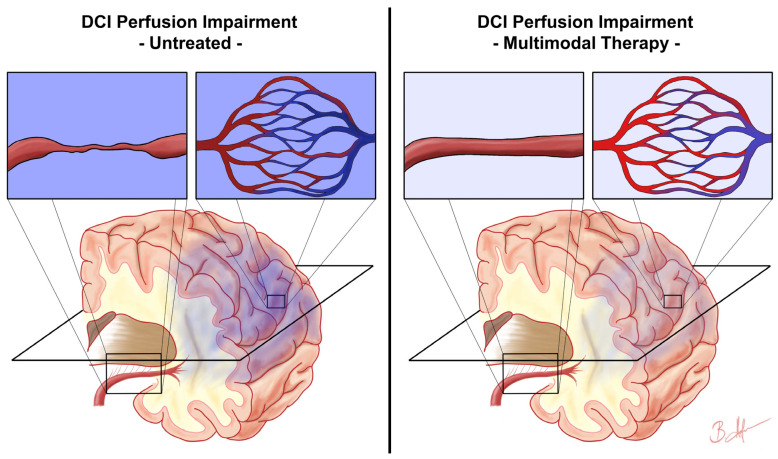
Figure 4.
Assumed impact of multimodal therapy on delayed cerebral ischemia microvascular perfusion impairment. This figure schematically illustrates the presumed impact of multimodal therapy on the perfusion impairment in delayed cerebral ischemia (DCI) based on the results of this study. The left side shows the DCI perfusion impairment consisting of disturbances in general microvascular perfusion due to, e.g., vasospasm (first enlarged rectangle) and microvascular perfusion heterogeneity (second enlarged rectangle), resulting in hypoxia of the affected brain tissue (dark blue colour). The right side represents the condition after initiation of multimodal therapy, where the general microvascular perfusion is improved, e.g., by dissolving macro-vasospasms (third enlarged rectangle), but microvascular perfusion heterogeneity remains unaffected (fourth enlarged rectangle), resulting in weaker but still present hypoxia of the affected brain tissue (light blue colour). The plane marked in black schematically represents the plane of CT perfusion imaging.