Abstract
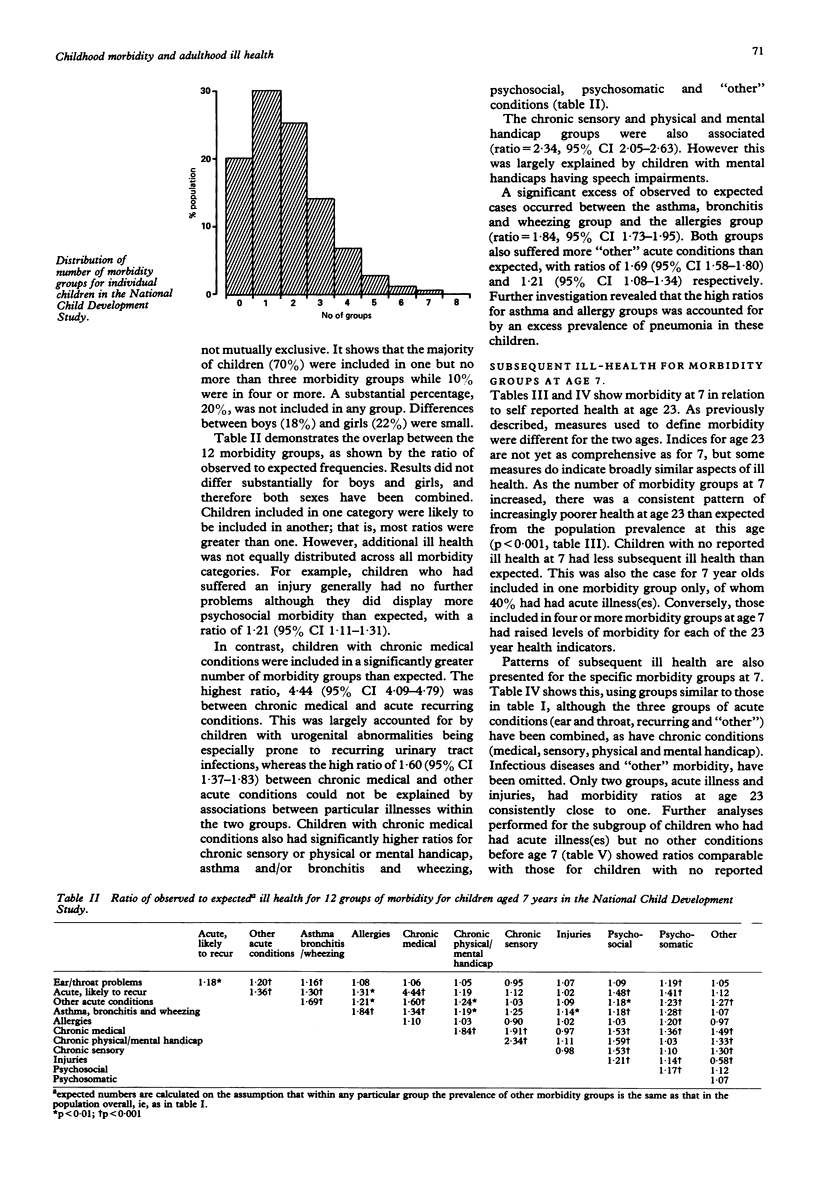
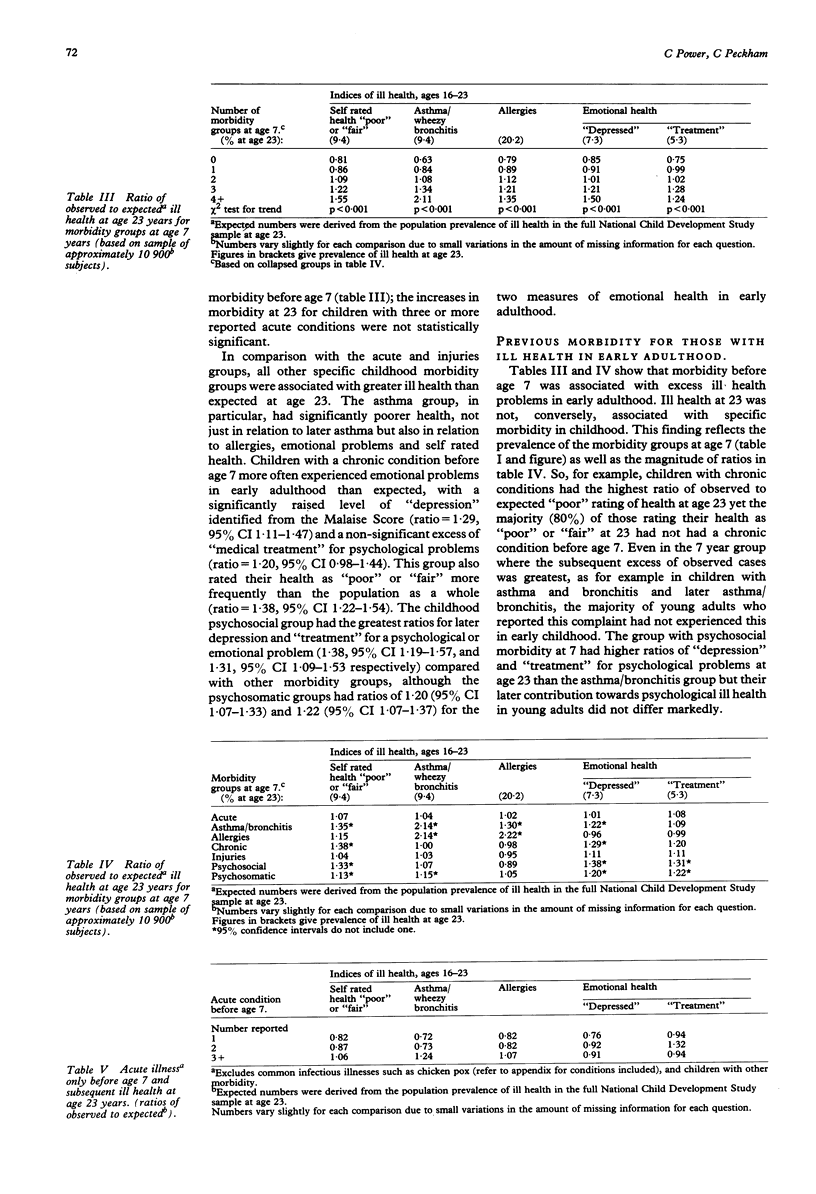
STUDY OBJECTIVE--The aim of the study was to investigate the relationship between the state of health in childhood and ill health in early adult life. DESIGN--The study used data collected as part of the National Child Development Study and related health at 7 years of age to that at 23. A wide range of information on child health in the cohort was available, which was used to construct a broader measure of health status than selected diagnostic categories. SETTING--The survey population was nationwide. PARTICIPANTS--The study population included all children born in the week 3-9 March 1958. They were followed up at 7, 11, 16, and 23 years. Of the target population of 17,733 births, 12,537 (76%) were retraced and interviewed at 23. MEASUREMENTS AND MAIN RESULTS--Children at age 7 were allocated to 13 morbidity groups; 20% of children had reported no ill-health apart from the common infectious diseases, but 10% were included in four or more of the morbidity groups. Children with no reported morbidity retained their health advantage into early adulthood: ratios of observed to expected ill health for four of the five indices examined at age 23 were all significantly below one (self rated health 0.81, asthma and/or wheezy bronchitis 0.63, allergies 0.79, emotional health 0.75). Children with more morbidity at age 7 had higher ratios of ill health in adulthood. A chronic condition in childhood was associated not only with excess morbidity in the short term but also with a poor health rating in early adult life (ratio = 1.38). Morbidity was significantly increased for most of the adulthood indices among children with asthma and/or wheezy bronchitis. However most ill health in young adulthood occurred in study members with a relatively healthy childhood. CONCLUSIONS--Although the state of health in childhood has long term implications, it does not form a substantial contribution to ill health in early adult life.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barker D. J., Osmond C. Childhood respiratory infection and adult chronic bronchitis in England and Wales. Br Med J (Clin Res Ed) 1986 Nov 15;293(6557):1271–1275. doi: 10.1136/bmj.293.6557.1271. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benson P., Gabriel A., Katz H., Steinwachs D., Hankin J., Starfield B. Preventive care and overall use of services. Are they related? Am J Dis Child. 1984 Jan;138(1):74–78. doi: 10.1001/archpedi.1984.02140390062019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colley J. R., Douglas J. W., Reid D. D. Respiratory disease in young adults: influence of early childhood lower respiratory tract illness, social class, air pollution, and smoking. Br Med J. 1973 Jul 28;3(5873):195–198. doi: 10.1136/bmj.3.5873.195. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marmot M. G., Shipley M. J., Rose G. Inequalities in death--specific explanations of a general pattern? Lancet. 1984 May 5;1(8384):1003–1006. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(84)92337-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peckham C. S., Stark O., Simonite V., Wolff O. H. Prevalence of obesity in British children born in 1946 and 1958. Br Med J (Clin Res Ed) 1983 Apr 16;286(6373):1237–1242. doi: 10.1136/bmj.286.6373.1237. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Power C., Moynihan C. Social class and changes in weight-for-height between childhood and early adulthood. Int J Obes. 1988;12(5):445–453. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richman N. Depression in mothers of young children. J R Soc Med. 1978 Jul;71(7):489–493. doi: 10.1177/014107687807100706. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross E. M., Peckham C. S., West P. B., Butler N. R. Epilepsy in childhood: findings from the National Child Development Study. Br Med J. 1980 Jan 26;280(6209):207–210. doi: 10.1136/bmj.280.6209.207. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rutter M., Tizard J., Yule W., Graham P., Whitmore K. Research report: Isle of Wight Studies, 1964-1974. Psychol Med. 1976 May;6(2):313–332. doi: 10.1017/s003329170001388x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Starfield B., Katz H., Gabriel A., Livingston G., Benson P., Hankin J., Horn S., Steinwachs D. Morbidity in childhood--a longitudinal view. N Engl J Med. 1984 Mar 29;310(13):824–829. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198403293101305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strachan D. P., Anderson H. R., Bland J. M., Peckham C. Asthma as a link between chest illness in childhood and chronic cough and phlegm in young adults. Br Med J (Clin Res Ed) 1988 Mar 26;296(6626):890–893. doi: 10.1136/bmj.296.6626.890. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


