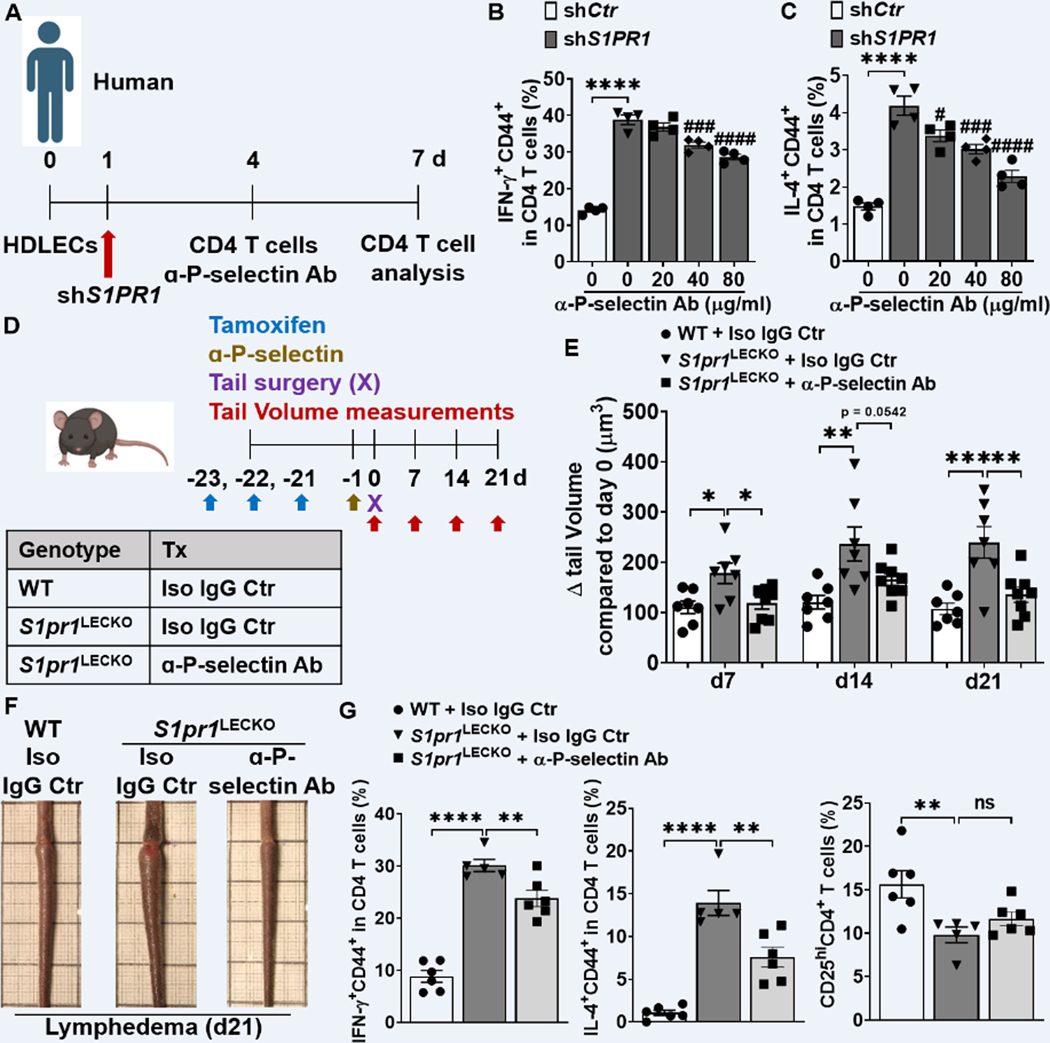
Figure 7. Blocking P-selectin decreases CD4 T cell activation and lymphedema.
(A) Timeline of the co-culture of purified naïve CD4 T cells and HDLEC. ɑ-human P-selectin Ab (Waps12.2) was added to shS1PR1-treated HDLECs 1h before purified memory CD4 T cell co-culture with HDLECs at day 4. (B and C) Flow cytometric analysis was performed d3 after co-culture. Quantification of IFN-ɣ+CD44+ in CD4+ T cells (B), IL-4+CD44+ in CD4+ T cells (C) (n = 4 per each group). (D) Schematic diagram of the experimental protocol. 5 mg/kg anti-mouse P-selectin Ab (RB40.34.4) or Isotype IgG control (Iso IgG Ctr) was retro-orbital-i.v. injected into S1pr1LECKO mice 1 day before lymphedema surgery and the tail size of animals was measured at days 0, 7, 14, and 21. (E and F) Quantification of tail volume changes (E) (n ≥ 7 per each group). Representative photographs of tail skin on day 21 after surgery (F). (G) Quantification of IFN-ɣ+CD44+, IL-4+CD44+, and CD25hi in CD4+ T cells from tail skin 21 day after lymphedema surgery (n ≥ 5 per each group). Data B and C are presented as the mean ± SEM; **** p < 0.0001, # p < 0.05, ### p < 0.001, and #### p < 0.0001 compared with the shS1PR1-treated HDLEC group; by Ordinary one-way ANOVA. Data in E and G are presented as mean ± SEM; * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01, *** p < 0.001, **** p < 0.0001, and ns (not significant) compared with the S1pr1LECKO + Iso Ctr group; by Ordinary one-way ANOVA.