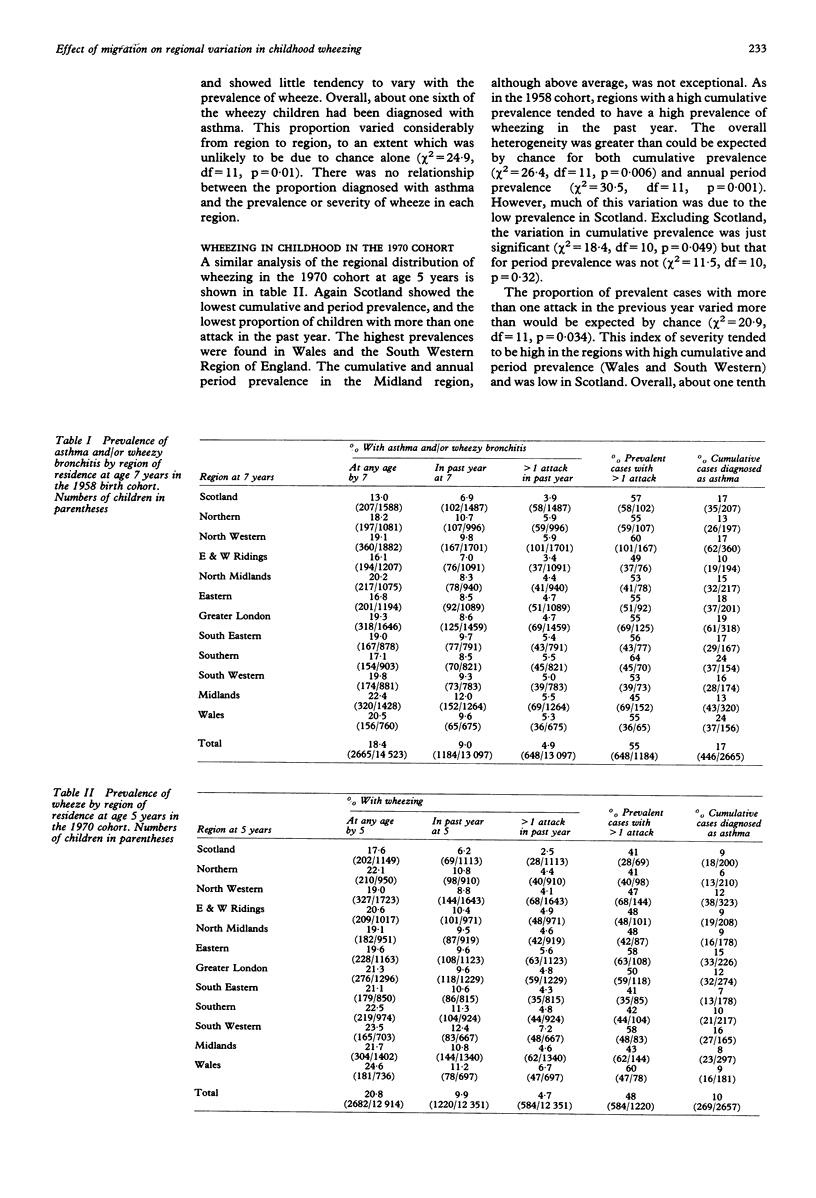
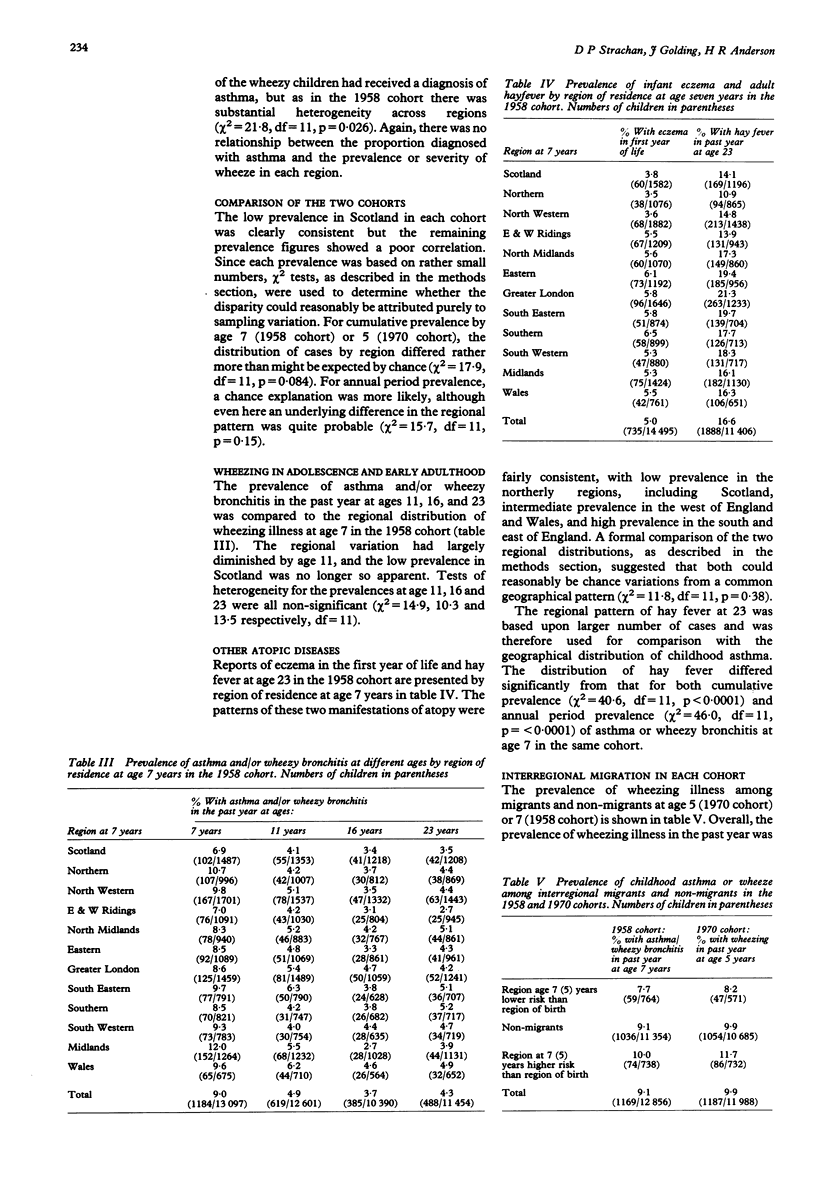
Abstract
STUDY OBJECTIVE--The aim was to examine the regional distribution of wheezing illness among British children, and the age at which geographical differences may be determined. DESIGN--Cross sectional analyses and study of interregional migrants were used. SUBJECTS--The subjects were national cohorts of British children born in 1958 and 1970. MEASUREMENTS AND MAIN RESULTS--The regional distribution of wheezing illness showed significant heterogeneity at age 5 (1970 cohort) and 7 (1958 cohort). In both cohorts, children in Scotland had a low prevalence of wheeze, which could not be attributed to underreporting of mild cases. There was a less consistent tendency for high prevalence in Wales, and in the South Western and Midlands regions of England. In the 1958 cohort, the regional differentials diminished progressively with age and were negligible at age 23. There was a poor correlation between the regional distribution of childhood asthma and the common geographical pattern shown by eczema in infancy and hay fever at age 23. Analysis of interregional migrants suggested that the regional variation in each cohort at age 5-7 was primarily related to the region of current residence, and not to the region of birth. CONCLUSIONS--Genetic constitution, perinatal exposures, or early childhood experiences are unlikely to account for the regional variation in wheezing illness. Although local patterns of symptom reporting or disease labelling may be acquired by parents who move to a new region, environmental factors operating at a regional level probably determine the prevalence of asthma in primary school children. These influences do not appear to have long lasting effects upon the tendency to wheeze in adolescence and early adulthood.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson H. R., Bland J. M., Patel S., Peckham C. The natural history of asthma in childhood. J Epidemiol Community Health. 1986 Jun;40(2):121–129. doi: 10.1136/jech.40.2.121. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson H. R. Respiratory disease in childhood. Br Med Bull. 1986 Apr;42(2):167–171. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.bmb.a072116. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burr M. L. Is asthma increasing? J Epidemiol Community Health. 1987 Sep;41(3):185–189. doi: 10.1136/jech.41.3.185. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carlsen K. H., Orstavik I., Leegaard J., Høeg H. Respiratory virus infections and aeroallergens in acute bronchial asthma. Arch Dis Child. 1984 Apr;59(4):310–315. doi: 10.1136/adc.59.4.310. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gregg I. Epidemiological research in asthma: the need for a broad perspective. Clin Allergy. 1986 Jan;16(1):17–23. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2222.1986.tb01949.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horn M. E., Reed S. E., Taylor P. Role of viruses and bacteria in acute wheezy bronchitis in childhood: a study of sputum. Arch Dis Child. 1979 Aug;54(8):587–592. doi: 10.1136/adc.54.8.587. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaplan B. A., Mascie-Taylor C. G. Biosocial factors in the epidemiology of childhood asthma in a British national sample. J Epidemiol Community Health. 1985 Jun;39(2):152–156. doi: 10.1136/jech.39.2.152. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee D. A., Winslow N. R., Speight A. N., Hey E. N. Prevalence and spectrum of asthma in childhood. Br Med J (Clin Res Ed) 1983 Apr 16;286(6373):1256–1258. doi: 10.1136/bmj.286.6373.1256. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Park E. S., Golding J., Carswell F., Stewart-Brown S. Preschool wheezing and prognosis at 10. Arch Dis Child. 1986 Jul;61(7):642–646. doi: 10.1136/adc.61.7.642. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Partridge M. R., Gibson G. J., Pride N. B. Asthma in Asian immigrants. Clin Allergy. 1979 Sep;9(5):489–494. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2222.1979.tb02513.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith J. M., Harding L. K., Cumming G. The changing prevalence of asthma in school children. Clin Allergy. 1971 Mar;1(1):57–61. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2222.1971.tb02447.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strachan D. P. Damp housing and childhood asthma: validation of reporting of symptoms. BMJ. 1988 Nov 12;297(6658):1223–1226. doi: 10.1136/bmj.297.6658.1223. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor B., Wadsworth J., Wadsworth M., Peckham C. Changes in the reported prevalence of childhood eczema since the 1939-45 war. Lancet. 1984 Dec 1;2(8414):1255–1257. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(84)92805-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Niekerk C. H., Weinberg E. G., Shore S. C., Heese H. V., Van Schalkwyk J. Prevalence of asthma: a comparative study of urban and rural Xhosa children. Clin Allergy. 1979 Jul;9(4):319–314. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2222.1979.tb02489.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waite D. A., Eyles E. F., Tonkin S. L., O'Donnell T. V. Asthma prevalence in Tokelauan children in two environments. Clin Allergy. 1980 Jan;10(1):71–75. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2222.1980.tb02082.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams H., McNicol K. N. Prevalence, natural history, and relationship of wheezy bronchitis and asthma in children. An epidemiological study. Br Med J. 1969 Nov 8;4(5679):321–325. doi: 10.1136/bmj.4.5679.321. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


