Abstract
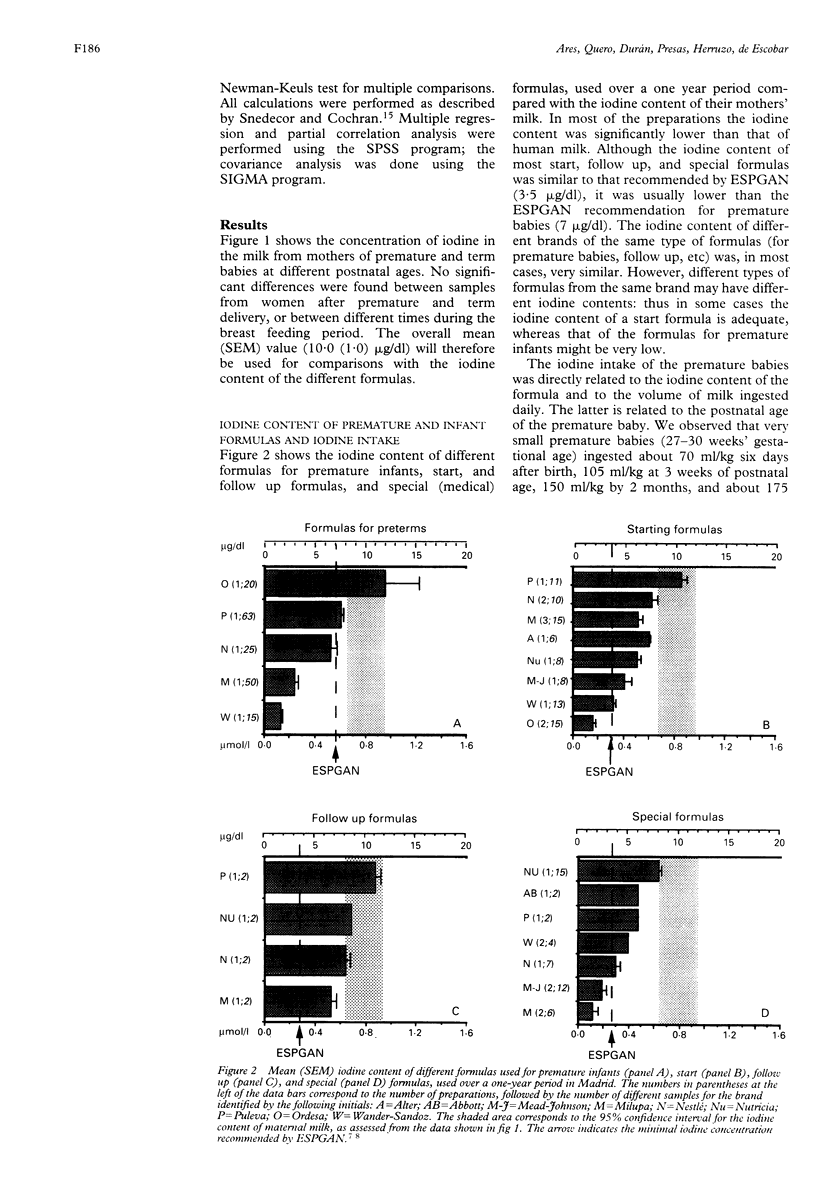
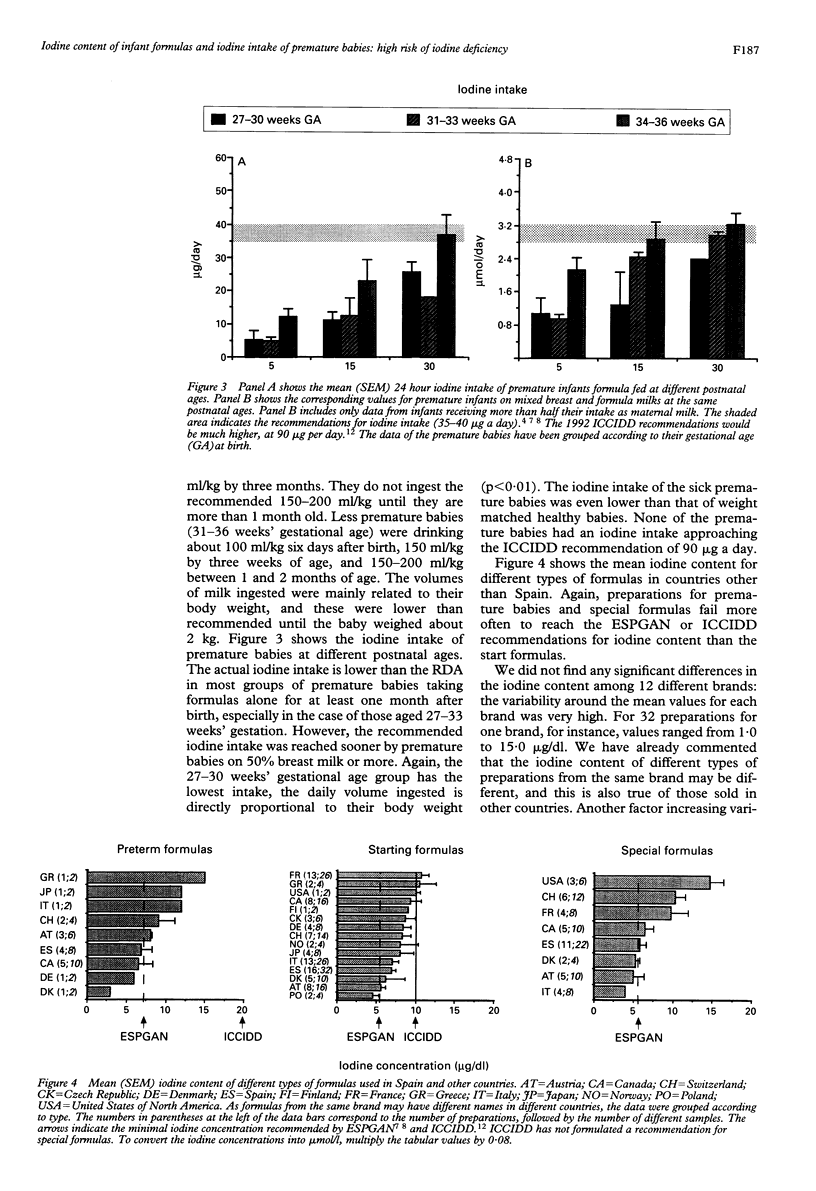
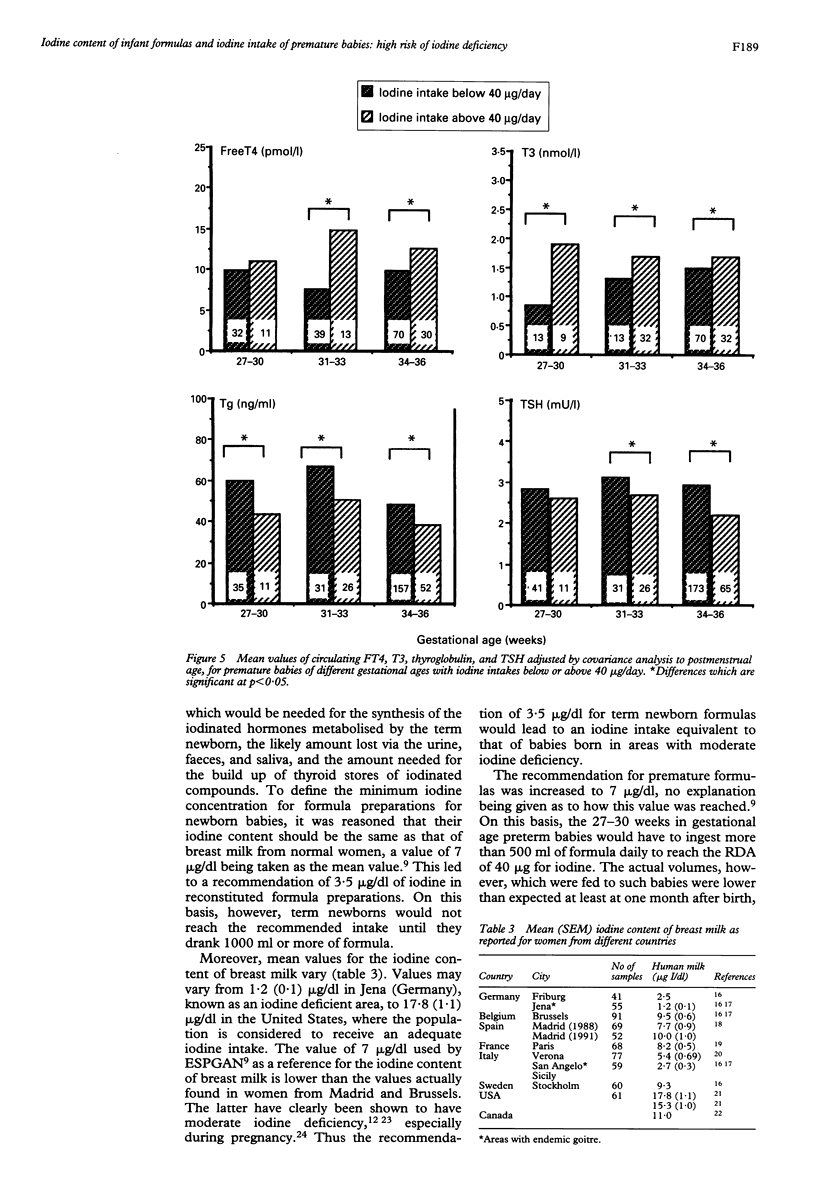
As part of a study of thyroid function in premature babies, the iodine content of their mothers' breast milk, that of 32 formulas from different brands used in Spain, and that of 127 formulas used in other countries was determined. Breast milk contained more iodine--mean (SEM) 10 (1) microgram/dl--than most of the formulas, especially those for premature babies. Iodine intakes were therefore below the recommended daily amount (RDA) for newborns: babies of 27-30 weeks' gestational age took 3.1 (1.1) micrograms/day at 5 days of age and 29.8 (2.7) micrograms by 2 months of age. This problem is not exclusive to Spanish premature babies as the iodine content of many of the formulas on sale in other countries was also inadequate. It is concluded that preterm infants who are formula fed are at high risk of iodine deficiency.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BENOTTI J., BENOTTI N. PROTEIN-BOUND IODINE, TOTAL IODINE, AND BUTANOL-EXTRACTABLE IODINE BY PARTIAL AUTOMATION. Clin Chem. 1963 Aug;12:408–416. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buchinger W., Langsteger W., Tiran B., Lorenz O., Eber O. Jodgehalt der Säuglingsnahrung in Osterreich. Acta Med Austriaca. 1993;20(5):131–133. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Vries L. S., Heckmatt J. Z., Burrin J. M., Dubowitz L. M., Dubowitz V. Low serum thyroxine concentrations and neural maturation in preterm infants. Arch Dis Child. 1986 Sep;61(9):862–866. doi: 10.1136/adc.61.9.862. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Delange F., Bürgi H. Iodine deficiency disorders in Europe. Bull World Health Organ. 1989;67(3):317–325. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Delange F., Dalhem A., Bourdoux P., Lagasse R., Glinoer D., Fisher D. A., Walfish P. G., Ermans A. M. Increased risk of primary hypothyroidism in preterm infants. J Pediatr. 1984 Sep;105(3):462–469. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(84)80030-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunn J. T. Iodine deficiency--the next target for elimination? N Engl J Med. 1992 Jan 23;326(4):267–268. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199201233260411. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Etling N., Gehin-Fouque F. Iodinated compounds and thyroxine binding to albumin in human breast milk. Pediatr Res. 1984 Sep;18(9):901–903. doi: 10.1203/00006450-198409000-00020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Etling N., Padovani E., Gehin-Fouque F., Tato L. Iodine and thyroid hormone levels in serum and urine of full term newborn infants. Helv Paediatr Acta. 1983 May;38(2):117–122. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fisher D. A. Upper limit of iodine in infant formulas. J Nutr. 1989 Dec;119(12 Suppl):1865–1868. doi: 10.1093/jn/119.12_Suppl.1865. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gushurst C. A., Mueller J. A., Green J. A., Sedor F. Breast milk iodide: reassessment in the 1980s. Pediatrics. 1984 Mar;73(3):354–357. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hetzel B. S. Iodine deficiency disorders (IDD) and their eradication. Lancet. 1983 Nov 12;2(8359):1126–1129. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(83)90636-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lucas A., Rennie J., Baker B. A., Morley R. Low plasma triiodothyronine concentrations and outcome in preterm infants. Arch Dis Child. 1988 Oct;63(10):1201–1206. doi: 10.1136/adc.63.10.1201. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pacini F., Lari R., La Ricca P., Grasso L., Taddei D., Bardini N., Fenzi G. F., Di Bartolo F., Baschieri L., Pinchera A. Serum thyroglobulin in newborns' cord blood, in childhood and adolescence: a physiological indicator of thyroidal status. J Endocrinol Invest. 1984 Oct;7(5):467–471. doi: 10.1007/BF03348452. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


