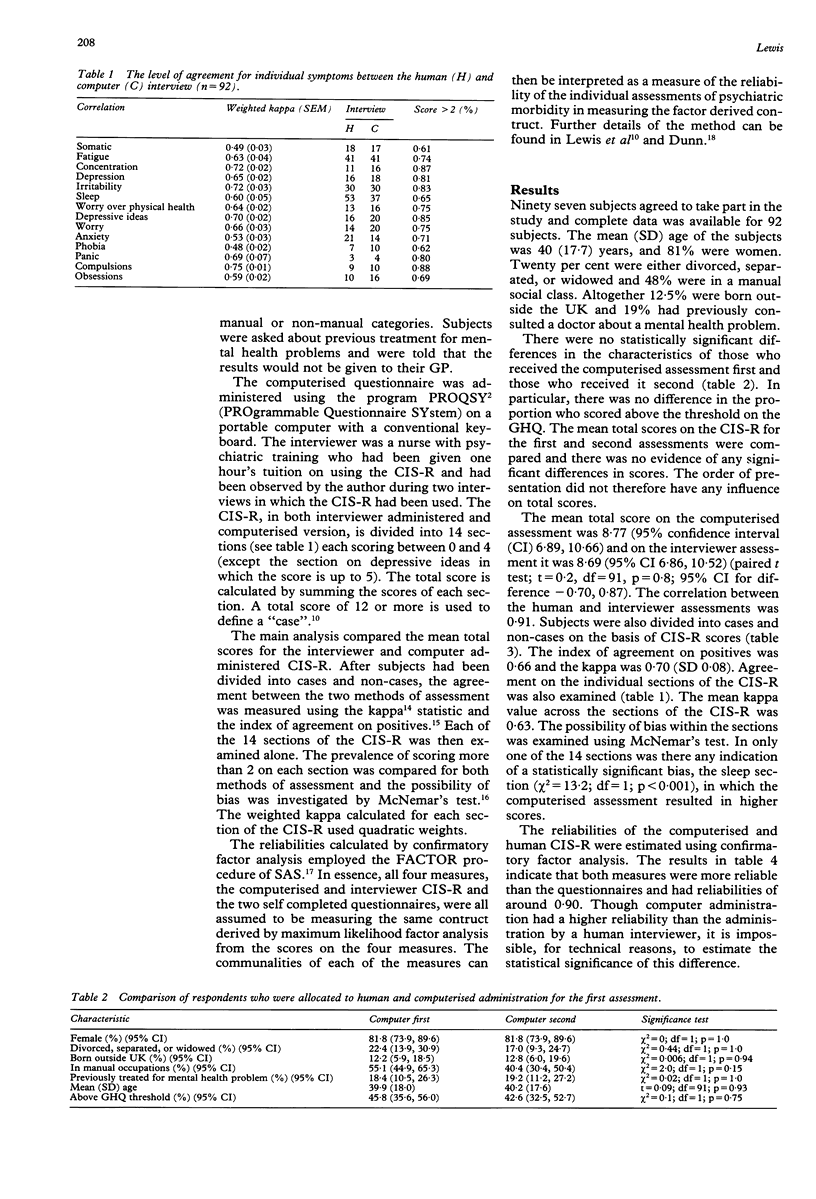
Abstract
OBJECTIVE--To compare a self administered computerised assessment of neurotic psychiatric disorder (psychiatric morbidity) with an identical assessment administered by a human interviewer. In particular, to discover whether a computerised assessment overestimates or underestimates the prevalence of psychiatric morbidity in relation to a human interviewer. SETTING--A health centre in south east London, UK. SUBJECTS--A non-consecutive series of health centre attenders. Complete data were available on 92 subjects. DESIGN--All subjects received both assessments on the same occasion but were randomised to receive either the computerised assessment first or the human interview first. RESULTS--The mean total score on the assessment was the same for both methods of administration; computer 8.77 v human 8.69 (95% confidence interval for difference -0.70, 0.87). The correlation between the human and interviewer assessments was 0.91. CONCLUSION--Self administered computerised assessments are valid, unbiased measures of psychiatric morbidity. In addition to their use as a research tool, they have potential uses in primary care including screening for psychiatric morbidity and in forming the basis for clinical guidelines.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bernadt M. W., Daniels O. J., Blizard R. A., Murray R. M. Can a computer reliably elicit an alcohol history? Br J Addict. 1989 Apr;84(4):405–411. doi: 10.1111/j.1360-0443.1989.tb00584.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brennan P., Silman A. Statistical methods for assessing observer variability in clinical measures. BMJ. 1992 Jun 6;304(6840):1491–1494. doi: 10.1136/bmj.304.6840.1491. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duffy J. C., Waterton J. J. Under-reporting of alcohol consumption in sample surveys: the effect of computer interviewing in fieldwork. Br J Addict. 1984 Sep;79(3):303–308. doi: 10.1111/j.1360-0443.1984.tb00278.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gask L., Goldberg D., Lesser A. L., Millar T. Improving the psychiatric skills of the general practice trainee: an evaluation of a group training course. Med Educ. 1988 Mar;22(2):132–138. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2923.1988.tb00423.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greist J. H., Klein M. H., Erdman H. P., Bires J. K., Bass S. M., Machtinger P. E., Kresge D. G. Comparison of computer- and interviewer-administered versions of the Diagnostic Interview Schedule. Hosp Community Psychiatry. 1987 Dec;38(12):1304–1311. doi: 10.1176/ps.38.12.1304. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis G., Pelosi A. J., Araya R., Dunn G. Measuring psychiatric disorder in the community: a standardized assessment for use by lay interviewers. Psychol Med. 1992 May;22(2):465–486. doi: 10.1017/s0033291700030415. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis G., Pelosi A. J., Glover E., Wilkinson G., Stansfeld S. A., Williams P., Shepherd M. The development of a computerized assessment for minor psychiatric disorder. Psychol Med. 1988 Aug;18(3):737–745. doi: 10.1017/s0033291700008448. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pelosi A. J., Lewis G. The computer will see you now. BMJ. 1989 Jul 15;299(6692):138–139. doi: 10.1136/bmj.299.6692.138. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robins L. N., Helzer J. E., Croughan J., Ratcliff K. S. National Institute of Mental Health Diagnostic Interview Schedule. Its history, characteristics, and validity. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 1981 Apr;38(4):381–389. doi: 10.1001/archpsyc.1981.01780290015001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skinner H. A., Allen B. A. Does the computer make a difference? Computerized versus face-to-face versus self-report assessment of alcohol, drug, and tobacco use. J Consult Clin Psychol. 1983 Apr;51(2):267–275. doi: 10.1037//0022-006x.51.2.267. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wing J. K., Nixon J. M., Mann S. A., Leff J. P. Reliability of the PSE (ninth edition) used in a population study. Psychol Med. 1977 Aug;7(3):505–516. doi: 10.1017/s0033291700004487. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zigmond A. S., Snaith R. P. The hospital anxiety and depression scale. Acta Psychiatr Scand. 1983 Jun;67(6):361–370. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0447.1983.tb09716.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


