Abstract
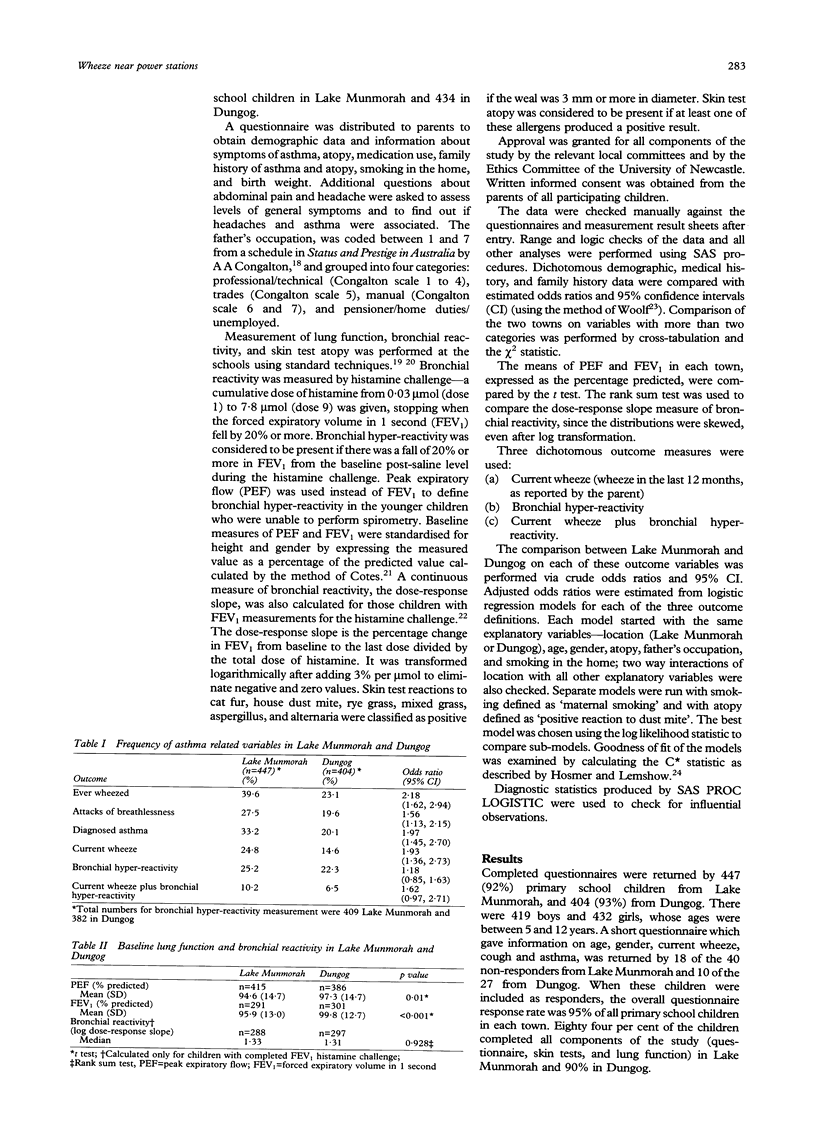
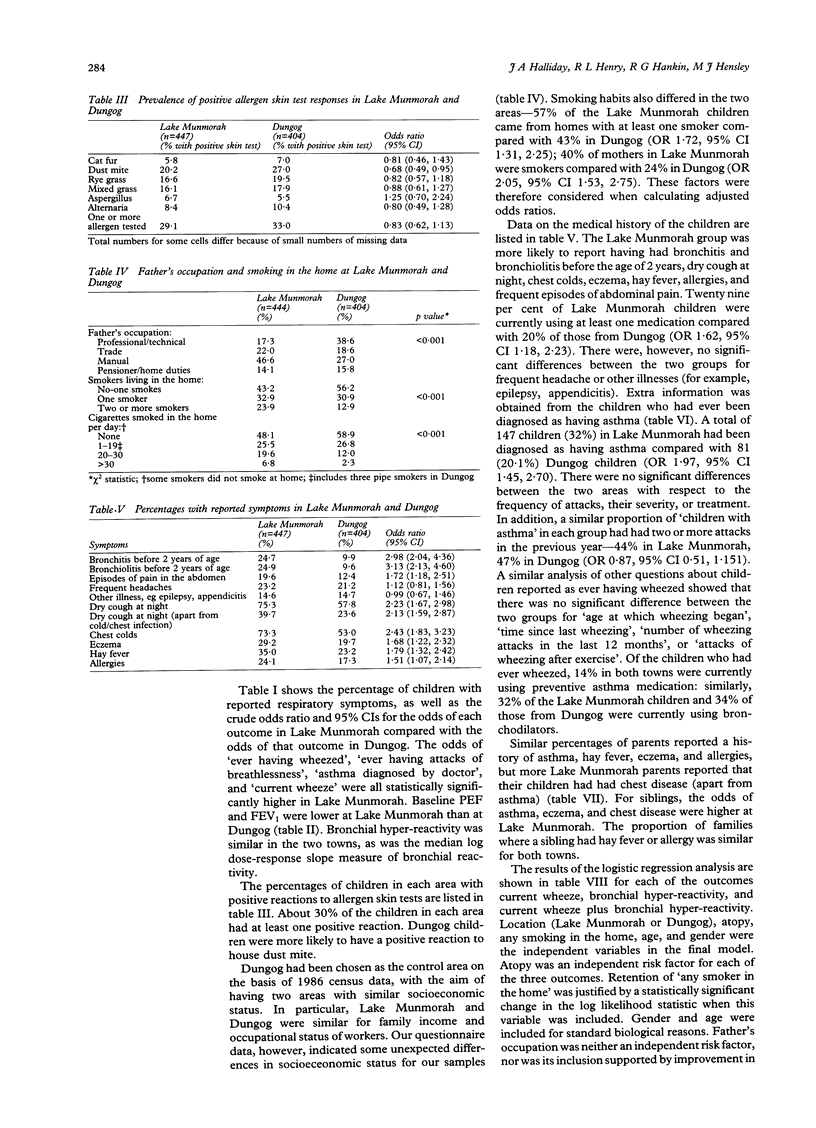
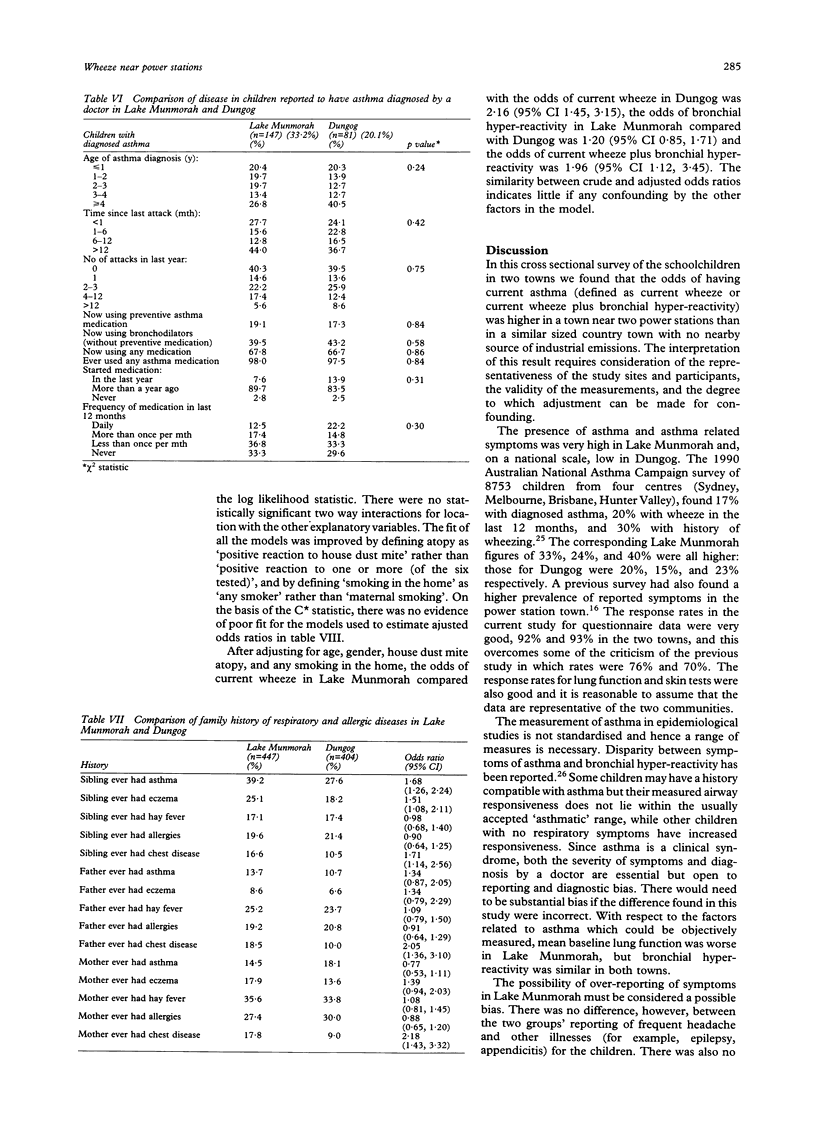
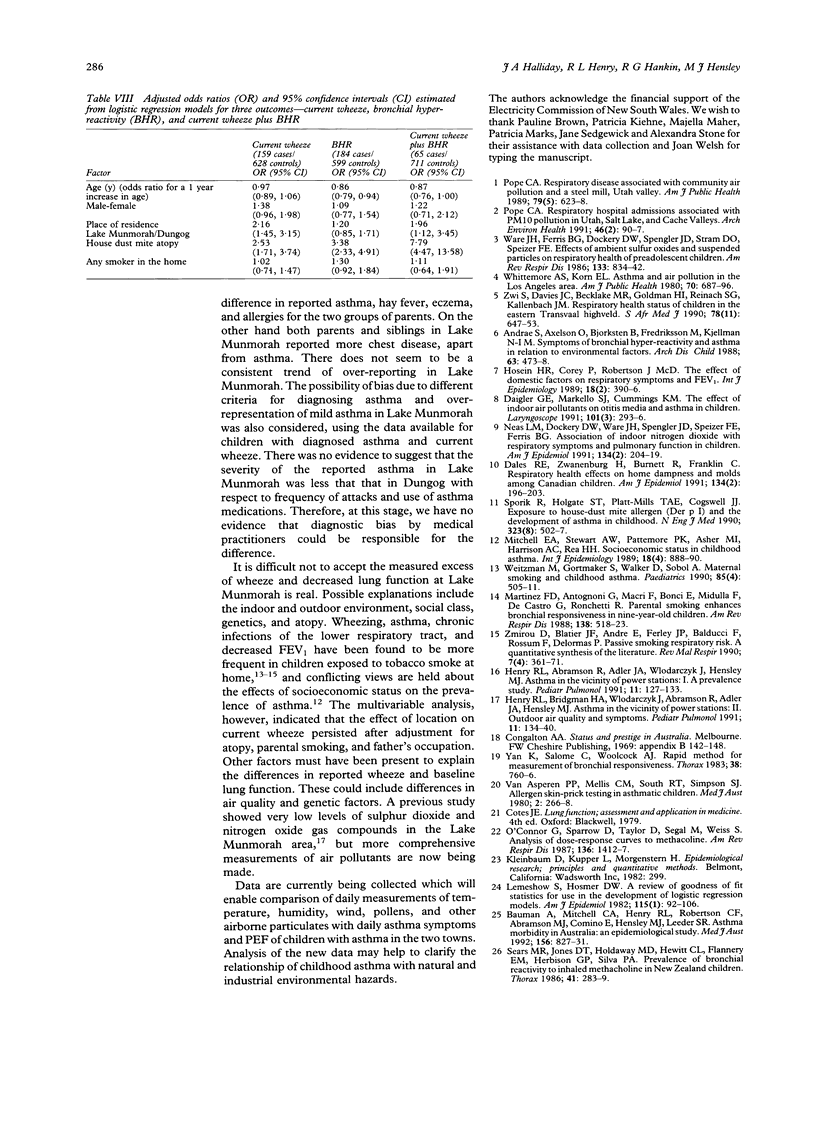
STUDY OBJECTIVE--In a previous study a higher than expected prevalence of asthma was found in Lake Munmorah, a coastal town near two power stations, compared with another coastal control town. This study aimed to compare atopy, bronchial hyperreactivity, and reported symptoms of asthma in the power station town and a second control area with greater socioeconomic similarity. DESIGN--A cross sectional survey was undertaken. SETTINGS--Lake Munmorah, a coastal town near two power stations, and Dungog, a country town in the Hunter Valley, NSW, Australia. PARTICIPANTS--All children attending kindergarten to year 6 at all schools in the two towns were invited to participate in 1990. The response rates for the questionnaire for reported symptoms and associated demographic data were 92% in Lake Munmorah and 93% in Dungog, with 84% and 90% of children respectively being measured for lung function, atopy, and bronchial reactivity. There were 419 boys and 432 girls aged 5 to 12 years. MEASUREMENTS AND MAIN RESULTS--Main outcome measures were current wheeze and bronchial hyper-reactivity, defined as a fall in forced expiratory volume in 1 second (FEV1) or peak expiratory flow (PEF) of 20% or more. Current wheeze was reported in 24.8% of the Lake Munmorah children compared with 14.6% of the Dungog children. Bronchial hyper-reactivity was similar for both groups--25.2% in Lake Munmorah and 22.3% in Dungog. The mean baseline FEV1 was lower in Lake Munmorah than in Dungog (p < 0.001). Dungog children were more likely to have positive skin test to house dust mite (Dungog 27.0%, Lake Munmorah 20.2%, p = 0.028) but there were no other differences in skin test atopy in the two towns. After adjusting for age, gender, any smoker in the house, and positive dust mite skin test, the odds of current wheeze in Lake Munmorah compared with Dungog was 2.16 (95% confidence interval 1.45, 3.15). CONCLUSIONS--Baseline lung function was lower and reported symptoms of asthma were higher in the power station town, but bronchial hyper-reactivity and skin test defined atopy were similar in the two communities. These results are consistent with the previous study and confirm the increased presence of reported symptomatic illness in the town near power stations.
Full text
PDF
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andrae S., Axelson O., Björkstén B., Fredriksson M., Kjellman N. I. Symptoms of bronchial hyperreactivity and asthma in relation to environmental factors. Arch Dis Child. 1988 May;63(5):473–478. doi: 10.1136/adc.63.5.473. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bauman A., Mitchell C. A., Henry R. L., Robertson C. F., Abramson M. J., Comino E. J., Hensley M. J., Leeder S. R. Asthma morbidity in Australia: an epidemiological study. Med J Aust. 1992 Jun 15;156(12):827–831. doi: 10.5694/j.1326-5377.1992.tb136992.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daigler G. E., Markello S. J., Cummings K. M. The effect of indoor air pollutants on otitis media and asthma in children. Laryngoscope. 1991 Mar;101(3):293–296. doi: 10.1288/00005537-199103000-00013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dales R. E., Zwanenburg H., Burnett R., Franklin C. A. Respiratory health effects of home dampness and molds among Canadian children. Am J Epidemiol. 1991 Jul 15;134(2):196–203. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a116072. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henry R. L., Bridgman H. A., Wlodarczyk J., Abramson R., Adler J. A., Hensley M. J. Asthma in the vicinity of power stations: II. Outdoor air quality and symptoms. Pediatr Pulmonol. 1991;11(2):134–140. doi: 10.1002/ppul.1950110210. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hosein H. R., Corey P., Robertson J. M. The effect of domestic factors on respiratory symptoms and FEV1. Int J Epidemiol. 1989 Jun;18(2):390–396. doi: 10.1093/ije/18.2.390. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lemeshow S., Hosmer D. W., Jr A review of goodness of fit statistics for use in the development of logistic regression models. Am J Epidemiol. 1982 Jan;115(1):92–106. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a113284. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martinez F. D., Antognoni G., Macri F., Bonci E., Midulla F., De Castro G., Ronchetti R. Parental smoking enhances bronchial responsiveness in nine-year-old children. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1988 Sep;138(3):518–523. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm/138.3.518. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell E. A., Stewart A. W., Pattemore P. K., Asher M. I., Harrison A. C., Rea H. H. Socioeconomic status in childhood asthma. Int J Epidemiol. 1989 Dec;18(4):888–890. doi: 10.1093/ije/18.4.888. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neas L. M., Dockery D. W., Ware J. H., Spengler J. D., Speizer F. E., Ferris B. G., Jr Association of indoor nitrogen dioxide with respiratory symptoms and pulmonary function in children. Am J Epidemiol. 1991 Jul 15;134(2):204–219. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a116073. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Connor G., Sparrow D., Taylor D., Segal M., Weiss S. Analysis of dose-response curves to methacholine. An approach suitable for population studies. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1987 Dec;136(6):1412–1417. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm/136.6.1412. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pope C. A., 3rd Respiratory disease associated with community air pollution and a steel mill, Utah Valley. Am J Public Health. 1989 May;79(5):623–628. doi: 10.2105/ajph.79.5.623. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pope C. A., 3rd Respiratory hospital admissions associated with PM10 pollution in Utah, Salt Lake, and Cache Valleys. Arch Environ Health. 1991 Mar-Apr;46(2):90–97. doi: 10.1080/00039896.1991.9937434. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sears M. R., Jones D. T., Holdaway M. D., Hewitt C. J., Flannery E. M., Herbison G. P., Silva P. A. Prevalence of bronchial reactivity to inhaled methacholine in New Zealand children. Thorax. 1986 Apr;41(4):283–289. doi: 10.1136/thx.41.4.283. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sporik R., Holgate S. T., Platts-Mills T. A., Cogswell J. J. Exposure to house-dust mite allergen (Der p I) and the development of asthma in childhood. A prospective study. N Engl J Med. 1990 Aug 23;323(8):502–507. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199008233230802. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ware J. H., Ferris B. G., Jr, Dockery D. W., Spengler J. D., Stram D. O., Speizer F. E. Effects of ambient sulfur oxides and suspended particles on respiratory health of preadolescent children. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1986 May;133(5):834–842. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weitzman M., Gortmaker S., Walker D. K., Sobol A. Maternal smoking and childhood asthma. Pediatrics. 1990 Apr;85(4):505–511. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whittemore A. S., Korn E. L. Asthma and air pollution in the Los Angeles area. Am J Public Health. 1980 Jul;70(7):687–696. doi: 10.2105/ajph.70.7.687. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yan K., Salome C., Woolcock A. J. Rapid method for measurement of bronchial responsiveness. Thorax. 1983 Oct;38(10):760–765. doi: 10.1136/thx.38.10.760. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zmirou D., Blatier J. F., André E., Ferley J. P., Balducci F., Rossum F., Delormas P. Tabagisme passif et risque respiratoire. Une synthèse quantitative de la littérature. Rev Mal Respir. 1990;7(4):361–371. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zwi S., Davies J. C., Becklake M. R., Goldman H. I., Reinach S. G., Kallenbach J. M. Respiratory health status of children in the eastern Transvaal highveld. S Afr Med J. 1990 Dec 1;78(11):647–653. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Asperen P. P., Mellis C. M., South R. T., Simpson S. J. Allergen skin-prick testing in asthmatic children. Med J Aust. 1980 Sep 6;2(5):266–268. doi: 10.5694/j.1326-5377.1980.tb132021.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


