57 mice, then transduction with oncogenic RAS (v-RAS) to induce OIS and transfection with teton-MYCT58A construct. Finally, Dox (2 μM) was added to induce MYCT58A expression. Cells were fixed and stained with crystal violet 10 days after Dox treatment.
MYC loss is associated with senescent cells in human oral dysplastic lesions
Thus far, our data indicates that MYC degradation is necessary for cells to enter and maintain the senescent state in vitro. To extend our model in vivo, we examined 40 human samples of oral mucosal lesions, representing increasing premalignant lesion grades in progression toward OSCC. Physiologically, senescence is one of the first defense mechanisms against tumor initiation and can be triggered in response to aberrant activation of oncogenic signaling in a process referred to as OIS.53–55 Previous studies have shown that premalignant lung lesions induced in mice are rich in senescent cells, while malignant tumors lacked senescent cells, suggesting that these cells may have either failed to undergo or maintain OIS. We hypothesized that MYC protein levels would be low in early stages of premalignant lesions, high in late-stage lesions and that the percentage of senescent cells would be inversely correlated with the grade of premalignant lesion.
Patient samples were sectioned and stained for MYC. Clinical data including age of patients at diagnosis, gender, site of the lesion, and 5-year recurrence rate are summarized in Table S1. In the normal oral mucosa, nuclear MYC immunostaining was observed only in the basal cell layer (Figure 7A). Mild dysplastic lesions exhibited hyperplasia in the basal cell layer, which is an indication of premalignancy. Interestingly, there was a negative MYC immunostaining in both the basal and parabasal cell layers, as well as larger cell area and larger cytoplasmic to nuclear ratios, indicating hypo-proliferation and potential OIS (Figures 7B, 7C, and 7E–7G). To further investigate and validate these findings, we used digital spatial profiling to measure additional markers of senescence in these tissue sections (Figures S8A and S8B). Consistent with our immunohistochemical staining, we observed that mild dysplastic lesions exhibit high levels of phospho-p38 and low Ki67 levels indicative of senescence (Figures 7H–7J).56–58 Epithelial cells in the carcinoma in situ showed intense nuclear MYC immunostaining, normal cell size, high levels of Ki67, and low levels of phopsho-p38 (Figures 7C and 7E–7J), and in OSCC, all malignant epithelial tumor cells as well as the entire dysplastic surface epithelium showed intense nuclear and cytoplasmic MYC immunostaining, normal cell size, high levels of Ki67, and low levels of phospho-p38 (Figures 7D–7J), indicating hyper-proliferation, and cancer progression. Thus, consistent with our model, cells within low grade premalignant lesions had several phenotypes associated with senescence including low MYC expression and large cell size, whereas in addition to dysplastic changes such as nuclear hyperchromatism and cellular polymorphism, cells in late-stage premalignant lesions and malignant tumors had phenotypes associated with proliferative cells including high MYC expression and normal cell size.
Figure 7. MYC loss is associated with senescent cells in human oral dysplastic lesions.
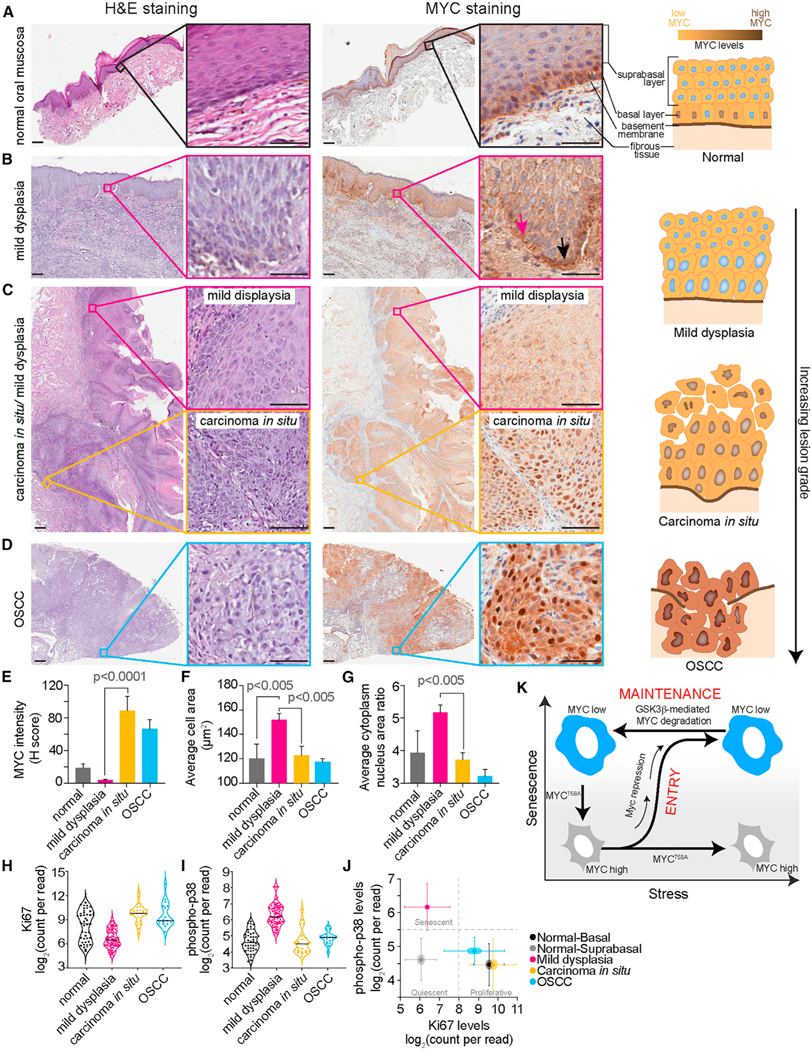
(A–D) Representative images of human oral tissue sections stained with H&E (left; scale bar, 100 μm; inset is 40× magnification) and immunohistochemical staining of MYC (right; scale bar, 100 μm; inset is 40× magnification).
(A) Tissue section of a normal oral mucosa showing a fibrous tissue stroma covered by keratinized stratified squamous epithelium. The inset shows normal stratification of epithelial cells with no evidence of cellular atypia, and sporadic nuclear MYC expression in the basal cells while the suprabasal cell layer show negative MYC immunostaining.
(B) Tissue section of a mild oral dysplasia showing fibrous tissue covered by keratinized, hyperplastic, stratified squamous epithelium. Basilar hyperplasia with loss of polarization is observed as shown in the inset. Immunohistochemical staining of the same tissue section shows negative MYC staining in the basal and suprabasal cell layer (pink arrow) compared with adjacent, normally behaving basal cells maintaining their proliferative phenotype as depicted by baseline MYC staining (black arrow).
(C) Tissue section showing fibrous tissue covered by keratinized, hyperplastic, stratified squamous epithelium. The epithelium shows foci of mild dysplasia (pink inset). Basilar hyperplasia, loss of polarization, and loss of cell-to-cell adhesion are limited to the basal cell layer. MYC immunostaining of the same tissue section shows negative MYC staining in the basal and parabasal cell layer. Other foci show dysplastic malignant changes throughout the whole thickness of the epithelium (black inset) including nuclear hyperchromatism, cellular pleomorphism, and abnormal mitosis. (Right) Immunohistochemical staining of the same tissue section showing intense nuclear MYC staining.
(D) Tissue section of oral squamous cell carcinoma (OSCC) showing fibrous tissue covered by severely dysplastic keratinized, squamous epithelium with multiple points of invasions of malignant epithelial cell strands infiltrating the underlying stroma. Inset is a higher magnification showing malignant epithelial cells exhibiting malignant criteria. (Right) Immunohistochemical staining of the same tissue section showing strong nuclear and cytoplasmic MYC staining in the malignant epithelial cells infiltrating the underlying fibrous tissue stroma.
(E–G) Quantification of various parameters from tissue sections shown in (A)–(D) including MYC intensity (H-score) (E), average cell area (μm2) (F), and average cytoplasmic-to-nuclear area ratio (G). Data are represented as mean ± SD. p values were obtained from one-way ANOVA with multiple-comparison test.
(H and I) Violin plot of Ki67 (H) and phospho-p38 (I) levels using GeoMx digital spatial profiling. Each dot represents a region of interest (ROI) from the indicated tissue type.
(J) Scatterplot of Ki67 and phospho-p38 levels from the same ROI. Center point is the mean Ki67 and phospho-p38 levels for all the ROIs of the indicated tissue type. Center circle represents SEM and lines represent SD.
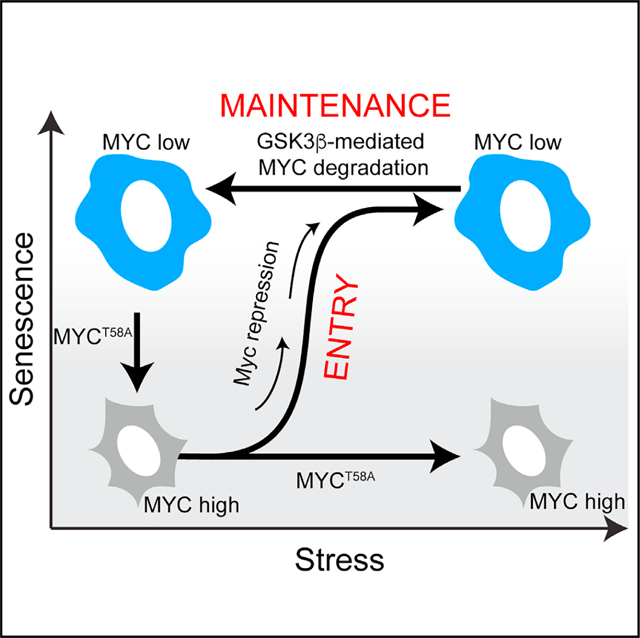
(K) Schematic diagram of our model of cellular senescence entry and maintenance. In response to various stresses, cells enter senescence via MYC transcriptional repression but maintain their senescence state by constitutively degrading MYC.
DISCUSSION
We used single-cell analysis, quantitative measurements, and reversible inhibitors to investigate the irreversibility of cell cycle exit associated with senescence. We showed in MCF10A and MCF7 cells that the probability of cells irreversibly committing to senescence increases with the duration of the perturbation rather than being a single time of commitment, and that the timing of senescence commitment correlates with MYC protein loss. Our data suggests that MYC loss is necessary and sufficient for cells to enter and irreversibly commit to the senescent fate in response to a number of stresses and support our model with three key pieces of evidence. First, MYC protein is irreversibly lost during entry into senescence, despite drug withdrawal. Second, we find that senescent cells can be forced to proliferate again by expressing a non-degradable MYC mutant, suggesting that low MYC levels underpins senescence maintenance. Third, premalignant lesions that downregulate MYC undergo OIS while cells that fail to downregulate MYC progress to late-stage premalignant lesions and eventually malignant tumors. Thus, MYC downregulation is both necessary for cells to undergo senescence and sufficient to maintain cells in the senescent state even when stress conditions are removed (Figure 7K).
Whether senescence is a state of permanent cell cycle exit (distinct terminal state) or reversible (biological continuum) is controversial.9,10,29,30 Our data aligns with the model suggesting that senescence is an irreversible, terminal cell fate because cells remained senescent despite washing off senescence-inducing drugs and recovery of the downstream signaling pathways. Our data confirmed that cells that re-enter the cell cycle and start dividing after removal of the initial perturbation, were quiescent rather than senescent cells because they had low SA-β Gal activity, did not release SASP, and had small cell size. Our data demonstrating that expressing a mutated, non-degradable version of MYC can cause a senescent cell to re-enter the cell cycle indicates the molecular mechanism ensuring irreversible cell cycle arrest under normal conditions relies on MYC degradation. It is possible however, that cancer cells could take advantage of this by either up-regulating MYC expression or by acquiring mutations in MYC that render it non-degradable. Such means of bypassing the mechanism of irreversibility may be one reason why senescence is sometimes thought to be reversible.
Carcinogenesis in human patients is a gradual, cumulative process of acquiring genetic mutations which culminate in invasion and thus cancer progression.59 For example, oral premalignant lesions are asymptomatic but often proceed to become OSCCs.60 Simple epithelial hyperplasia progresses through mild oral epithelial dysplasia to carcinoma in situ with increasing genetic and cellular alterations, which ultimately leads to invasion and OSCC. Senescence is one of the first defense mechanisms against epithelial cancer progression and OIS can be triggered in response to aberrant activation of oncogenic signaling.53–55 Premalignant lesions are rich in senescent cells, but malignant tumors are not, suggesting that these cells may have failed to undergo OIS or escaped senescence.54 We expanded on this model with live, single-cell experiments in vitro and human tissue immunostaining. Our data are consistent with these previous models and suggests that premalignant tumors bypass OIS by upregulating MYC.
In cancer treatment, senescence is often a therapeutic endpoint of many chemotherapeutic drugs. Previous studies have reported that CDK4/6is such as palbociclib induce senescence in breast cancer cells (therapy-induced senescence) both in vitro and in vivo.19,20,61–63 Interestingly, in our study, MCF7 cells treated with the CDK4/6i stopped dividing, exhibited elevated SA-β Gal activity and SASP levels, but cells resumed proliferation, recovered SASP levels to baseline, and showed negative SA-β Gal staining upon drug removal. This suggests that palbociclib induces a reversible quiescent state rather than senescence in these cells. However, knocking down MYC in combination with palbociclib induced irreversible senescence, even after removal of palbociclib suggesting that inhibiting MYC in combination with clinically approved CDK4/6is could be a more effective strategy for the treatment of cancer by inducing a more durable cell cycle exit and thus senescence. This is consistent with previous data showing that MYC inhibition induces CDK4/6i sensitivity in otherwise resistant breast cancer cells,64 and that MYC overexpression is a common mechanism mediating CDK4/6i resistance.65,66
Our study provides new insights into the irreversibility of senescence, the timing of commitment, and the molecular mechanism controlling entry and maintenance of cellular senescence. Moreover, our data provide a foundation for new intervention strategies to halt tumor initiation during early carcinogenesis and the potential to improve cancer treatment by promoting more durable responses to therapeutics.
Limitations of study
These studies delineate the molecular mechanism underlying the irreversible cell cycle exit associated with senescence. We found that MYC degradation was necessary to maintain cells in the senescent state and expressing a non-degradable MYC caused cells to start dividing again. Interestingly, spatial proteomic analysis and immunohistochemistry staining of human oral tissue sections revealed a correlation in the expression of MYC protein and the stage of the premalignant lesion, supporting our model. However, because these tissue sections are from different patients and are simply snapshots of tumor development, we cannot distinguish whether pre-cancerous cells in carcinoma in situ were previously senescent and then escaped because of failure to degrade MYC or never went senescent in the first place and therefore avoided OIS. Although either of these routes are possible, they both are consistent with our model that MYC degradation is necessary both for senescence entry and for senescence maintenance.
STAR★METHODS
RESOURCE AVAILABILITY
Lead contact
Further information and requests for resources and reagents should be directed to and will be fulfilled by the lead contact, Steven D. Cappell (steven.cappell@nih.gov).
Materials availability
This study did not generate new unique reagents.
Data and code availability
All data reported in this paper will be shared by the lead contact upon request.
All original code has been deposited at https://github.com/scappell/Cell_tracking and is publicly available as of the date of publication. DOIs are listed in the key resources table.
Any additional information required to reanalyze the data reported in this paper is available from the lead contact upon request.
KEY RESOURCES TABLE
| REAGENT or RESOURCE | SOURCE | IDENTIFIER |
|---|---|---|
| Antibodies | ||
|
| ||
| Rabbit monoclonal anti-c-Jun | Cell Signaling Technology | Cat# 9165; RRID: AB_2130165 |
| Rabbit monoclonal anti-p27 (Kip1) | Cell Signaling Technology | Cat# 3686; RRID: AB_2077850 |
| Rabbit monoclonal anti-p21 (Waf1/Cip1) | Cell Signaling Technology | Cat# 2947; RRID: AB_823586 |
| Rabbit monoclonal anti-c-MYC (for WB and IF) | Cell Signaling Technology | Cat# 5605; RRID: AB_1903938 |
| Rabbit monoclonal anti-phospho-cMYC (T58) | Cell Signaling Technology | Cat# 46650; RRID: AB_2151830 |
| Rabbit monoclonal anti-phospho-cMYC (S62) | Cell Signaling Technology | Cat# 13748; RRID: AB_2687518 |
| Rabbit monoclonal anti-C/EBPα | Cell Signaling Technology | Cat# 8178; RRID: AB_11178517 |
| Mouse monoclonal anti-p53 | Santa Cruz Biotechnology | Cat# sc-126; RRID: AB_628082 |
| Mouse monoclonal anti-β-actin | Abcam | Cat# ab6276; RRID: AB_2223210 |
| HRP-conjugated anti-rabbit IgG | Cell Signaling Technology | Cat# 7074; RRID: AB_2099233 |
| HRP-conjugated anti-mouse IgG | Cell Signaling Technology | Cat# 7076; RRID: AB_330924 |
| Rabbit monoclonal anti-c-MYC (for IHC) | Abcam | Cat# ab32072; RRID: AB_731658 |
| Rabbit monoclonal anti-phospho-Rb (Ser807/811) | Cell Signaling Technology | Cat# 8974; RRID: AB_2688037 |
| Rabbit polyclonal phospho-p44/42 MAPK (ERK1/2) (Thr202/Tyr204) | Cell Signaling Technology | Cat# 9101; RRID: AB_331646 |
| Rabbit monoclonal anti-Ki67 | Cell Signaling Technology | Cat# 9129; RRID: AB_2687446 |
| Rabbit monoclonal anti-phospho-Histone H2A.X (Ser139) | Cell Signaling Technology | Cat# 9718; RRID: AB_2118009 |
| Mouse monoclonal anti-Vinculin | Sigma-Aldrich | Cat# V9131; RRID: AB_477629 |
|
| ||
| Biological samples | ||
|
| ||
| Glass slides of oral tissue sections of premalignant and malignant lesions from adult patients | Oral pathology department, School of Dentistry, Alexandria University, Egypt |
N/A |
|
| ||
| Chemicals, peptides, and recombinant proteins | ||
|
| ||
| Trametinib | Selleckchem | Cat#: S2673; CAS: 871700-17-3 |
| Palbociclib | Selleckchem | Cat#: S1116; CAS: 827022-32-2 |
| CHIR-98014 | Selleckchem | Cat#: S2745; CAS: 252935-94-7 |
| MLN-4924 | Sigma-Aldrich | Cat#: 505477; CAS: 951950-33-7 |
| MG132 | Sigma-Aldrich | Cat#: 474790; CAS: 133407-82-6 |
| Hoechst-33343 | Thermo Scientific | Cat# 62249; CAS: 23491-52-3 |
| Doxycycline | Sigma-Aldrich | Cat#: D98910 |
| Doxorubicin hydrochloride | Sigma-Aldrich | Cat#: D1515 |
| Hydrogen peroxide 30% | Sigma-Aldrich | Cat#: H1009 |
| Puromycin | InvivoGen | Cat#: ant-pr-1 |
| Crystal Violet | Sigma-Aldrich | Cat#: C3886-25G |
| Methanol | Fisher | Cat#: A452SK-4 |
|
| ||
| Critical commercial assays | ||
|
| ||
| SPiDER-bgal kit | Dojindo | Cat# SG04-01 |
| Human Discovery Luminex Assay | R&D Systems | Cat# LXSAHM-02 |
| Human Discovery Luminex Assay | R&D Systems | Cat# LXSAHM-13 |
| Senescence β-galactosidase staining kit | Cell Signaling technology | Cat#:9860S |
| GeoMx Solid Tumor TME Morphology Kit | NanoString Technologies | Cat#: GMX-PRO-MORPH-HST-12 |
| GeoMx Seq Code Pack A&B | NanoString Technologies | GMX-NGS-SEQ-AB |
| GeoMx Mouse Protein Core for NGS | NanoString Technologies | GMX-PROCO-NGS-MCORE-12 |
| GeoMx MAPK Signaling Panel Human Protein Module for NGS | NanoString Technologies | GMX-PROMOD-NGS-HMAPK-12 |
|
| ||
| Experimental models: Cell lines | ||
|
| ||
| Human: MCF7 cells | ATCC | Cat#: HTB-22; RRID: CVCL_0031 |
| Human: U2OS cells | ATCC | Cat#: HTB-96; RRID: CVCL_0042 |
| Human: MCF10A cells | ATCC | Cat#: CRL-10317; RRID: CVCL_0598 |
| Human: CAL33 cells | DSMZ | Cat#: ACC447 RRID: CVCL_1108 |
| Human: Primary human lung fibroblasts | ATCC | Cat#: #PCS-201-013 |
|
| ||
| Oligonucleotides | ||
|
| ||
| On-Target plus control siRNA | Dharmacon | Cat#: D-001810-10-05 |
| CDKN1B siRNA (On-Target plus pooled set of four) | Dharmacon | Cat#: L-003472-00-0005 |
| CDKN1A siRNA (On-Target plus pooled set of four) | Dharmacon | Cat#: LQ-003471-00 |
| TP53 (On-Target plus pooled set of four) | Dharmacon | Cat#: L-003329-00-0005 |
| Primers for RT-PCR | see Table S2 | N/A |
|
| ||
| Recombinant DNA | ||
|
| ||
| CSII-pEF1a-H2B-mTurquoise | Spencer et al.28 | N/A |
| CSII-pEF1a-DHB(aa994-1087)-mVenus | Spencer et al.28 | N/A |
| CSII-pEF1a-DHB(aa994-1087)-mCherry | Nathans et al.67 | N/A |
| CSII-pEF1a-mCherry-Geminin(aa1-110) | Cappell et al.68 | N/A |
| pCMV(CAT)T7-SB100 | Mates et al.69 | Cat#: 34879 |
| pSBtet-MYCT58A-emiRFP | This work | N/A |
| pUltra-puro-RTTA2 | Unpublished | Gift from Yildirim Dogan and Kitai Kim Addgene #: 58750 |
| FU-tet-o-hc-MYC | Maherali et al.70 | Gift from Konrad Hochedlinger Addgene #: 19775 |
| pLV-tetO-MYC T58A | Maherali et al.70 | Gift from Konrad Hochedlinger Addgene #: 19763 |
| TRIPZ hMYC lentiviral shRNA | Dharmacon | Cat#: RHS4696-200675280 |
| TRIPZ non-silencing shRNA | Dharmacon | Cat#: RSH4743 |
|
| ||
| Software and algorithms | ||
|
| ||
| FIJI | FIJI | Version: 2.3.0/1.53f |
| MATLAB | MATHWORKS | Version: 2019B |
| MATLAB Tracking Scripts | Cappell et al.68 | N/A |
| Prism | Graphpad | Version: 9.2.0 |
| Illustrator | Adobe | Version: 26.3.1 |
| Incucyte Cell-by-Cell Analysis Software | Sartorius | Version: 9600-0031 |
| Halo imaging analysis software | Indica Labs | Version:3.3.2541.423 |
| BD FACSDiVa Software | BD Biosciences | Version: 9.0 |
| FlowJo | FlowJo | Version:10.8.01 |
| Bio-Plex Manager software | Bio-Rad | Version: 6.2 Build175 |
EXPERIMENTAL MODEL AND SUBJECT PARTICIPANT DETAILS
Human tissue samples
This study was reviewed and approved by the institute’s ethical board (IORG0008839). The cases were retrospectively retrieved between 2012 and 2019 and obtained either from incisional or excisional oral leukoplakic or erythroplakic lesion during the same period, from the files of Oral Pathology Department, Faculty of Dentistry, Alexandria University, Egypt. Clinical data, including age, sex, site, and duration were obtained from the original pathology reports and are reported in Table S1. Two independent pathologists reviewed the hematoxylin and eosin-stained specimens to confirm their diagnosis.
Cell culture
MCF7 human breast adenocarcinoma (ATCC, #HTB-22), MCF10A human mammary epithelial (ATCC, #CRL-10317), and U2OS human osteosarcoma (ATCC, #HTB-96) cell lines were used in this study. These cell lines have wild type p53 and p16 null. MCF7 and U2OS cell lines were cultured in phenol red DMEM (Invitrogen, #11–995-073) supplemented with 10% fetal bovine serum (FBS, R&D Systems, #S11150), 100 I.U./mL penicillin and 100 μg/mL streptomycin (pen-strep, Gibco, #15–140-163). MCF10A cell line was grown in phenol red free DMEM-F12 (Invitrogen, #11–039-047) supplemented with 5% horse serum (R&D Systems, #S12150), 20 ng/mL EGF (Peprotech, #AF-100–15), 10 μg/mL insulin (Sigma-Aldrich, #I1882–100MG), 500 μg/mL hydrocortisone (Sigma-Aldrich, H0888–1MG), 100 ng/mL cholera toxin (Sigma-Aldrich, C8052–1MG), 100 I.U./mL penicillin, and 100 μg/mL streptomycin (Gibco, #15–140-163). CAL33 human oral squamous cell carcinoma (DSMZ, #ACC447) cells were maintained in phenol red DMEM (Invitrogen, #11–995-073) supplemented with 10% tetracycline-tested FBS, 1% pen-strep and 2 mM GlutaMAX (Gibco, #35050061). Primary human lung fibroblasts (ATCC, #PCS-201–013) were cultured in Fibroblast Basal Medium (ATCC, # PCS-201–030) supplemented with 5 ng/mL rh FGF-b (ATCC, # PCS-999–020), 7.5 mM L-glutamine (ATCC, # PCS-999–020), 50 μg/mL ascorbic acid (ATCC, # PCS-999–006), 1 μg/mL hydrocortisone (ATCC, # PCS-999–014), 5 μg/mL rh insulin (ATCC, # PCS-999–022), and 2% FBS (ATCC, # PCS-999–010). Incubation was at 37°C and 5% CO2 for all cells. All cells were tested for mycoplasma.
Cell line generation
Cells were transduced with H2B-mTurqoise lentivirus for cell tracking, mCherry-Geminin lentivirus for measurement of anaphase promoting complex/cyclosome (APC/C) activity, a ubiquitin ligase, and either DHB-mVenus or DHB-mCherry lentivirus for measurement of CDK2 activity. Both CDK2 and APC/C activities are proxies for cell cycle progression. Cells expressing teton-shMYC were generated by transducing the cells with TRIPZ Human MYC lentiviral shRNA using a trans-lentiviral shRNA packaging kit with calcium phosphate transfection agent (Dharmacon, #TLP5912) following a previously established method.71,72 Transduced cells were sorted on a BD Biosciences FACSAria Fusion to obtain pure populations expressing the desired fluorescent reporters. Cells were transduced with teton-MYCT58A and teton-MYCWT using lentiviral packaging system and successfully transduced cells were enriched using antibiotic selection. Primary mouse fibroblasts and keratinocytes expressing teton-MYCT58A were established using a pSBtet Sleeping Beauty (SB) transposase system.73 Briefly, we cloned the MYCT58A-emiRFP gene into a modified pSBtet-BP plasmid without the BFP reporter, hereafter pSBtet-MYCT58A-emiRFP. We co-transfected the pSBtet-MYCT58A-emiRFP and the sleeping beauty transposase plasmid pCMV(CAT)T7-SB100 (10:1 ratio) cells using Lipofectamine 3000 (Invitrogen L3000015) according to the manufacturer’s instructions and selected for cells that successfully incorporated the introduced DNA using Puromycin (InvivoGen ant-pr-1). We obtained mix-populations and validated the expression of MYCT58A-emiRFP by incubating the cells with 2 μg/mL doxycycline and performing Western blotting and Live-cell imaging analyses.
METHOD DETAILS
Constructs
CSII-pEF1a-H2B-mTurquoise, CSII-pEF1a-DHB (aa994–1087)-mVenus, CSII-pEF1a-mCherry-Geminin (aa1–110) were described previously.28,68 CSII-pEF1a-DHB (aa994–1087)-mCherry was described previously.67 pUltra-puro-RTTA2 was a gift from Yildirim Dogan and Kitai Kim (Addgene plasmid #58750). FU-tet-o-hc-MYC (Teton-MYCWT) was a gift from Konrad Hochedlinger (Addgene plasmid #19775).70 pLV-tetO-MYC T58A (teton-MYCT58A) was a gift from Konrad Hochedlinger (Addgene plasmid #19763).74 TRIPZ Human MYC lentiviral shRNA and non-silencing shRNA were purchased from Dharmacon (#RHS4696–200675280 and RSH4743). pSBtet-BP was a gift from Eric Kowarz (Addgene plasmid #60496).73 The emiRFP tag was cloned from pH2B-emiRFP670, which was a gift from Vladislav Verkusha (Addgene plasmid #136571).75 pCMV(CAT)T7-SB100 was a gift from Zsuz-sanna Izsvak (Addgene plasmid # 34879).69
siRNA transfection
Cells were transfected with siRNAs using Dharmafect 1 (Horizon Discovery, Ltd, T-2001–03) according to the manufacturer’s instructions. The following siRNAs were used: On-Target plus control siRNA (nontargeting, Dharmacon, D-001810–10-05), On-Target plus pooled sets of four siRNAs were used: CDKN1B (p27, L-003472–00-0005); CDKN1A (p21, LQ-003471–00); TP53 (P5, L-003329–00-0005). All siRNAs were used at a concentration of 20 nM unless noted. Six hours post-transfection, cells were washed with full growth medium and then imaging was started 18 h later.
Drugs, inhibitors, and other treatments
Cells were treated with either vehicle (DMSO) or the following drugs/inhibitors; trametinib (MEKI; S2673, Selleckchem, USA), palbociclib (CDK4/6i; S1116, Selleckchem, USA), CHIR-98014 (GSK3βi; S2745, Selleckchem, USA), MLN-4924 (Sigma-Aldrich, USA), H2O2 (H1009, Sigma-Aldrich, USA), doxorubicin hydrochloride (D1515, Sigma-Aldrich, USA), and MG132 (Sigma-Aldrich, USA). Growth medium with or without drugs was replenished every 2–3 days. Where indicated, cells were exposed to 10–20 Gy dose of 137Cs gamma-rays (dose rate: 0.50 Gy min−1) in a Mark-1 gamma-irradiator (JL Sherpherd & Associates, San Fernando, CA). Doxycycline used to express tet-dependent constructs was purchased from Sigma-Aldrich (#D98910–1G) and used at the indicated concentration.
Senescence-associated b-galactosidase assay
Colorimetric β-galactosidase staining was done using the Senescence β-Galactosidase Staining kit (Cell Signaling Technology, CST, #9860S) and following the manufacturers protocol in 60 mm2 culture dishes. Fluorescent β-galactosidase staining was done using the SPiDER-βgal kit (Dojindo, #SG04–01) following manufacturers protocol in 24 or 96-well dishes. Colorimetric β-galactosidase staining was imaged using an EVOS FL Auto2 (Thermo Fisher Scientific) and SA-β Gal positive cells were manually counted on Fiji software (Version: 2.3.0/1.53f) blinded to the conditions.
Immunofluorescence
Cells were fixed in 4% paraformaldehyde, washed three times in PBS, blocked and permeabilized for 1 h at room temperature with PBS containing 10% FBS, 1% bovine serum albumin, 0.1% Triton, and 0.01% sodium azide, and stained overnight at 4°C with anti-phospho-Rb (807/811) (CST, #8974), anti-phospho-p44/42 MAPK (Erk1/2, Thr202/Tyr204) (CST, #9101), anti-Ki67 (D3B5, CST, #19129), anti-c-MYC (D84C12, CST, #5605), and anti-phospho-Histone H2A.X (S139, CST, #9718). Hoechst 33343 (Thermo Scientific 62249) was used to stain the nuclei. Unconjugated primary antibodies were visualized using a secondary fluorescent antibody and cells were imaged at the corresponding filters.
Time-lapse microscopy
Cells were plated 24 h prior to imaging in full growth media in a 96-well dish (Ibidi, #89626) such that the density would remain sub-confluent until the end of the imaging period. Time-lapse imaging was performed in 300 μL full growth media. Images were taken in CFP, YFP, and RFP channels every 12 min on a Nikon Ti2-E inverted microscope with a 20X 0.45NA objective. Total light exposure time was kept under 600 msec for each time point. Cells were imaged in a humidified, 37°C chamber in 5% CO2.
For cell confluence measurements, cells were plated 24 h prior to imaging in full growth media in a 6-well dish. Time-lapse imaging in the brightfield channel was done using the S3 Incucyte Analyzer (Sartorius) and the cell confluence was quantified using the Incucyte software.
Flow cytometry
Indicated cells were stained for fluorescent β-galactosidase using the SPiDER-βgal kit (Dojindo, #SG04–01) following the manufacturer’s protocol. After which, the cells were trypsinized, fixed in 4% paraformaldehyde for 10 min at room temperature, washed 3 times in PBS supplemented with 2% FBS, then permeabilized by adding ice-cold 100% methanol for 30 min on ice. Cells were washed and stained with anti-phospho-Rb (807/811) (CST, #8974) diluted in the same PBS buffer for 1 h at room temperature. Cells were then stained with Hoechst 33343 (Thermo Scientific, 62249) and analyzed using an LSR Fortessa SORP I cytometer (BD Biosciences).
Quantifying cytokines and growth factors
Conditioned media from indicated cells were collected, and the cells were trypsinized and counted using a Cytometer (Nexcelom Biosciences). Media samples were then normalized based on cell number by diluting with culture media. Aliquots (50 μL) of the conditioned media were used for quantification using the Bio-Plex 200 system according to manufacturer’s protocol (Bio-Rad, CA, USA). The human Discovery Luminex assay kit was purchased from R&D systems (#LXSAHM-13 and LXSAHM-02).
Immunoblotting
Cell lysis was performed using cell lysis buffer (50 mM Tris (pH 7.4), 200 mM NaCl, 50 mM NaF, 1 mM Na3VO4, 0.5% Triton X-100) supplemented with protease inhibitors (Omplete, EDTA-free Protease Inhibitor Cocktail, Roche). Protein concentration was determined using a Pierce BCA Protein Assay Kit (Thermo Scientific 23225). Proteins were separated by SDS-PAGE (Bio-Rad) and transferred to polyvinylidene difluoride (PVDF) membranes (Millipore) using the Bio-Rad Trans-blot Turbo transfer system. Membranes were then blocked in either 5% skimmed milk (Bio-Rad), or 3% BSA (Sigma-Aldrich) in TBS/Tween (0.1%). Membranes were immunoblotted with antibodies against c-Jun (9165), p27Kip1 (3686), p21 Waf1/Cip1 (2947), c-MYC (5605), p-cMYC T58 (46650), p-cMYC S62 (13748), C/EBPα (D56F10) (8178) from Cell Signaling Technology, p53 (sc-126) from Santa Cruz, and β-Actin (ab6276), from abcam in blocking buffer at 4°C overnight. After primary antibody incubation, membranes were washed using TBS/Tween and incubated with an HRP-conjugated anti-rabbit IgG (7074) or anti-mouse IgG (7076) secondary antibody (1:10,000) from Cell Signaling Technology and imaged using the SuperSignal West Femto Maximum Sensitivity Substrate (Thermo Scientific 34095) on a Bio-Rad ChemiDoc apparatus. The images were then processed using Image Lab (Bio-Rad). Western blot quantification was also conducted using Image Lab software by manually detecting lanes and bands. The total band volumes for MYC were then extracted and first normalized to the loading control (actin), and then normalized to the untreated DMSO condition within the same membrane. Statistical analyses were conducted in Prism (GraphPad Software).
qRT-PCR
RNA was isolated from cultured cells using RLT RNeasy 96 Qiacube HT Kit (Qiagen, 74171) and on-column DNA digest (Qiagen, 79254). The concentration of RNA was determined using a NanoDrop. Complementary DNA synthesis was done using iScript cDNA synthesis kit (Bio-Rad) according to the manufacturer’s protocol. Real-time PCR analyses were conducted was conducted using iQ SYBR Green supermix (Biorad). GAPDH was used as an internal control. Relative expression was calculated based on the threshold cycle with the different efficiency of each primer by the 2−ΔΔCT (‘‘delta-delta CT’’) method. A list of primers used can be found in Table S2. All primers were purchased from Integrated DNA Technologies (IDT).
Immunohistochemistry of tissue sections
Immunohistochemistry (IHC) staining was performed on 4 μm thick formalin fixed paraffin embedded sections of oral mucosal lesions on Leica Biosystem’s BondRX autostainer with the following conditions: Epitope Retrieval 1 (Citrate) 20′ for c-MYC sections, Epitope Retrieval 2 (EDTA) 20′ for c-MYC sections, c-MYC (abcam #ab32072, 1:40 incubated 30′), and the Bond Polymer Refine Detection Kit (LeicaBiosystems #DS9800). Rabbit monoclonal isotype control reagent (Cell Signaling Technology, #3900) was used in place of primary antibodies for negative controls. Slides were removed from the Bond autostainer, dehydrated through ethanol, cleared with xylenes, and cover slipped.
H&E and IHC slides were scanned at 20× using an Aperio AT2 scanner (Leica Biosystems, Buffalo Grove, IL) into whole slide digital images. All image analysis was performed using HALO imaging analysis software (v3.3.2541.423; Indica Labs), and image annotations were performed by one pathologist. We used the HALO cytonuclear (V2.0.9) algorithm to quantify the percentage of c-MYC-positive nuclei. The HALO Nuclei Seg classifier was used to segment and measure nuclei. The HALO tissue DenseNet AI was used to choose the epithelial cells and to exclude stroma. Areas with artifacts, such as folds and tears, were also excluded from the analysis.
Image analysis
All image analyses were performed with custom MATLAB scripts as previously described.63 Briefly, optical illumination bias was empirically derived by sampling background areas across all wells in an imaging session and subsequently used to flatten all images. This enabled measurement and subtraction of a global background for each image. Cells were segmented for their nuclei based on either Hoechst staining (fixed-cell imaging) or H2B-mTurquoise (live-cell imaging). To measure CDK2 activity the cytoplasm was sampled by expanding a ring outside the nucleus (with inner radius of 0.65 μm and outer radius of 3.25 μm) without overlapping with cytoplasm from a neighboring cell. Nuclear immunofluorescence, nuclear DHB-mVenus, nuclear DHB-mCherry, and mCherry-Geminin signals were calculated as median nuclear intensity, as these signals were often excluded from the nucleoli. Cytoplasmic DHB-mVenus or DHB-mCherry signals were calculated as the median intensity within the cytoplasmic ring, excluding pixel intensities indistinguishable from background. Whole-cell fluorescent SA β-Gal measurements were made by generating a whole-cell mask by expanding the nucleus mask up to 3x the nucleus radius using the MATLAB function bwmorph and quantifying the total fluorescence intensity within this mask. Quantification of mCherry-Geminin signals were used, together with CDK2 activity, to categorize cell fates (Figures 3D and 3E).
GeoMx digital spatial profiling (DSP)
Whole-slide tissue sections were profiled using the commercial GeoMx DSP platform (NanoString Technologies).76 See Figure S8A for a schematic of the workflow. The formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded tissue blocks were cut at 5 μm thickness onto positively charged slides. After baking at 60°C for 60 min, deparaffinization and antigen retrieval was performed on Leica BOND RX autostainer using HIER1 (citrate based) for 20 min. Tissue morphology was visualized using Syto13, pancytokeratin, and CD45 fluorescent immunostaining and was used to identify regions of interest (ROIs). ROIs (total of 381 from 8 tissues) were selected in either normal, mild dysplasia, carcinoma in situ, or OSCC areas based on tissue architecture and cell morphology – mainly pancytokeratin, using polygonal shapes without masking. DSP Human Protein Core and MAPK signaling panels were assessed using an NGS-based readout. Oligonucleotide barcodes from each ROI were then UV-photocleaved, collected, followed by library preparation as recommended by the NanoString GeoMx protocol. Sequencing was performed on Novaseq 6000 using S1 flow cell kit (27 × 27 and index 8 × 8).
GeoMX proteomic analysis
Digital spatial proteomic profiling data were analyzed using the toolset in DSP analysis suite ver 2.4. The data were normalized to IgG isotype controls per ROI to account for differences in staining efficiency, background signal, cellularity, and size of ROIs. GAPDH, Histone H3 and S6 were used as internal control. Digital Count Conversion files, including expression counts, probe assay metadata, and annotation information were processed using the Nanostring GeoMx analysis suite.
In vitro oncogene induced senescence (OIS)
Primary mouse keratinocytes isolated from newborn C57BL/6J pups were cultured in modified Eagle’s medium (S-MEM, Lonza), 8% Chelex-treated fetal calf serum (Gemini Bio Products), and 0.05 mmol/L calcium unless otherwise specified.77 To induce OIS, cultured primary keratinocytes were transduced with v-RasHa retrovirus (referred to as RAS) on Day 2 at a multiplicity of infection (MOI) of 1 in medium containing polybrene (4 μg/mL; Sigma-Aldrich). The v-RasHa replication-defective ectopic retrovirus was prepared using Psi2 producer cells; retrovirus titers were routinely 1 × 107 virus/ml78 These cells were transfected with teton-MYCT58A two days after V-RAS transduction as described in Cell line generation. Similarly as above, primary mouse dermal fibroblasts were isolated and cultured in phenol red DMEM (Invitrogen, #11–995-073) supplemented with 10% fetal bovine serum (FBS, R&D Systems, #S11150), 100 I.U./mL penicillin and 100 μg/mL streptomycin (pen-strep, Gibco, #15–140-163). OIS was induced as described above.
In vitro replicative senescence
Primary mouse fibroblasts, acquired and cultured as noted previously and transfected with teton-MYCT58A at passage 2–3, were grown for 7–9 passages until cells were observed to enter replicative senescence.
Survival assay
Primary mouse cells were cultured as mentioned above. Mouse keratinocytes or fibroblasts were seeded and transduced with v-RasHa retrovirus as noted above. Once senescent (9–11 days post-Ras), they were either treated or not with Dox to induce MYCT58A expression and grown for 19–21 more days. Cells were then washed once with PBS and incubated in cold methanol (−20°C) for 1 min. The methanol was removed, and cells were incubated with a Crystal Violet solution (0.5% wt/vl Crystal Violet (Sigma-Aldrich C3886), 20% methanol (Fisher A452SK-4)) at room temperature overnight. The plates were then washed using distilled H2O until the water was clear and dried. Images were acquired using the Bio-Rad ChemiDoc imager and cropped in Adobe Illustrator.
QUANTIFICATION AND STATISTICAL ANALYSIS
Statistical analyses were performed in MATLAB (Mathworks) and Prism (GraphPad Software). Details about specific statistical tests can be found in the Figure legends.
Supplementary Material
Highlights.
The probability of cells irreversibly committing to senescence increases over time
Irreversible cell cycle exit is mediated by constitutive MYC loss
Expressing non-degradable MYC allows senescent cells to start dividing again
Oral premalignant lesions bypass oncogene-induced senescence by overexpressing MYC
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
We thank David Levens for helpful discussions and critical reading of the manuscript. We thank Brandi Carofino and Christina Ross for critical reading of the manuscript. We thank the department of Oral Pathology, Faculty of Dentistry, Alexandria University in Egypt, for providing the paraffin-embedded human tissue samples. We also thank the Flow Cytometry Core Facility of the Center for Cancer Research at the National Cancer Institute (NCI) for technical support, and all the members of the Cappell Lab for helpful comments and support. This research was supported by the European Molecular Biology Organization (grant ALTF 247-2022 to A.C.) and the National Institutes of Health Intramural Research Program (grant ZIA BC 011832 to S.D.C.).
Footnotes
SUPPLEMENTAL INFORMATION
Supplemental information can be found online at https://doi.org/10.1016/j.celrep.2023.113079.
DECLARATION OF INTERESTS
The authors declare no competing interests.
REFERENCES
- 1.Di Leonardo A, Linke SP, Clarkin K, and Wahl GM (1994). DNA damage triggers a prolonged p53-dependent G1 arrest and long-term induction of Cip1 in normal human fibroblasts. Genes Dev. 8, 2540–2551. 10.1101/gad.8.21.2540. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Sedelnikova OA, Horikawa I, Zimonjic DB, Popescu NC, Bonner WM, and Barrett JC (2004). Senescing human cells and ageing mice accumulate DNA lesions with unrepairable double-strand breaks. Nat. Cell Biol 6, 168–170. 10.1038/ncb1095. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Hayflick L, and Moorhead PS (1961). The serial cultivation of human diploid cell strains. Exp. Cell Res 25, 585–621. 10.1016/0014-4827(61)90192-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Bodnar AG, Ouellette M, Frolkis M, Holt SE, Chiu CP, Morin GB, Harley CB, Shay JW, Lichtsteiner S, and Wright WE (1998). Extension of life-span by introduction of telomerase into normal human cells. Science 279, 349–352. 10.1126/science.279.5349.349. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Collado M, Blasco MA, and Serrano M. (2007). Cellular senescence in cancer and aging. Cell 130, 223–233. 10.1016/j.cell.2007.07.003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Coppé JP, Desprez PY, Krtolica A, and Campisi J. (2010). The senescence-associated secretory phenotype: the dark side of tumor suppression. Annu. Rev. Pathol 5, 99–118. 10.1146/annurevpathol-121808-102144. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Neurohr GE, Terry RL, Lengefeld J, Bonney M, Brittingham GP, Moretto F, Miettinen TP, Vaites LP, Soares LM, Paulo JA, et al. (2019). Excessive Cell Growth Causes Cytoplasm Dilution And Contributes to Senescence. Cell 176, 1083–1097.e18, e1018. 10.1016/j.cell.2019.01.018. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Narita M, Nuñez S, Heard E, Narita M, Lin AW, Hearn SA, Spector DL, Hannon GJ, and Lowe SW (2003). Rb-mediated heterochromatin formation and silencing of E2F target genes during cellular senescence. Cell 113, 703–716. 10.1016/s0092-8674(03)00401-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Dimri GP, Lee X, Basile G, Acosta M, Scott G, Roskelley C, Medrano EE, Linskens M, Rubelj I, Pereira-Smith O, et al. (1995). A biomarker that identifies senescent human cells in culture and in aging skin in vivo. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 92, 9363–9367. 10.1073/pnas.92.20.9363. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Sharpless NE, and Sherr CJ (2015). Forging a signature of in vivo senescence. Nat. Rev. Cancer 15, 397–408. 10.1038/nrc3960. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Gorgoulis V, Adams PD, Alimonti A, Bennett DC, Bischof O, Bishop C, Campisi J, Collado M, Evangelou K, Ferbeyre G, et al. (2019). Cellular Senescence: Defining a Path Forward. Cell 179, 813–827. 10.1016/j.cell.2019.10.005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Baker DJ, Jeganathan KB, Cameron JD, Thompson M, Juneja S, Kopecka A, Kumar R, Jenkins RB, de Groen PC, Roche P, and van Deursen JM (2004). BubR1 insufficiency causes early onset of aging-associated phenotypes and infertility in mice. Nat. Genet 36, 744–749. 10.1038/ng1382. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Baker DJ, Wijshake T, Tchkonia T, LeBrasseur NK, Childs BG, van de Sluis B, Kirkland JL, and van Deursen JM (2011). Clearance of p16Ink4a-positive senescent cells delays ageing-associated disorders. Nature 479, 232–236. 10.1038/nature10600. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Jun JI, and Lau LF (2010). Cellular senescence controls fibrosis in wound healing. Aging (Albany NY) 2, 627–631. 10.18632/aging.100201. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Muñoz-Espıń D, Cañamero M, Maraver A, Gómez-López G, Contreras J, Murillo-Cuesta S, Rodríguez-Baeza A, Varela-Nieto I, Ruberte J, Collado M, and Serrano M. (2013). Programmed cell senescence during mammalian embryonic development. Cell 155, 1104–1118. 10.1016/j.cell.2013.10.019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Storer M, Mas A, Robert-Moreno A, Pecoraro M, Ortells MC, DiGiacomo V, Yosef R, Pilpel N, Krizhanovsky V, Sharpe J, and Keyes WM (2013). Senescence is a developmental mechanism that contributes to embryonic growth and patterning. Cell 155, 1119–1130. 10.1016/j.cell.2013.10.041. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Schmitt CA, Fridman JS, Yang M, Lee S, Baranov E, Hoffman RM, and Lowe SW (2002). A senescence program controlled by p53 and p16INK4a contributes to the outcome of cancer therapy. Cell 109, 335–346. 10.1016/s0092-8674(02)00734-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Petrova NV, Velichko AK, Razin SV, and Kantidze OL (2016). Small molecule compounds that induce cellular senescence. Aging Cell 15, 999–1017. 10.1111/acel.12518. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Vilgelm AE, Johnson CA, Prasad N, Yang J, Chen SC, Ayers GD, Pawlikowski JS, Raman D, Sosman JA, Kelley M, et al. (2016). Connecting the Dots: Therapy-Induced Senescence and a Tumor-Suppressive Immune Microenvironment. J. Natl. Cancer Inst 108, djv406. 10.1093/jnci/djv406. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Tao YF, Wang NN, Xu LX, Li ZH, Li XL, Xu YY, Fang F, Li M, Qian GH, Li YH, et al. (2017). Molecular mechanism of G1 arrest and cellular senescence induced by LEE011, a novel CDK4/CDK6 inhibitor, in leukemia cells. Cancer Cell Int. 17, 35. 10.1186/s12935-017-0405-y. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Ruscetti M, Morris JP 4th, Mezzadra R, Russell J, Leibold J, Romesser PB, Simon J, Kulick A, Ho YJ, Fennell M, et al. (2020). Senescence-Induced Vascular Remodeling Creates Therapeutic Vulnerabilities in Pancreas Cancer. Cell 181, 424–441.e21. 10.1016/j.cell.2020.03.008. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Prasanna PG, Citrin DE, Hildesheim J, Ahmed MM, Venkatachalam S, Riscuta G, Xi D, Zheng G, Deursen JV, Goronzy J, et al. (2021). Therapy-Induced Senescence: Opportunities to Improve Anti-cancer Therapy. J. Natl. Cancer Inst 113, 1285–1298. 10.1093/jnci/djab064. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Ewald JA, Desotelle JA, Wilding G, and Jarrard DF (2010). Therapy-induced senescence in cancer. J. Natl. Cancer Inst 102, 1536–1546. 10.1093/jnci/djq364. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Pearson M, Carbone R, Sebastiani C, Cioce M, Fagioli M, Saito S, Higashimoto Y, Appella E, Minucci S, Pandolfi PP, and Pelicci PG (2000). PML regulates p53 acetylation and premature senescence induced by oncogenic Ras. Nature 406, 207–210. 10.1038/35018127. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Paramio JM, Segrelles C, Ruiz S, Martin-Caballero J, Page A, Martinez J, Serrano M, and Jorcano JL (2001). The ink4a/arf tumor suppressors cooperate with p21cip1/waf in the processes of mouse epidermal differentiation, senescence, and carcinogenesis. J. Biol. Chem 276, 44203–44211. 10.1074/jbc.M105650200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Yao G, Lee TJ, Mori S, Nevins JR, and You L. (2008). A bistable Rb-E2F switch underlies the restriction point. Nat. Cell Biol 10, 476–482. 10.1038/ncb1711. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Korotchkina LG, Demidenko ZN, Gudkov AV, and Blagosklonny MV (2009). Cellular quiescence caused by the Mdm2 inhibitor nutlin-3A. Cell Cycle 8, 3777–3781. 10.4161/cc.8.22.10121. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Spencer SL, Cappell SD, Tsai FC, Overton KW, Wang CL, andMeyer T. (2013). The proliferation-quiescence decision is controlled by a bifurcation in CDK2 activity at mitotic exit. Cell 155, 369–383. 10.1016/j.cell.2013.08.062. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Campisi J, and d’Adda di Fagagna F. (2007). Cellular senescence: when bad things happen to good cells. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol 8, 729–740. 10.1038/nrm2233. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Lee S, and Schmitt CA (2019). The dynamic nature of senescence in cancer. Nat. Cell Biol 21, 94–101. 10.1038/s41556-018-0249-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Ruscetti M, Leibold J, Bott MJ, Fennell M, Kulick A, Salgado NR, Chen CC, Ho YJ, Sanchez-Rivera FJ, Feucht J, et al. (2018). NK cell-mediated cytotoxicity contributes to tumor control by a cytostatic drug combination. Science 362, 1416–1422. 10.1126/science.aas9090. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Alessio N, Del Gaudio S, Capasso S, Di Bernardo G, Cappabianca S, Cipollaro M, Peluso G, and Galderisi U. (2015). Low dose radiation induced senescence of human mesenchymal stromal cells and impaired the autophagy process. Oncotarget 6, 8155–8166. 10.18632/oncotarget.2692. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Fletcher-Sananikone E, Kanji S, Tomimatsu N, Di Cristofaro LFM, Kollipara RK, Saha D, Floyd JR, Sung P, Hromas R, Burns TC, et al. (2021). Elimination of Radiation-Induced Senescence in the Brain Tumor Microenvironment Attenuates Glioblastoma Recurrence. Cancer Res. 81, 5935–5947. 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-21-0752. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Liao EC, Hsu YT, Chuah QY, Lee YJ, Hu JY, Huang TC, Yang PM, and Chiu SJ (2014). Radiation induces senescence and a bystander effect through metabolic alterations. Cell Death Dis. 5, e1255. 10.1038/cddis.2014.220. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Sherr CJ, and Roberts JM (1999). CDK inhibitors: positive and negative regulators of G1-phase progression. Genes Dev. 13, 1501–1512. 10.1101/gad.13.12.1501. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Heldt FS, Barr AR, Cooper S, Bakal C, and Nová k B. (2018). A comprehensive model for the proliferation-quiescence decision in response to endogenous DNA damage in human cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 115, 2532–2537. 10.1073/pnas.1715345115. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Itahana K, Dimri GP, Hara E, Itahana Y, Zou Y, Desprez PY, and Campisi J. (2002). A role for p53 in maintaining and establishing the quiescence growth arrest in human cells. J. Biol. Chem 277, 18206–18214. 10.1074/jbc.M201028200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Reyes J, Chen JY, Stewart-Ornstein J, Karhohs KW, Mock CS, and Lahav G. (2018). Fluctuations in p53 Signaling Allow Escape from Cell-Cycle Arrest. Mol. Cell 71, 581–591.e5. 10.1016/j.molcel.2018.06.031. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Collins NL, Reginato MJ, Paulus JK, Sgroi DC, Labaer J, and Brugge JS (2005). G1/S cell cycle arrest provides anoikis resistance through Erk-mediated Bim suppression. Mol. Cell Biol 25, 5282–5291. 10.1128/MCB.25.12.5282-5291.2005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Jönsson G, Staaf J, Olsson E, Heidenblad M, Vallon-Christersson J, Osoegawa K, de Jong P, Oredsson S, Ringnér M, Höglund M, and Borg A. (2007). High-resolution genomic profiles of breast cancer cell lines assessed by tiling BAC array comparative genomic hybridization. Genes Chromosomes Cancer 46, 543–558. 10.1002/gcc.20438. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Martínez-Zamudio RI, Roux PF, de Freitas JANLF, Robinson L, Doré G, Sun B, Belenki D, Milanovic M, Herbig U, Schmitt CA, et al. (2020). AP-1 imprints a reversible transcriptional programme of senescent cells. Nat. Cell Biol 22, 842–855. 10.1038/s41556-020-0529-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Jing X, Sun W, Yang X, Huang H, Wang P, Luo Q, Xia S, Fang C,Zhang Q, Guo J, and Xu Z. (2022). CCAAT/enhancer-binding protein (C/EBP) homologous protein promotes alveolar epithelial cell senescence via the nuclear factor-kappa B pathway in pulmonary fibrosis. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol 143, 106142. 10.1016/j.biocel.2021.106142. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Timchenko NA, Wilde M, Nakanishi M, Smith JR, and Darlington GJ (1996). CCAAT/enhancer-binding protein alpha (C/EBP alpha) inhibits cell proliferation through the p21 (WAF-1/CIP-1/SDI-1) protein. Genes Dev. 10, 804–815. 10.1101/gad.10.7.804. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Deschênes-Simard X, Gaumont-Leclerc MF, Bourdeau V, Lessard F, Moiseeva O, Forest V, Igelmann S, Mallette FA, Saba-El-Leil MK, Meloche S, et al. (2013). Tumor suppressor activity of the ERK/MAPK pathway by promoting selective protein degradation. Genes Dev. 27, 900–915. 10.1101/gad.203984.112. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Hayes TK, Neel NF, Hu C, Gautam P, Chenard M, Long B, Aziz M, Kassner M, Bryant KL, Pierobon M, et al. (2016). Long-Term ERK Inhibition in KRAS-Mutant Pancreatic Cancer Is Associated with MYC Degradation and Senescence-like Growth Suppression. Cancer Cell 29, 75–89. 10.1016/j.ccell.2015.11.011. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Nie Z, Hu G, Wei G, Cui K, Yamane A, Resch W, Wang R, Green DR, Tessarollo L, Casellas R, et al. (2012). c-Myc is a universal amplifier of expressed genes in lymphocytes and embryonic stem cells. Cell 151, 68–79. 10.1016/j.cell.2012.08.033. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Wasylishen AR, and Penn LZ (2010). Myc: the beauty and the beast. Genes Cancer 1, 532–541. 10.1177/1947601910378024. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Sears RC (2004). The life cycle of C-myc: from synthesis to degradation. Cell Cycle 3, 1133–1137. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Cheng M, Olivier P, Diehl JA, Fero M, Roussel MF, Roberts JM,and Sherr CJ (1999). The p21(Cip1) and p27(Kip1) CDK ‘inhibitors’ are essential activators of cyclin D-dependent kinases in murine fibroblasts. EMBO J 18, 1571–1583. 10.1093/emboj/18.6.1571. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Sears R, Nuckolls F, Haura E, Taya Y, Tamai K, and Nevins JR(2000). Multiple Ras-dependent phosphorylation pathways regulate Myc protein stability. Genes Dev. 14, 2501–2514. 10.1101/gad.836800. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Welcker M, Orian A, Jin J, Grim JE, Harper JW, Eisenman RN,and Clurman BE (2004). The Fbw7 tumor suppressor regulates glycogen synthase kinase 3 phosphorylation-dependent c-Myc protein degradation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 101, 9085–9090. 10.1073/pnas.0402770101. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Yada M, Hatakeyama S, Kamura T, Nishiyama M, Tsunematsu R, Imaki H, Ishida N, Okumura F, Nakayama K, and Nakayama KI (2004). Phosphorylation-dependent degradation of c-Myc is mediated by the F-box protein Fbw7. EMBO J 23, 2116–2125. 10.1038/sj.emboj.7600217. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Braig M, Lee S, Loddenkemper C, Rudolph C, Peters AHFM, Schlegelberger B, Stein H, Dörken B, Jenuwein T, and Schmitt CA (2005). Oncogene-induced senescence as an initial barrier in lymphoma development. Nature 436, 660–665. 10.1038/nature03841. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Collado M, Gil J, Efeyan A, Guerra C, Schuhmacher AJ, Barradas M, Benguría A, Zaballos A, Flores JM, Barbacid M, et al. (2005). Tumour biology: senescence in premalignant tumours. Nature 436, 642. 10.1038/436642a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Sarkisian CJ, Keister BA, Stairs DB, Boxer RB, Moody SE, and Chodosh LA (2007). Dose-dependent oncogene-induced senescence in vivo and its evasion during mammary tumorigenesis. Nat. Cell Biol 9, 493–505. 10.1038/ncb1567. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Xu Y, Li N, Xiang R, and Sun P. (2014). Emerging roles of the p38 MAPK and PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathways in oncogene-induced senescence. Trends Biochem. Sci 39, 268–276. 10.1016/j.tibs.2014.04.004. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Debacq-Chainiaux F, Boilan E, Dedessus Le Moutier J, Weemaels G, and Toussaint O. (2010). p38(MAPK) in the senescence of human and murine fibroblasts. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol 694, 126–137. 10.1007/978-1-4419-7002-2_10. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Freund A, Patil CK, and Campisi J. (2011). p38MAPK is a novel DNA damage response-independent regulator of the senescence-associated secretory phenotype. EMBO J 30, 1536–1548. 10.1038/emboj.2011.69. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Gale N, Michaels L, Luzar B, Poljak M, Zidar N, Fischinger J, and Cardesa A. (2009). Current review on squamous intraepithelial lesions of the larynx. Histopathology 54, 639–656. 10.1111/j.1365-2559.2008.03111.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60.Ranganathan K, and Kavitha L. (2019). Oral epithelial dysplasia: Classifications and clinical relevance in risk assessment of oral potentially malignant disorders. J. Oral Maxillofac. Pathol 23, 19–27. 10.4103/jomfp.JOMFP_13_19. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61.Valenzuela CA, Vargas L, Martinez V, Bravo S, and Brown NE(2017). Palbociclib-induced autophagy and senescence in gastric cancer cells. Exp. Cell Res 360, 390–396. 10.1016/j.yexcr.2017.09.031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62.Crozier L, Foy R, Mouery BL, Whitaker RH, Corno A, Spanos C,Ly T, Gowen Cook J, and Saurin AT (2022). CDK4/6 inhibitors induce replication stress to cause long-term cell cycle withdrawal. The EMBO journal 41, e108599. 10.15252/embj.2021108599. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 63.Wang B, Varela-Eirin M, Brandenburg SM, Hernandez-Segura A, vanVliet T, Jongbloed EM, Wilting SM, Ohtani N, Jager A, and Demaria M. (2022). Pharmacological CDK4/6 inhibition reveals a p53-dependent senescent state with restricted toxicity. EMBO J 41, e108946. 10.15252/embj.2021108946. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 64.Ji W, Zhang W, Wang X, Shi Y, Yang F, Xie H, Zhou W, Wang S, and Guan X. (2020). c-myc regulates the sensitivity of breast cancer cells to palbociclib via c-myc/miR-29b-3p/CDK6 axis. Cell Death Dis. 11, 760. 10.1038/s41419-020-02980-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 65.Pandey K, Park N, Park KS, Hur J, Cho YB, Kang M, An HJ, Kim S, Hwang S, and Moon YW (2020). Combined CDK2 and CDK4/6 Inhibition Overcomes Palbociclib Resistance in Breast Cancer by Enhancing Senescence. Cancers 12, 3566. 10.3390/cancers12123566. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 66.Liu C, Konagaya Y, Chung M, Daigh LH, Fan Y, Yang HW, Terai K, Matsuda M, and Meyer T. (2020). Altered G1 signaling order and commitment point in cells proliferating without CDK4/6 activity. Nat. Commun 11, 5305. 10.1038/s41467-020-18966-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 67.Nathans JF, Cornwell JA, Afifi MM, Paul D, and Cappell SD (2021). Cell cycle inertia underlies a bifurcation in cell fates after DNA damage. Sci. Adv 7, eabe3882. 10.1126/sciadv.abe3882. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 68.Cappell SD, Chung M, Jaimovich A, Spencer SL, and Meyer T. (2016). Irreversible APC(Cdh1) Inactivation Underlies the Point of No Return for Cell-Cycle Entry. Cell 166, 167–180. 10.1016/j.cell.2016.05.077. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 69.Mátés L, Chuah MKL, Belay E, Jerchow B, Manoj N, Acosta-Sanchez A, Grzela DP, Schmitt A, Becker K, Matrai J, et al. (2009). Molecular evolution of a novel hyperactive Sleeping Beauty transposase enables robust stable gene transfer in vertebrates. Nat. Genet 41, 753–761. 10.1038/ng.343. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 70.Maherali N, Ahfeldt T, Rigamonti A, Utikal J, Cowan C, and Hochedlinger K. (2008). A high-efficiency system for the generation and study of human induced pluripotent stem cells. Cell Stem Cell 3, 340–345. 10.1016/j.stem.2008.08.003. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 71.Kappes JC, Wu X, and Wakefield JK (2003). Production of trans-lentiviral vector with predictable safety. Methods Mol. Med 76, 449–465. 10.1385/1-59259-304-6:449. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 72.Naldini L, Blömer U, Gallay P, Ory D, Mulligan R, Gage FH, Verma IM, and Trono D. (1996). In vivo gene delivery and stable transduction of nondividing cells by a lentiviral vector. Science 272, 263–267. 10.1126/science.272.5259.263. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 73.Kowarz E, Löscher D, and Marschalek R. (2015). Optimized Sleeping Beauty transposons rapidly generate stable transgenic cell lines. Biotechnol. J 10, 647–653. 10.1002/biot.201400821. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 74.Stadtfeld M, Maherali N, Breault DT, and Hochedlinger K. (2008). Defining molecular cornerstones during fibroblast to iPS cell reprogramming in mouse. Cell Stem Cell 2, 230–240. 10.1016/j.stem.2008.02.001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 75.Matlashov ME, Shcherbakova DM, Alvelid J, Baloban M, Pennacchietti F, Shemetov AA, Testa I, and Verkhusha VV (2020). A set of monomeric near-infrared fluorescent proteins for multicolor imaging across scales. Nat. Commun 11, 239. 10.1038/s41467-019-13897-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 76.Merritt CR, Ong GT, Church SE, Barker K, Danaher P, Geiss G,Hoang M, Jung J, Liang Y, McKay-Fleisch J, et al. (2020). Multiplex digital spatial profiling of proteins and RNA in fixed tissue. Nat. Biotechnol 38, 586–599. 10.1038/s41587-020-0472-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 77.Lichti U, Anders J, and Yuspa SH (2008). Isolation and short-term culture of primary keratinocytes, hair follicle populations and dermal cells from newborn mice and keratinocytes from adult mice for in vitro analysis and for grafting to immunodeficient mice. Nat. Protoc 3, 799–810. 10.1038/nprot.2008.50. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 78.Cataisson C, Ohman R, Patel G, Pearson A, Tsien M, Jay S, Wright L, Hennings H, and Yuspa SH (2009). Inducible cutaneous inflammation reveals a protumorigenic role for keratinocyte CXCR2 in skin carcinogenesis. Cancer Res. 69, 319–328. 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-08-2490. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Data Availability Statement
All data reported in this paper will be shared by the lead contact upon request.
All original code has been deposited at https://github.com/scappell/Cell_tracking and is publicly available as of the date of publication. DOIs are listed in the key resources table.
Any additional information required to reanalyze the data reported in this paper is available from the lead contact upon request.
KEY RESOURCES TABLE
| REAGENT or RESOURCE | SOURCE | IDENTIFIER |
|---|---|---|
| Antibodies | ||
|
| ||
| Rabbit monoclonal anti-c-Jun | Cell Signaling Technology | Cat# 9165; RRID: AB_2130165 |
| Rabbit monoclonal anti-p27 (Kip1) | Cell Signaling Technology | Cat# 3686; RRID: AB_2077850 |
| Rabbit monoclonal anti-p21 (Waf1/Cip1) | Cell Signaling Technology | Cat# 2947; RRID: AB_823586 |
| Rabbit monoclonal anti-c-MYC (for WB and IF) | Cell Signaling Technology | Cat# 5605; RRID: AB_1903938 |
| Rabbit monoclonal anti-phospho-cMYC (T58) | Cell Signaling Technology | Cat# 46650; RRID: AB_2151830 |
| Rabbit monoclonal anti-phospho-cMYC (S62) | Cell Signaling Technology | Cat# 13748; RRID: AB_2687518 |
| Rabbit monoclonal anti-C/EBPα | Cell Signaling Technology | Cat# 8178; RRID: AB_11178517 |
| Mouse monoclonal anti-p53 | Santa Cruz Biotechnology | Cat# sc-126; RRID: AB_628082 |
| Mouse monoclonal anti-β-actin | Abcam | Cat# ab6276; RRID: AB_2223210 |
| HRP-conjugated anti-rabbit IgG | Cell Signaling Technology | Cat# 7074; RRID: AB_2099233 |
| HRP-conjugated anti-mouse IgG | Cell Signaling Technology | Cat# 7076; RRID: AB_330924 |
| Rabbit monoclonal anti-c-MYC (for IHC) | Abcam | Cat# ab32072; RRID: AB_731658 |
| Rabbit monoclonal anti-phospho-Rb (Ser807/811) | Cell Signaling Technology | Cat# 8974; RRID: AB_2688037 |
| Rabbit polyclonal phospho-p44/42 MAPK (ERK1/2) (Thr202/Tyr204) | Cell Signaling Technology | Cat# 9101; RRID: AB_331646 |
| Rabbit monoclonal anti-Ki67 | Cell Signaling Technology | Cat# 9129; RRID: AB_2687446 |
| Rabbit monoclonal anti-phospho-Histone H2A.X (Ser139) | Cell Signaling Technology | Cat# 9718; RRID: AB_2118009 |
| Mouse monoclonal anti-Vinculin | Sigma-Aldrich | Cat# V9131; RRID: AB_477629 |
|
| ||
| Biological samples | ||
|
| ||
| Glass slides of oral tissue sections of premalignant and malignant lesions from adult patients | Oral pathology department, School of Dentistry, Alexandria University, Egypt |
N/A |
|
| ||
| Chemicals, peptides, and recombinant proteins | ||
|
| ||
| Trametinib | Selleckchem | Cat#: S2673; CAS: 871700-17-3 |
| Palbociclib | Selleckchem | Cat#: S1116; CAS: 827022-32-2 |
| CHIR-98014 | Selleckchem | Cat#: S2745; CAS: 252935-94-7 |
| MLN-4924 | Sigma-Aldrich | Cat#: 505477; CAS: 951950-33-7 |
| MG132 | Sigma-Aldrich | Cat#: 474790; CAS: 133407-82-6 |
| Hoechst-33343 | Thermo Scientific | Cat# 62249; CAS: 23491-52-3 |
| Doxycycline | Sigma-Aldrich | Cat#: D98910 |
| Doxorubicin hydrochloride | Sigma-Aldrich | Cat#: D1515 |
| Hydrogen peroxide 30% | Sigma-Aldrich | Cat#: H1009 |
| Puromycin | InvivoGen | Cat#: ant-pr-1 |
| Crystal Violet | Sigma-Aldrich | Cat#: C3886-25G |
| Methanol | Fisher | Cat#: A452SK-4 |
|
| ||
| Critical commercial assays | ||
|
| ||
| SPiDER-bgal kit | Dojindo | Cat# SG04-01 |
| Human Discovery Luminex Assay | R&D Systems | Cat# LXSAHM-02 |
| Human Discovery Luminex Assay | R&D Systems | Cat# LXSAHM-13 |
| Senescence β-galactosidase staining kit | Cell Signaling technology | Cat#:9860S |
| GeoMx Solid Tumor TME Morphology Kit | NanoString Technologies | Cat#: GMX-PRO-MORPH-HST-12 |
| GeoMx Seq Code Pack A&B | NanoString Technologies | GMX-NGS-SEQ-AB |
| GeoMx Mouse Protein Core for NGS | NanoString Technologies | GMX-PROCO-NGS-MCORE-12 |
| GeoMx MAPK Signaling Panel Human Protein Module for NGS | NanoString Technologies | GMX-PROMOD-NGS-HMAPK-12 |
|
| ||
| Experimental models: Cell lines | ||
|
| ||
| Human: MCF7 cells | ATCC | Cat#: HTB-22; RRID: CVCL_0031 |
| Human: U2OS cells | ATCC | Cat#: HTB-96; RRID: CVCL_0042 |
| Human: MCF10A cells | ATCC | Cat#: CRL-10317; RRID: CVCL_0598 |
| Human: CAL33 cells | DSMZ | Cat#: ACC447 RRID: CVCL_1108 |
| Human: Primary human lung fibroblasts | ATCC | Cat#: #PCS-201-013 |
|
| ||
| Oligonucleotides | ||
|
| ||
| On-Target plus control siRNA | Dharmacon | Cat#: D-001810-10-05 |
| CDKN1B siRNA (On-Target plus pooled set of four) | Dharmacon | Cat#: L-003472-00-0005 |
| CDKN1A siRNA (On-Target plus pooled set of four) | Dharmacon | Cat#: LQ-003471-00 |
| TP53 (On-Target plus pooled set of four) | Dharmacon | Cat#: L-003329-00-0005 |
| Primers for RT-PCR | see Table S2 | N/A |
|
| ||
| Recombinant DNA | ||
|
| ||
| CSII-pEF1a-H2B-mTurquoise | Spencer et al.28 | N/A |
| CSII-pEF1a-DHB(aa994-1087)-mVenus | Spencer et al.28 | N/A |
| CSII-pEF1a-DHB(aa994-1087)-mCherry | Nathans et al.67 | N/A |
| CSII-pEF1a-mCherry-Geminin(aa1-110) | Cappell et al.68 | N/A |
| pCMV(CAT)T7-SB100 | Mates et al.69 | Cat#: 34879 |
| pSBtet-MYCT58A-emiRFP | This work | N/A |
| pUltra-puro-RTTA2 | Unpublished | Gift from Yildirim Dogan and Kitai Kim Addgene #: 58750 |
| FU-tet-o-hc-MYC | Maherali et al.70 | Gift from Konrad Hochedlinger Addgene #: 19775 |
| pLV-tetO-MYC T58A | Maherali et al.70 | Gift from Konrad Hochedlinger Addgene #: 19763 |
| TRIPZ hMYC lentiviral shRNA | Dharmacon | Cat#: RHS4696-200675280 |
| TRIPZ non-silencing shRNA | Dharmacon | Cat#: RSH4743 |
|
| ||
| Software and algorithms | ||
|
| ||
| FIJI | FIJI | Version: 2.3.0/1.53f |
| MATLAB | MATHWORKS | Version: 2019B |
| MATLAB Tracking Scripts | Cappell et al.68 | N/A |
| Prism | Graphpad | Version: 9.2.0 |
| Illustrator | Adobe | Version: 26.3.1 |
| Incucyte Cell-by-Cell Analysis Software | Sartorius | Version: 9600-0031 |
| Halo imaging analysis software | Indica Labs | Version:3.3.2541.423 |
| BD FACSDiVa Software | BD Biosciences | Version: 9.0 |
| FlowJo | FlowJo | Version:10.8.01 |
| Bio-Plex Manager software | Bio-Rad | Version: 6.2 Build175 |