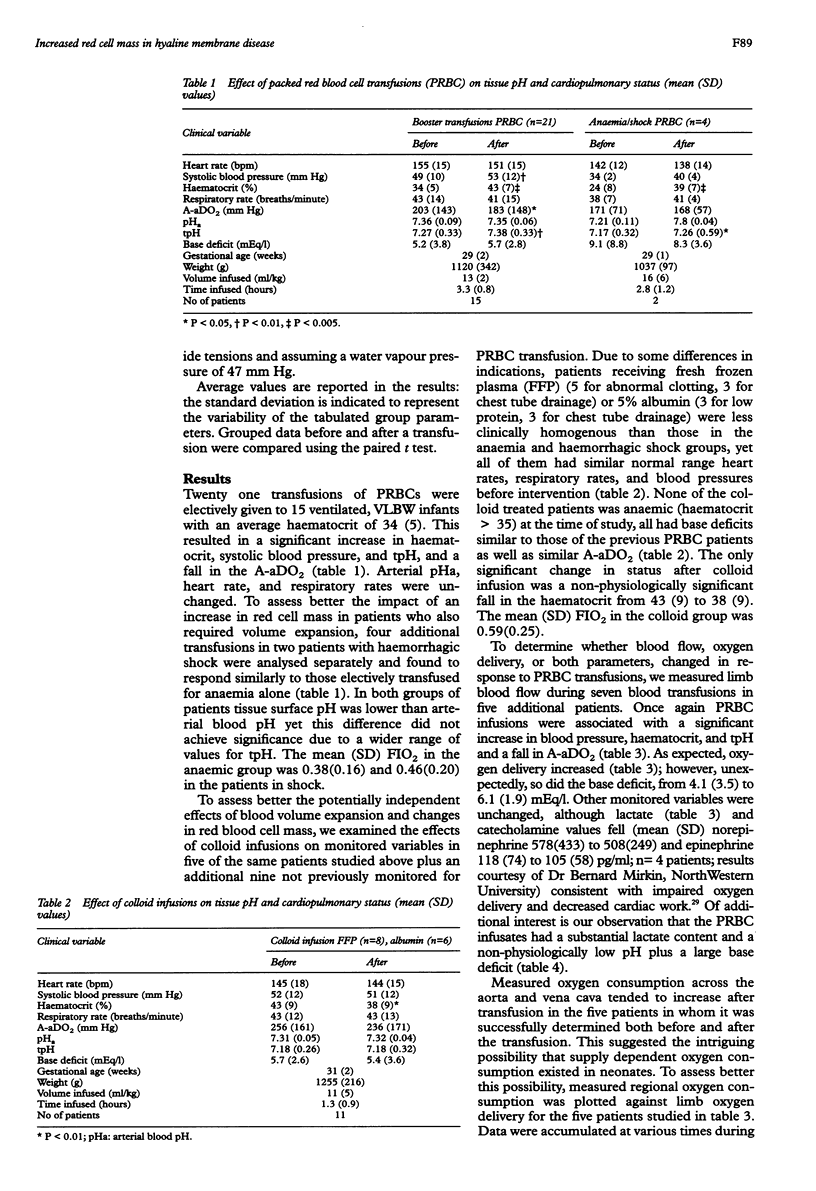
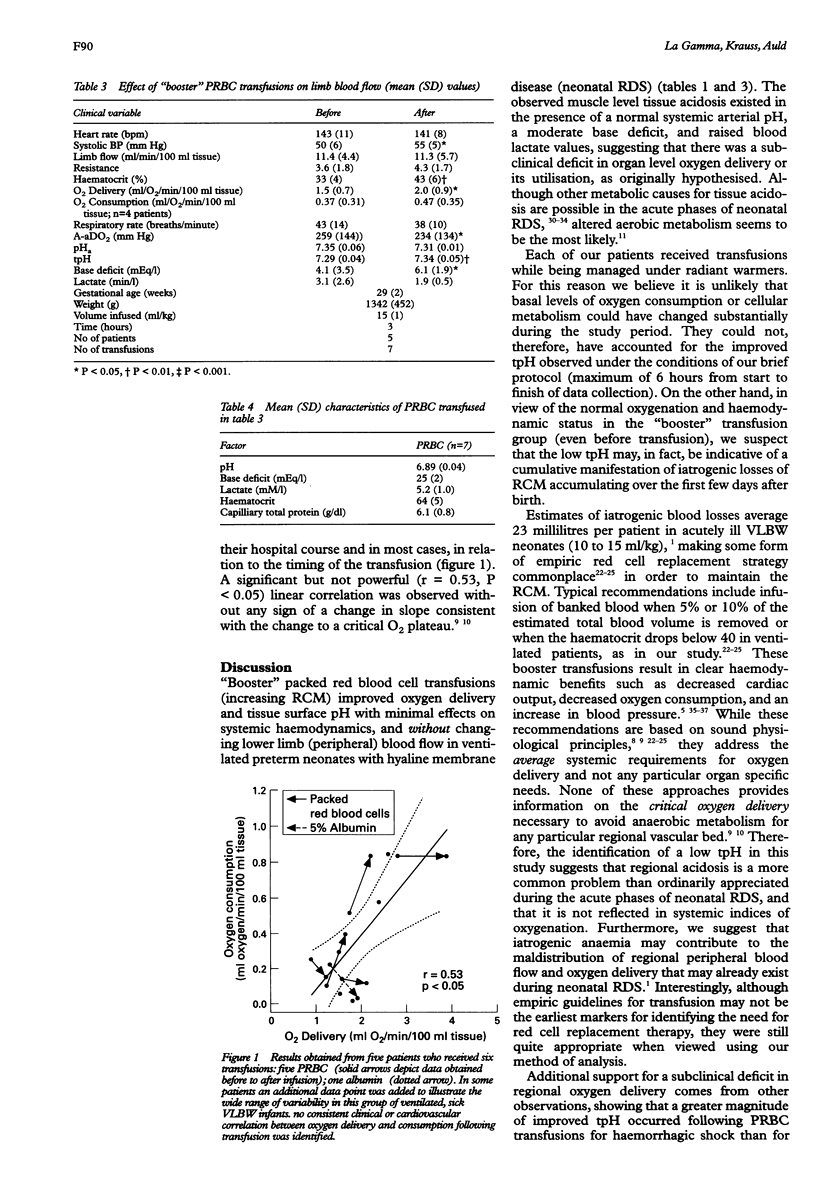
Abstract
AIM: To determine whether there are subclinical deficits in oxygen delivery in ventilated premature neonates. METHOD: Ventilated premature neonates weighing less than 1500 g, who were transfused for anaemia or who were given colloids for clotting abnormalities (or oedema), were haemodynamically monitored during the first week of life. Calf muscle surface pH (pH) was measured in conjunction with peripheral limb blood flow by occlusion plethysmography. RESULTS: Packed red blood cell transfusions corrected a subclinical regional tissue acidosis (low tpH) without affecting arterial pH or limb blood flow. This observation also correlated with an increase in regional oxygen delivery. The data were also suggestive of a pattern of pathological, supply dependent, oxygen delivery and are similar to other observations made in adults with adult respiratory distress syndrome. CONCLUSIONS: Packed red blood cells increase regional oxygen delivery and tissue surface pH. In contrast, colloid infusion provided no substantial cardiovascular or metabolic benefit to these patients and should be avoided when oxygen delivery is at issue and when there may be leaky pulmonary capillaries.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adan D., La Gamma E. F., Browne L. E. Nutritional management and the multisystem organ failure/systemic inflammatory response syndrome in critically ill preterm neonates. Crit Care Clin. 1995 Jul;11(3):751–784. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alverson D. C., Isken V. H., Cohen R. S. Effect of booster blood transfusions on oxygen utilization in infants with bronchopulmonary dysplasia. J Pediatr. 1988 Oct;113(4):722–726. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(88)80389-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barr P. A., Bailey P. E., Sumners J., Cassady G. Relation between arterial blood pressure and blood volume and effect of infused albumin in sick preterm infants. Pediatrics. 1977 Sep;60(3):282–289. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bauer K., Bovermann G., Roithmaier A., Götz M., Pröiss A., Versmold H. T. Body composition, nutrition, and fluid balance during the first two weeks of life in preterm neonates weighing less than 1500 grams. J Pediatr. 1991 Apr;118(4 Pt 1):615–620. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(05)83390-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beal A. L., Cerra F. B. Multiple organ failure syndrome in the 1990s. Systemic inflammatory response and organ dysfunction. JAMA. 1994 Jan 19;271(3):226–233. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bifano E. M., Smith F., Borer J. Relationship between determinants of oxygen delivery and respiratory abnormalities in preterm infants with anemia. J Pediatr. 1992 Feb;120(2 Pt 1):292–296. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(05)80447-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bignall S., Bailey P. C., Bass C. A., Cramb R., Rivers R. P., Wadsworth J. The cardiovascular and oncotic effects of albumin infusion in premature infants. Early Hum Dev. 1989 Dec;20(3-4):191–201. doi: 10.1016/0378-3782(89)90005-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bishop M. H., Shoemaker W. C., Appel P. L., Wo C. J., Zwick C., Kram H. B., Meade P., Kennedy F., Fleming A. W. Relationship between supranormal circulatory values, time delays, and outcome in severely traumatized patients. Crit Care Med. 1993 Jan;21(1):56–63. doi: 10.1097/00003246-199301000-00013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang M. C., Cheatham M. L., Nelson L. D., Rutherford E. J., Morris J. A., Jr Gastric tonometry supplements information provided by systemic indicators of oxygen transport. J Trauma. 1994 Sep;37(3):488–494. doi: 10.1097/00005373-199409000-00026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Costeloe K., Rolfe P. Continuous limb blood flow estimation in the newborn using electrical impedance plethysmography. Pediatr Res. 1980 Sep;14(9):1053–1060. doi: 10.1203/00006450-198009000-00007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Couch N. P., Dmochowski J. R., Van de Water J. M., Harken D. E., Moore F. D. Muscle surface pH as an index of peripheral perfusion in man. Ann Surg. 1971 Feb;173(2):173–183. doi: 10.1097/00000658-197102000-00001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dantzker D. R. Adequacy of tissue oxygenation. Crit Care Med. 1993 Feb;21(2 Suppl):S40–S43. doi: 10.1097/00003246-199302001-00008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dantzker D. Oxygen delivery and utilization in sepsis. Crit Care Clin. 1989 Jan;5(1):81–98. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doglio G. R., Pusajo J. F., Egurrola M. A., Bonfigli G. C., Parra C., Vetere L., Hernandez M. S., Fernandez S., Palizas F., Gutierrez G. Gastric mucosal pH as a prognostic index of mortality in critically ill patients. Crit Care Med. 1991 Aug;19(8):1037–1040. doi: 10.1097/00003246-199108000-00011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emery E. F., Greenough A., Gamsu H. R. Randomised controlled trial of colloid infusions in hypotensive preterm infants. Arch Dis Child. 1992 Oct;67(10 Spec No):1185–1188. doi: 10.1136/adc.67.10_spec_no.1185. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Filler R. M., Das J. B., Espinosa H. M. Clinical experience with continuous muscle pH monitoring as an index of tissue perfusion and oxygenation and acid-base status. Surgery. 1972 Jul;72(1):23–33. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaudry P. L., Duffy C., Joseph D. The pH and titratable acidity of stored CPD blood. Anaesth Intensive Care. 1980 Aug;8(3):353–355. doi: 10.1177/0310057X8000800312. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenough A., Greenall F., Gamsu H. R. Immediate effects of albumin infusion in ill premature neonates. Arch Dis Child. 1988 Mar;63(3):307–309. doi: 10.1136/adc.63.3.307. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grum C. M. Tissue oxygenation in low flow states and during hypoxemia. Crit Care Med. 1993 Feb;21(2 Suppl):S44–S49. doi: 10.1097/00003246-199302001-00009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gutierrez G., Palizas F., Doglio G., Wainsztein N., Gallesio A., Pacin J., Dubin A., Schiavi E., Jorge M., Pusajo J. Gastric intramucosal pH as a therapeutic index of tissue oxygenation in critically ill patients. Lancet. 1992 Jan 25;339(8787):195–199. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(92)90002-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hotchkiss R. S., Karl I. E. Reevaluation of the role of cellular hypoxia and bioenergetic failure in sepsis. JAMA. 1992 Mar 18;267(11):1503–1510. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hudson I., Cooke A., Holland B., Houston A., Jones J. G., Turner T., Wardrop C. A. Red cell volume and cardiac output in anaemic preterm infants. Arch Dis Child. 1990 Jul;65(7 Spec No):672–675. doi: 10.1136/adc.65.7_spec_no.672. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- La Gamma E. F., Krauss A. N., Auld P. A. Tissue surface pH monitoring during reduced blood flow: Metabolic implications and sources of error. J Perinat Med. 1982;10(3):174–180. doi: 10.1515/jpme.1982.10.3.174. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lachance C., Chessex P., Fouron J. C., Widness J. A., Bard H. Myocardial, erythropoietic, and metabolic adaptations to anemia of prematurity. J Pediatr. 1994 Aug;125(2):278–282. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(94)70211-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lay K. S., Bancalari E., Malkus H., Baker R., Strauss J. Acute effects of albumin infusion on blood volume and renal function in premature infants with respiratory distress syndrome. J Pediatr. 1980 Oct;97(4):619–623. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(80)80025-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marik P. E., Sibbald W. J. Effect of stored-blood transfusion on oxygen delivery in patients with sepsis. JAMA. 1993 Jun 16;269(23):3024–3029. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maynard N., Bihari D., Beale R., Smithies M., Baldock G., Mason R., McColl I. Assessment of splanchnic oxygenation by gastric tonometry in patients with acute circulatory failure. JAMA. 1993 Sep 8;270(10):1203–1210. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mizock B. A. Controversies in lactic acidosis. Implications in critically ill patients. JAMA. 1987 Jul 24;258(4):497–501. doi: 10.1001/jama.1987.03400040095029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mortola J. P., Frappell P. B., Dotta A., Matsuoka T., Fox G., Weeks S., Mayer D. Ventilatory and metabolic responses to acute hyperoxia in newborns. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1992 Jul;146(1):11–15. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm/146.1.11. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nexø E., Christensen N. C., Olesen H. Volume of blood removed for analytical purposes during hospitalization of low-birthweight infants. Clin Chem. 1981 May;27(5):759–761. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phillips H. M., Holland B. M., Abdel-Moiz A., Fayed S., Jones J. G., Turner T. L., Wardrop C. A., Cockburn F. Determination of red-cell mass in assessment and management of anaemia in babies needing blood transfusion. Lancet. 1986 Apr 19;1(8486):882–884. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(86)90988-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rackow E. C., Astiz M. E. Pathophysiology and treatment of septic shock. JAMA. 1991 Jul 24;266(4):548–554. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ronco J. J., Fenwick J. C., Tweeddale M. G., Wiggs B. R., Phang P. T., Cooper D. J., Cunningham K. F., Russell J. A., Walley K. R. Identification of the critical oxygen delivery for anaerobic metabolism in critically ill septic and nonseptic humans. JAMA. 1993 Oct 13;270(14):1724–1730. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russell J. A., Phang P. T. The oxygen delivery/consumption controversy. Approaches to management of the critically ill. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 1994 Feb;149(2 Pt 1):533–537. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm.149.2.8306058. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russell J. A., Ronco J. J., Lockhat D., Belzberg A., Kiess M., Dodek P. M. Oxygen delivery and consumption and ventricular preload are greater in survivors than in nonsurvivors of the adult respiratory distress syndrome. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1990 Mar;141(3):659–665. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm/141.3.659. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sasidharan P., Heimler R. Alterations in pulmonary mechanics after transfusion in anemic preterm infants. Crit Care Med. 1990 Dec;18(12):1360–1362. doi: 10.1097/00003246-199012000-00010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seear M., Wensley D., MacNab A. Oxygen consumption-oxygen delivery relationship in children. J Pediatr. 1993 Aug;123(2):208–214. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(05)81690-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stockman J. A., 3rd Anemia of prematurity. Current concepts in the issue of when to transfuse. Pediatr Clin North Am. 1986 Feb;33(1):111–128. doi: 10.1016/s0031-3955(16)34972-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strauss R. G., Sacher R. A., Blazina J. F., Blanchette V. S., Schloz L. M., Butch S. H., Hume H., Levy G. J., McMican A., Sotelo-Avila C. Commentary on small-volume red cell transfusions for neonatal patients. Transfusion. 1990 Jul-Aug;30(6):565–570. doi: 10.1046/j.1537-2995.1990.30690333489.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strauss R. G. Transfusion therapy in neonates. Am J Dis Child. 1991 Aug;145(8):904–911. doi: 10.1001/archpedi.1991.02160080082025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van de Water J. M., Philips P. A., Linton L. A., Borst R. W., Fisher W. R. Muscle surface pH monitoring. Evaluation and clinical application. Arch Surg. 1972 Jun;104(6):799–805. doi: 10.1001/archsurg.1972.04180060049013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waldman S., Krauss A. N., Auld P. A. Baroreceptors in preterm infants: their relationship to maturity and disease. Dev Med Child Neurol. 1979 Dec;21(6):714–722. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-8749.1979.tb01692.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wardrop C. A., Holland B. M., Jacobs S., Jones J. G. Optimization of the blood for oxygen transport and tissue perfusion in critical care. Postgrad Med J. 1992;68 (Suppl 2):S2–S6. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weg J. G. Oxygen transport in adult respiratory distress syndrome and other acute circulatory problems: relationship of oxygen delivery and oxygen consumption. Crit Care Med. 1991 May;19(5):650–657. doi: 10.1097/00003246-199105000-00011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Welch H. G., Meehan K. R., Goodnough L. T. Prudent strategies for elective red blood cell transfusion. Ann Intern Med. 1992 Mar 1;116(5):393–402. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-116-5-393. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu P. Y., Wong W. H., Guerra G., Miranda R., Godoy R. R., Preston B., Schoentgen S., Levan N. E. Peripheral blood flow in the neonate; 1. Changes in total, skin, and muscle blood flow with gestational and postnatal age. Pediatr Res. 1980 Dec;14(12):1374–1378. doi: 10.1203/00006450-198012000-00023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


