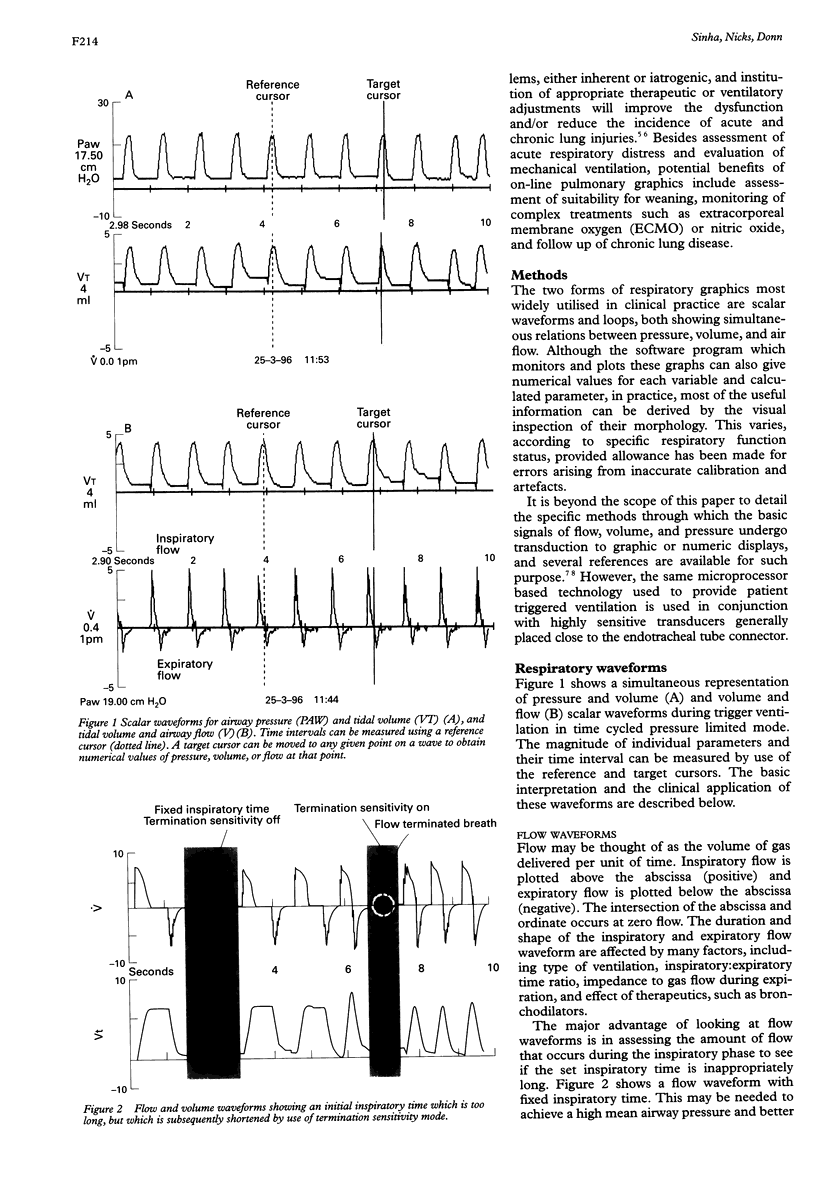
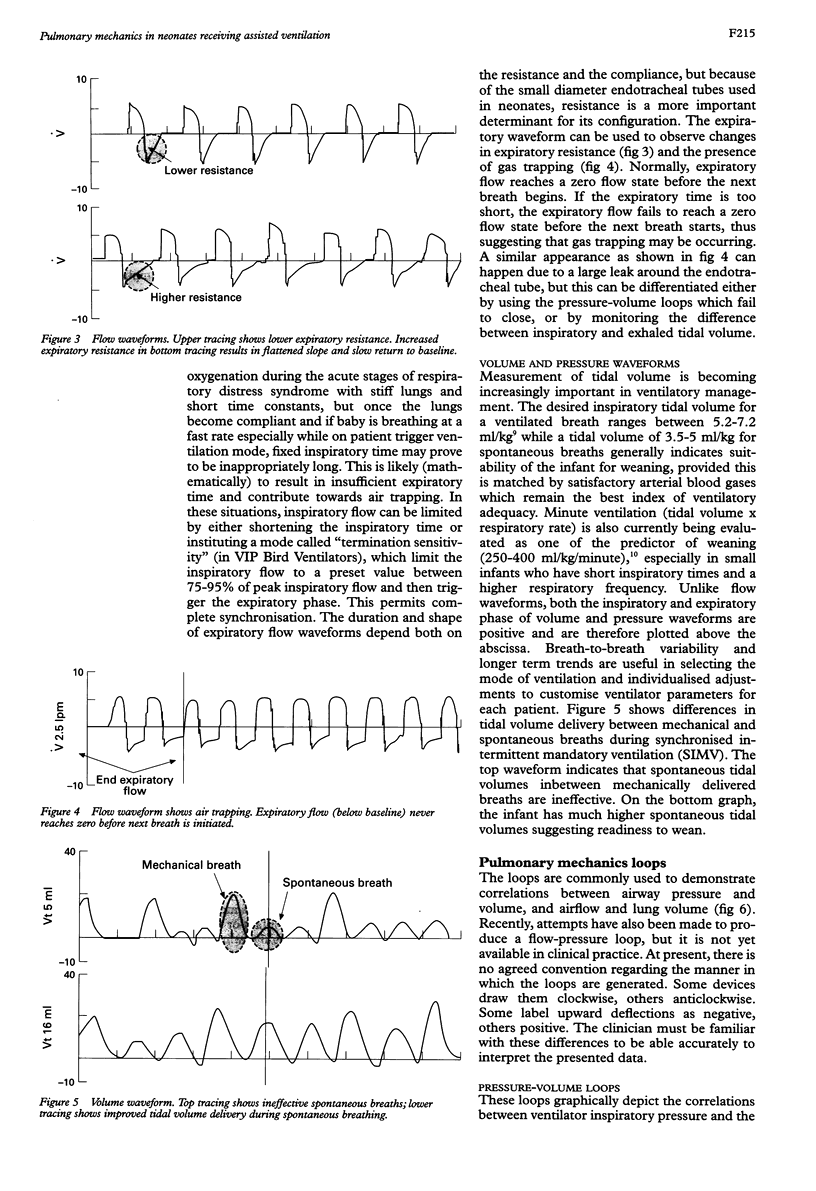
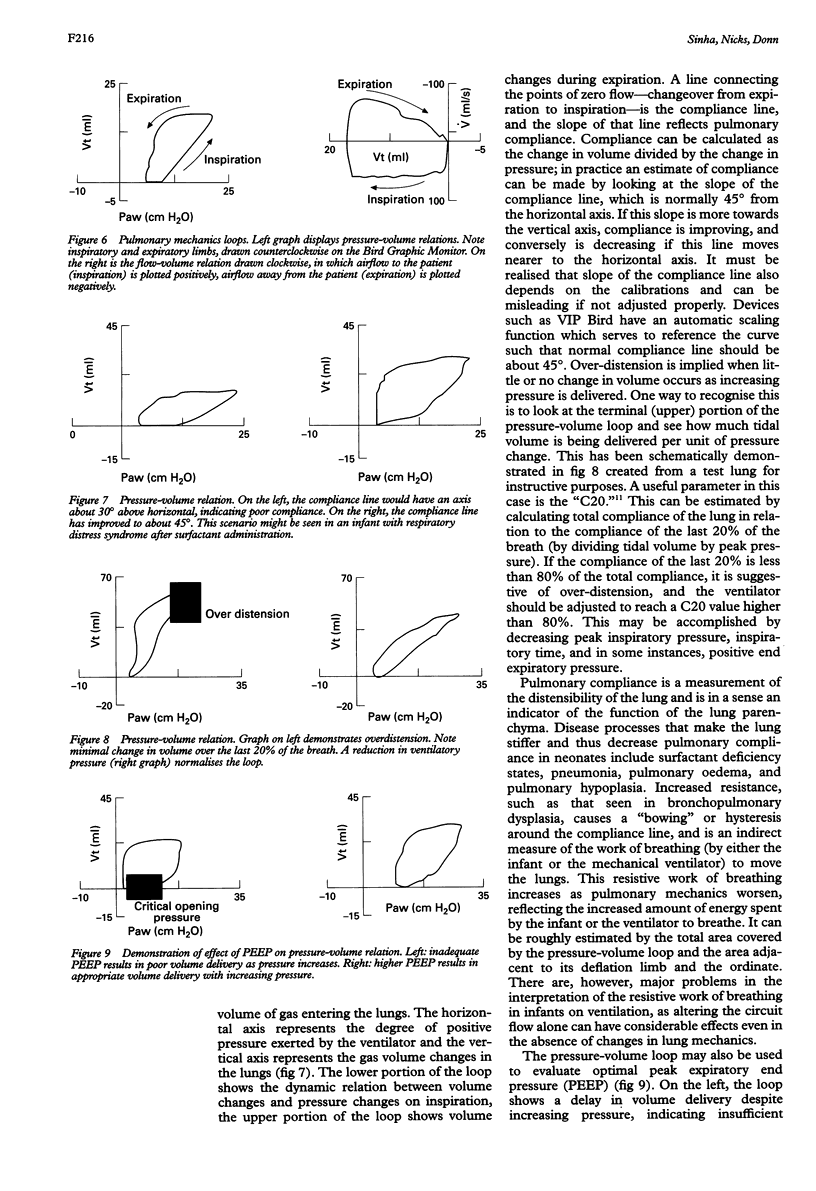
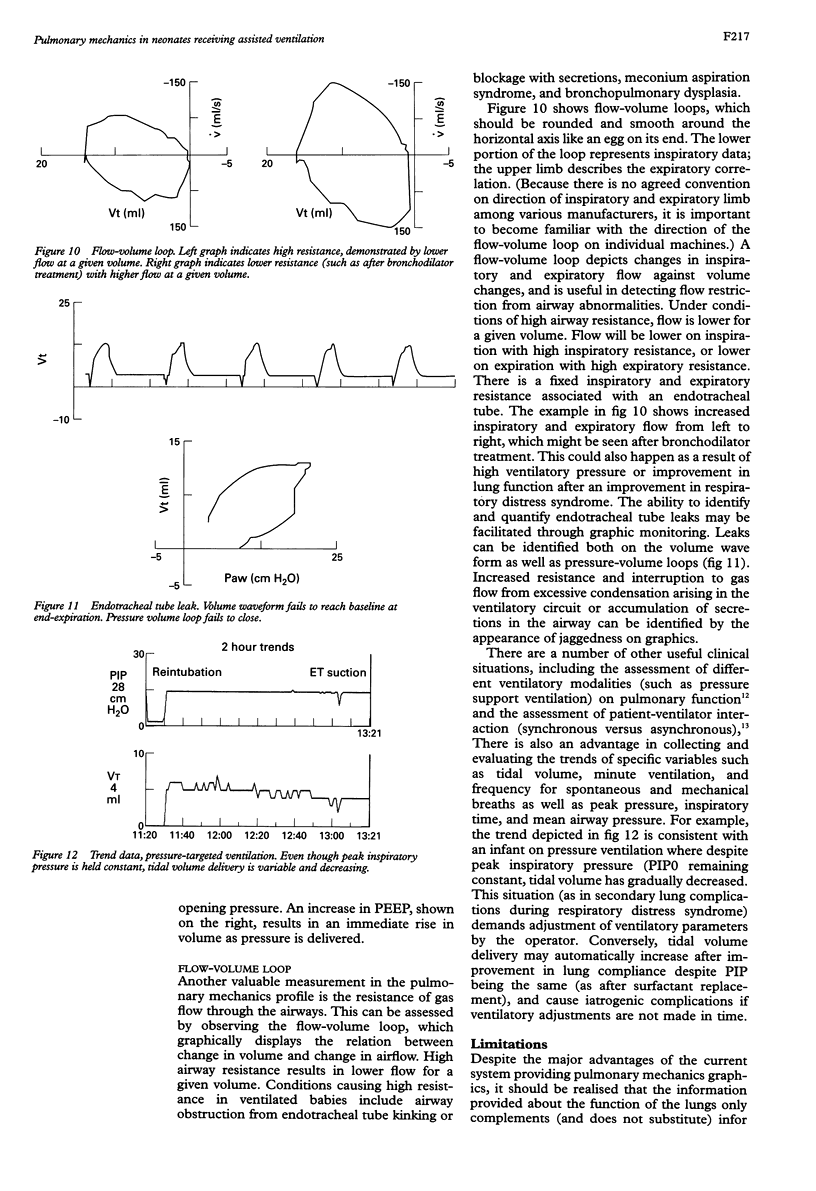
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Fisher J. B., Mammel M. C., Coleman J. M., Bing D. R., Boros S. J. Identifying lung overdistention during mechanical ventilation by using volume-pressure loops. Pediatr Pulmonol. 1988;5(1):10–14. doi: 10.1002/ppul.1950050104. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lloyd J. S., Cvetnic W. G. Continuous in-line respiratory monitoring in the critically ill preterm infant. Neonatal Intensive Care. 1994 May-Jun;7(3):14-6, 64. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacDonald K. D., Wirtschafter D. D. Continuous neonatal pulmonary mechanics with the BICORE CP-100 monitor. Neonatal Intensive Care. 1992 Nov-Dec;5(6):55–61. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicks J. J., Becker M. A., Donn S. M. Ventilatory management casebook. Bronchopulmonary dysplasias. Response to pressure support ventilation. J Perinatol. 1994 Nov-Dec;14(6):495–497. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


