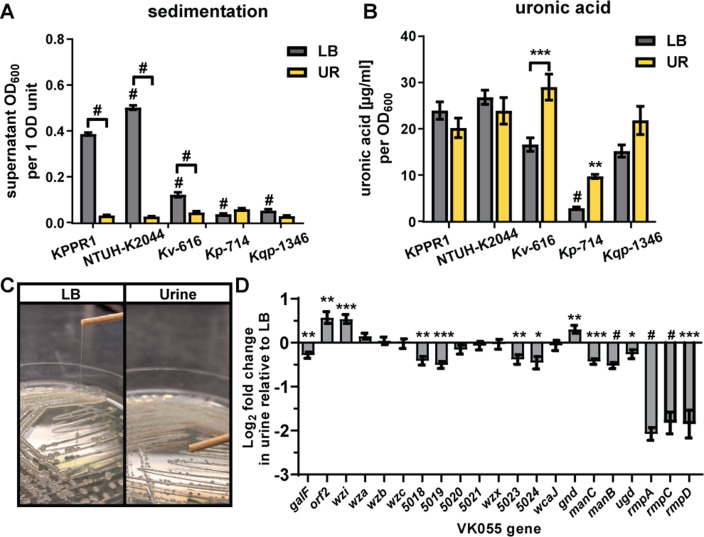
Fig 1.
Urine suppresses mucoidy but not CPS biosynthesis. K. pneumoniae (Kp) strains KPPR1, NTUH-K2044, 714; K. variicola (Kv) 616; and K. quasipneumoniae (Kqp) 1364 were cultured in LB medium or sterile-filtered human urine (UR). (A) Mucoidy was determined by quantifying the supernatant OD600 after sedimenting 1 OD600 unit of culture at 1,000 × g for 5 min. (B) The uronic acid content of crude CPS extracts was determined after washing 1 OD600 unit of bacterial cells in PBS. (C) KPPR1 was cultured on LB agar or urine agar plates at 30°C overnight and then a string test was performed. (D) In addition, the relative abundance of each gene in the CPS biosynthesis and Rmp operons in UR relative to LB medium was determined by qRT-PCR and normalized to gap2 transcript abundance. Data presented are the mean, and error bars represent the standard error of the mean. All experiments were performed ≥3 independent times, in triplicate. Statistical significance in panels A and B was determined using two-way ANOVA with a Bonferroni post-test to compare specific groups. Horizontal bars indicate LB medium versus UR comparisons, while symbols alone indicate comparisons to KPPR1 cultured in the same growth medium. In panel D, a Student’s t test was used to determine if each value was significantly different from 1.0. *P < 0.0332; **P < 0.0021; ***P < 0.0002; # P < 0.0001.