Abstract
The genetic diversity of Borrelia burgdorferi sensu lato was assessed in a focus of Lyme borreliosis in southern Britain dominated by game birds. Ticks, rodents, and pheasants were analyzed for spirochete infections by PCR targeting the 23S-5S rRNA genes, followed by genotyping by the reverse line blot method. In questing Ixodes ricinus ticks, three genospecies of B. burgdorferi sensu lato were detected, with the highest prevalences found for Borrelia garinii and Borrelia valaisiana. B. burgdorferi sensu stricto was rare (<1%) in all tick stages. Borrelia afzelii was not detected in any of the samples. More than 50% of engorged nymphs collected from pheasants were infected with borreliae, mainly B. garinii and/or B. valaisiana. Although 19% of the rodents harbored B. burgdorferi sensu stricto and/or B. garinii in internal organs, only B. burgdorferi sensu stricto was transmitted to xenodiagnostic tick larvae (it was transmitted to 1% of the larvae). The data indicate that different genospecies of B. burgdorferi sensu lato can be maintained in nature by distinct transmission cycles involving the same vector tick species but different vertebrate host species. Wildlife management may have an influence on the relative risk of different clinical forms of Lyme borreliosis.
Lyme borreliosis is a tick-borne disease of humans in temperate climates of the northern hemisphere, whose causative agent, a spirochete belonging to the genus Borrelia, was described and named Borrelia burgdorferi in 1984 (13). On the basis of DNA-DNA relatedness and other molecular criteria, B. burgdorferi sensu lato is now considered to comprise at least nine genospecies and genomic groups (1, 30, 33). Phylogenetic analyses of various genes have suggested that the population structure of B. burgdorferi sensu lato is clonal (6). Here we ask whether the diverse spirochete strains have differential transmission patterns.
In Eurasia, six genospecies of B. burgdorferi sensu lato have been recorded; B. burgdorferi sensu stricto, Borrelia garinii, and Borrelia afzelii are causative agents of Lyme disease in humans (38), while the pathogenic potentials of Borrelia japonica, Borrelia valaisiana (formerly genomic group VS116 [39]), and Borrelia lusitaniae (formerly genomic group PotiB2 [18]) have not yet been demonstrated. Culturing Borrelia is commonly considered the “gold standard” for detection of B. burgdorferi sensu lato. Approaches based on the PCR (33), however, appear to be more accurate in assessing the diversity and distribution of borreliae in nature, as culturing may favor particular genotypes (27). Furthermore, strains of B. burgdorferi sensu lato prevalent in the United Kingdom (known to be variants of B. garinii, B. afzelii, B. burgdorferi sensu stricto, and B. valaisiana) have been found to be unusually difficult to isolate and culture from ticks and hosts by standard techniques (20). There is increasing evidence that the kinds of borreliae in ticks and hosts vary considerably (9, 14, 28, 29, 32, 33). In The Netherlands, for example, B. afzelii appears to be the most frequent genospecies in ticks, whereas in Ireland B. garinii and B. valaisiana seem to dominate (14, 32, 33). Surprisingly, B. burgdorferi sensu stricto, the most common genospecies in northeastern North America, appears to be comparatively rare in Europe and virtually absent in central and east Asia (7, 24, 26). The reasons for this variation remain unknown but may be related to the structure of the vertebrate host cenosis; it has been postulated that genospecies are associated with particular groups of vertebrate hosts, such as birds or rodents (24). This suggestion appears to conflict with the observation that different genospecies of B. burgdorferi sensu lato may coexist in individual vertebrate hosts (7, 26). Such concurrent infections, however, do not imply that the transmissibilities of the genospecies or strains between hosts and ticks are equal; any differential transmission of the genospecies in the various natural tick-host systems would influence the prevalence of the genospecies and the degree of ecological diversity observed. While the transmission behavior of B. burgdorferi sensu stricto has been studied in detail with both laboratory and natural rodent hosts (5, 16, 22), the relative transmissibilities of other genospecies of B. burgdorferi sensu lato in rodents and other hosts have not been investigated previously.
Small mammals, particularly mice, have always been considered the principal hosts of B. burgdorferi sensu lato (10, 16, 17, 22, 25), but a role for avian hosts as reservoirs of B. burgdorferi sensu lato is gradually gaining credence (11, 12, 15, 31, 36) despite early claims to the contrary (21, 23). The potential role of birds in the transmission dynamics of B. burgdorferi sensu lato is substantial. In England, approximately 20 million farm-reared pheasants (Phasianus colchicus) are released into the woodlands each year to supplement natural populations for recreational shooting. As a result, pheasants constitute the vast majority of the land-based avifauna, especially in woodlands of southern England (34), and are present alongside high densities of mammals, such as woodmice, voles, squirrels, and deer. All of these hosts feed considerable numbers of Ixodes ricinus, the European vector of B. burgdorferi sensu lato (4, 15, 31).
In this paper, we present field data that reveal differential transmission of B. burgdorferi sensu lato genospecies through pheasant and rodent populations to different developmental stages of I. ricinus ticks.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Study site.
Animals were caught in a Dorset woodland 10 miles west of Fordingbridge (1°56′W, 50°53′N) within a focus of Lyme borreliosis in southern England. This site contains mainly oak (Quercus spp.), ash (Fraxinus excelsior), and patchy conifer plantations (mainly Pinus sylvestris), and the undergrowth is dominated by bluebells (Hyacinthoides non-scripta) and dog’s mercury (Mercurialis perennis) in the spring and bracken fern (Pteridium aquilinum) from late summer until winter.
Rodents.
In May 1996, 47 rodents belonging to the species Apodemus sylvaticus (woodmouse) and Clethrionomys glareolus (bank vole) were trapped alive with Longworth traps (Penlon Ltd., Abingdon, United Kingdom) and taken to a laboratory. The spirochetal infectivity of the rodents for ticks was assayed by larval xenodiagnosis (16) commencing 1 week after trapping; 30 uninfected I. ricinus larvae (colony maintained at the NERC Institute of Virology and Environmental Microbiology, Oxford, United Kingdom) were introduced to each animal. After repletion, the engorged ticks were kept for 14 days above a saturated solution of MgSO4 at 18°C and then frozen at −20°C. The rodents were finally autopsied under aseptic conditions in a building in which no Borrelia DNA was handled. Biopsies from internal organs (heart, urinary bladder, kidney, brain) and earlobes were taken and stored at −20°C until PCR analysis.
Birds.
Thirty adult male pheasants were shot in April 1996. All of the I. ricinus ticks infesting these birds were recorded and allowed to drop off naturally. No fully engorged larvae or adult ticks were recovered, but 150 fed nymphs from the 30 birds (five ticks per bird) were collected and kept alive for 2 weeks before they were preserved in 70% ethanol at −20°C. Of these, the 122 most fully engorged ticks were selected and analyzed for the presence of spirochetal DNA.
Questing ticks.
I. ricinus ticks were collected fortnightly by blanket dragging from the same site as their vertebrate hosts. Some of these ticks (larvae collected in the summer of 1995, nymphs collected in the spring, summer, and autumn of 1995 and spring of 1996, and adults collected in the autumn of 1996) were analyzed to determine whether they were infected with particular genospecies of B. burgdorferi sensu lato by PCR and the reverse line blot method.
PCR and reverse line blotting.
Genomic DNA was extracted from ticks and animal biopsies by alkaline hydrolysis (8). A PCR with a nested set of primers (primers 23SN1 [5′-ACCATAGACTCTTATTACTTTGAC], 23SC1 [5′-TAAGCTGACTAATACTAATTACCC], 23SN2 [5′-ACCATAGACTCTTATTACTTTGACCA], and 5SC2 [5′-biotin-GAGAGTAGGTTATTGCCAGGG]) was performed by targeting the tandemly duplicated rrf (5S)-rrl (23S) rRNA gene clusters (19, 30, 33). All of the steps were separated temporally and spatially (different laboratories) and were performed under strictly aseptic conditions. As B. japonica is not present in Europe, a culture of this genospecies was used as a positive control in order to avoid DNA contamination. Negative controls at a ratio of approximately 2:3 were incorporated into the PCR procedures at the DNA extraction level and at the first- and second-round amplification levels and into the electrophoresis of PCR products. All amplicons were electrophoresed with 2% agarose gels, stained with ethidium bromide, and visualized by UV transillumination. All samples that produced bands at approximately 380 and/or 225 to 270 bp were subjected to DNA-DNA hybridization by the reverse line blot method, a modification of the reverse dot blot method performed with a line blotter (Miniblotter 45; Immunetics, Cambridge, Mass.). Briefly, biotin-labelled amplicons were hybridized with DNA probes which were covalently bound to an activated membrane by the 5′ aminolink (a) group. The probes were specific for B. burgdorferi sensu lato (5′-a-CTTTGACCATATTTTTATCTTCCA), B. burgdorferi sensu stricto (5′-a-AACACCAATATTTAAAAAACATAA), B. afzelii (5′-a-AACATTTAAAAAATAAATTCAAGG), B. garinii (5′-a-AACATGAACATCTAAAAACATAAA), and B. valaisiana (5′-a-CATTAAAAAAATATAAAAAATAAATTTAAGG). PCR products of DNA templates derived from cloned cultures of B. burgdorferi sensu stricto, B. garinii, B. afzelii, and B. japonica were included as positive controls for the reverse line blot. After incubation with streptavidin-peroxidase conjugate (Boehringer Mannheim GmbH, Mannheim, Germany), hybrids were visualized with an enhanced chemiluminescence system (type ECL; Amersham Life Sciences, Amersham, United Kingdom).
Inhibition of specific DNA amplification by an excess of host-derived and/or tick-derived tissue was tested with flat and engorged ticks and rodent tissues spiked with variable numbers of cultured B. burgdorferi sensu stricto, B. garinii, B. afzelii, and B. japonica. Consistent with previous studies (2, 35, 36), high concentrations of tissue in a lysate (>10 mg/ml), particularly tissue from blood-fed ticks, proved to be inhibitory for the PCR (data not shown), so all DNA lysates were diluted appropriately to adjust the sensitivity of the PCR to the amount of DNA equivalent to two spirochetes in a given reaction mixture.
RESULTS
A total of 780 questing I. ricinus ticks (100 larvae, 100 adults, and 580 nymphs) were analyzed for B. burgdorferi sensu lato infection by PCR. The levels of infection with B. burgdorferi sensu lato in larvae and nymphs were 1 and 2.6%, respectively (not significantly different), but the level of infection in questing adult ticks was significantly higher (16%) (χ2 = 14.70, P < 0.001) (Table 1). All of the larvae and adults and 200 of the nymphs were subjected to genotyping, which revealed three genospecies, B. burgdorferi sensu stricto, B. garinii, and B. valaisiana (Table 1). The most abundant genospecies was B. garinii (found in all developmental stages of I. ricinus), followed by B. valaisiana, while B. burgdorferi sensu stricto was rare (≤1%) and there was no detectable difference in the levels of B. burgdorferi sensu stricto infection in nymphs and adult ticks. The levels of B. garinii and B. valaisiana infection in questing larvae and nymphs were low (≤3.0%), but the level of infection in questing adults was significantly higher (13%) (χ2 = 25.85, P < 0.001). Three of the infected adult ticks were infected with both B. garinii and B. valaisiana, and two B. burgdorferi sensu lato infections in adult ticks could not be identified to genospecies. B. afzelii was not detected in any tick.
TABLE 1.
Levels of infection for four genospecies of B. burgdorferi sensu lato in I. ricinus collected in 1995 and 1996 and in xenodiagnostic ticks
| Tick developmental stage | Collection season | No. examined | % Infected with:
|
||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
B. burgdorferi sensu lato |
B. burgdorferi sensu stricto | B. garinii | B. afzelii | B. valaisiana | B. garinii + B. valaisiana | Untypeable borreliaef |
|||
| Questing larvae | Summer ’95 | 100 | 1.0 | 0 | 1.0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Questing nymphsa | Spring, summer, and autumn ’95 | 380 | 2.1 | NAg | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA |
| Spring ’95 | 100 | 3.0 | 0 | 3.0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| Spring ’96 | 100 | 4.0 | 1.0 | 2.0 | 0 | 1.0 | 0 | 0 | |
| Questing adults | Autumn ’96 | 100 | 16.0 | 1.0 | 10.0d | 0 | 6.0d | 3.0e | 2.0 |
| Larvae fed on rodentsb | Spring ’96 | 771 | 1.3 | 1.3 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Nymphs fed on pheasants | Spring ’96 | 122c | 56.6 | 0 | 37.7d | 0 | 27.0d | 10.6e | 2.5 |
The mean level of infection of B. burgdorferi sensu lato in all questing nymphs was 2.6% (15 of 580 nymphs).
Xenodiagnostic larvae were introduced to 47 wild rodents trapped alive.
Number of pheasant-derived engorged nymphs tested.
Ticks had single and mixed infections.
Ticks had only mixed infections.
The borreliae did not hybridize with species-specific DNA probes.
NA, not applicable.
Spirochetal DNA was detected in 5 of 26 C. glareolus individuals (19.2%) and in 4 of 21 A. sylvaticus individuals (19.0%). Two genospecies were detected, B. burgdorferi sensu stricto and B. garinii. All nine infected rodents were positive for B. garinii (seven brain infections and two kidney infections) (Fig. 1), while two animals had mixed infections with B. garinii and B. burgdorferi sensu stricto in their brains (Table 2). None of the skin, urinary bladder, and heart samples proved to be infected.
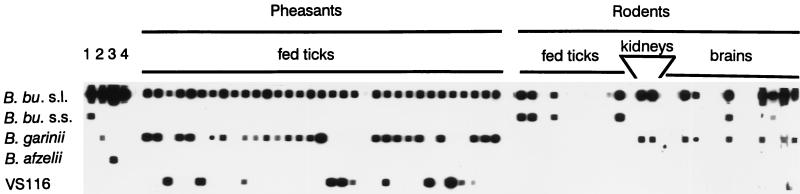
FIG. 1.
Reverse line blot to identify the genospecies of B. burgdorferi sensu lato prevalent in ticks and host tissues. Lanes 1 to 4 contained positive controls that were PCR products of cloned isolates (lane 1, B. burgdorferi sensu stricto; lane 2, B. garinii; lane 3, B. afzelii; lane 4, B. japonica). The results for hybrids of representative PCR products from pheasant- and rodent-derived ticks and from tissues are also shown. Untypeable samples reacted with the B. burgdorferi sensu lato-specific DNA probe, but not with any of the genospecies-specific probes. Genomic group VS116 has recently been named B. valaisiana (39) and was not included as a positive control in the blot shown. Abbreviations: B. bu. s.l., B. burgdorferi sensu lato; B. bu. s.s., B. burgdorferi sensu stricto.
TABLE 2.
Results of PCR and genotyping of tissues and xenodiagnostic tick larvae from wild-trapped A. sylvaticus and C. glareolus
| Animal species | Animal no. | Results of PCR and genotypinga
|
|||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Heart | Bladder | Kidney | Brain | Skin | Xenodiagnostic ticks | ||
| A. sylvaticus | 1 | − | NT | − | − | − | − |
| 2 | − | − | − | − | − | − | |
| 3 | − | − | − | − | − | − | |
| 4 | − | NT | − | − | − | − | |
| 5 | − | NT | − | − | − | − | |
| 6 | − | − | − | − | − | − | |
| 7 | − | NT | − | − | − | − | |
| 8 | − | NT | − | − | − | − | |
| 9 | − | − | − | − | − | − | |
| 10 | − | − | − | − | − | B.b.ss | |
| 11 | − | NT | − | − | − | − | |
| 12 | − | − | − | − | − | − | |
| 13 | − | − | − | − | − | − | |
| 14 | − | − | − | − | − | − | |
| 15 | − | − | − | B.g. | − | − | |
| 16 | − | − | − | B.g. + B.b.ss | − | − | |
| 17 | − | − | − | B.g. | − | − | |
| 18 | − | − | − | B.g. | − | − | |
| 19 | − | − | − | − | − | − | |
| 20 | − | − | − | − | − | − | |
| 21 | − | − | − | − | − | − | |
| C. glareolus | 22 | − | − | − | − | − | − |
| 23 | − | − | − | − | − | − | |
| 24 | − | NT | − | − | − | − | |
| 25 | − | − | − | − | − | − | |
| 26 | − | − | − | − | − | − | |
| 27 | − | NT | − | − | − | − | |
| 28 | − | NT | − | − | − | − | |
| 29 | − | − | − | B.g. | − | − | |
| 30 | − | − | − | − | − | − | |
| 31 | − | − | − | − | − | − | |
| 32 | − | − | − | B.g. | − | − | |
| 33 | − | − | − | − | − | B.b.ss | |
| 34 | − | − | − | − | − | B.b.ss | |
| 35 | − | NT | − | − | − | − | |
| 36 | − | − | − | − | − | − | |
| 37 | − | − | − | − | − | − | |
| 38 | − | − | − | − | − | − | |
| 39 | − | NT | − | − | − | − | |
| 40 | − | − | − | − | − | − | |
| 41 | − | NT | − | − | − | − | |
| 42 | − | − | − | − | − | − | |
| 43 | − | NT | − | − | − | − | |
| 44 | − | − | − | B.g. + B.b.ss | − | B.b.ss | |
| 45 | − | − | − | − | − | − | |
| 46 | − | − | B.g. | − | − | − | |
| 47 | − | − | B.g. | − | − | − | |
B.b.ss, B. burgdorferi sensu stricto; B.g., B. garinii; −, negative result; NT, not tested.
Spirochete-free I. ricinus larvae were introduced to the 47 rodents (30 larvae per animal). A total of 771 engorged larvae were analyzed by PCR. Ten of these were positive for B. burgdorferi sensu lato, giving an overall level of infection in xenodiagnostic ticks of 1.3% (Table 1). All positive samples were identified as containing B. burgdorferi sensu stricto (Fig. 1). The infected xenodiagnostic larvae came from four individual rodents, only one of which had tested positive for tissue infections with B. burgdorferi sensu lato (Table 2).
Of the 122 fed I. ricinus nymphs from pheasants that were analyzed, 69 (56.6%) were infected with B. burgdorferi sensu lato. The organisms in all but three of these samples could be identified to species; 33 ticks were infected with B. garinii, 20 ticks were infected with B. valaisiana, and 13 ticks were found to have mixed infections with both of these genospecies (Table 1). Of the 30 birds, 27 yielded at least one Borrelia-infected tick; 14 birds yielded at least one tick infected with B. garinii and another tick infected with B. valaisiana or ticks infected concurrently with both genospecies, while 13 birds yielded ticks infected with only one of the two genospecies.
None of the negative controls incorporated into the PCR procedures performed throughout the present study gave a positive signal.
In summary, the transmission of spirochetes to ticks from rodents and the transmission of spirochetes to ticks from pheasants differed both qualitatively and quantitatively. Not only were different genospecies of B. burgdorferi sensu lato transmitted, but the level of infection by any genospecies was significantly lower in xenodiagnostic larvae that fed on rodents (1.3%) than in nymphs that had fed on pheasants (56.6%) (χ2 = 398.6, df = 1, P ≪ 0.001).
DISCUSSION
This study showed that three different genospecies of the B. burgdorferi sensu lato species complex, B. burgdorferi sensu stricto, B. garinii, and B. valaisiana (formerly genomic group VS116), are circulating in an endemic focus of Lyme borreliosis in southern England. B. afzelii, one of the most abundant genospecies in continental Europe, was not detected. Although 19% of the rodents harbored B. garinii, only B. burgdorferi sensu stricto was transmitted by the rodents to ticks. The infectivity of the rodent population was surprisingly low; only 1.3% of the xenodiagnostic ticks were infected. In contrast, more than 50% of the nymphal ticks derived from pheasants were infected with B. garinii and B. valaisiana. This pattern and the matching genotypic composition of B. burgdorferi sensu lato in the questing ticks indicate that B. garinii and B. valaisiana are preferentially transmitted to ticks by pheasants, while B. burgdorferi sensu stricto appears to be maintained at a low level by a rodent-tick cycle.
The detection of spirochetes in the present study was based on successful amplification of spirochetal DNA, which cannot distinguish between viable and nonviable borreliae. However, as all of the ticks were allowed to engorge and digest their bloodmeal for 14 days postrepletion, it is unlikely that the PCR detected only naked DNA from spirochetes in the ticks’ midguts, particularly because the target of this PCR is located on the chromosome rather than on a plasmid (19, 30). Similarly, the presence of naked chromosomal DNA in host tissues was unlikely as the animals were autopsied more than 2 weeks after trapping, their last possible contact with infected ticks.
The observed level of infection with B. burgdorferi sensu lato in questing larval I. ricinus, 1%, is within the range previously described for endemic foci of Lyme borreliosis in Europe (17, 32), while the level of infection in questing nymphs, 2.6%, appears to be rather low compared with the levels of infection in endemic foci in North America (37) and continental Europe (10, 17, 31). The overall level of infection in adults was fivefold higher than the level of infection in nymphs, indicating that hosts of I. ricinus nymphs were particularly infective. Within the questing tick population, B. garinii was the most frequent genospecies and was detected at all developmental stages, followed by B. valaisiana. The levels of infection for both of these genospecies were markedly higher in adults than in questing nymphs. In contrast, the level of infection with B. burgdorferi sensu stricto, the most abundant genospecies in northern North America, did not exceed 1% even in adult ticks. This pattern of infection indicates that the hosts that were feeding large numbers of nymphal ticks were selectively infective for B. garinii and B. valaisiana.
I. ricinus larvae feed in large numbers on mice and voles, in addition to squirrels and deer (4, 10, 17). The low level of infection with B. burgdorferi sensu lato in questing nymphs, as found in the present study, is consistent with the low infectivity of the trapped small rodents as assessed by larval xenodiagnosis. Compared with the data from the present study, the reservoir capacity of the rodent populations in foci in continental Europe (10, 17) and many parts of northern North America (22) is much higher. This may be related to the particular genospecies of B. burgdorferi sensu lato circulating in each location; B. afzelii, for which rodents are particularly transmission competent, is widely distributed in continental Europe (9, 32, 33), whereas in our study site B. afzelii was not found. In North America, rodents, particularly rodents belonging to the genus Peromyscus, are highly transmission competent for B. burgdorferi sensu stricto (5, 22), whereas European rodent species were found to have a lower degree of reservoir competence and reservoir capacity for this genospecies (16), perhaps explaining its rarity in the present study site and throughout Eurasia (7, 24, 26). B. garinii, on the other hand, has the potential to persist in rodents concurrently with other genospecies (7, 26), but there is emerging evidence that it is only rarely passed from rodents to ticks (9, 25, 26). This is consistent with the results of the present study, in which 19% of the small rodents were infected with B. garinii but none of the 771 xenodiagnostic I. ricinus ticks acquired B. garinii from these animals. Moreover, B. garinii infections were not detected in the skin of the rodents, but were confined to internal organs, particularly the brain. None of the rodents or the xenodiagnostic ticks fed on these rodents was found to be infected with B. valaisiana, despite the prevalence of this organism in questing I. ricinus ticks collected in the same study site. This finding, together with the fact that B. valaisiana has never been detected in rodent hosts, may indicate that this genospecies does not survive and persist in small mammals.
Ground-foraging birds, particularly pheasants, which may occur in the United Kingdom at densities up to 50 birds per hectare (34), constitute a major part of the tick host community in the woodland studied. Pheasants feed more than four times as many nymphs as larvae of I. ricinus (15). In the present study pheasants were highly infective to nymphs of I. ricinus. The vast majority of bird-derived infected nymphs carried B. garinii and B. valaisiana, but not B. burgdorferi sensu stricto. Most infraspecific variants of B. garinii, the most polymorphic genospecies of the B. burgdorferi sensu lato species complex (40), have previously been associated with ticks derived from birds (24, 28, 29). In the present study mixed infections in ticks were found only for B. garinii and B. valaisiana, suggesting that the transmission of these two genospecies is associated. This finding is consistent with the results of a recent study in Ireland on mixed infections of B. garinii and B. valaisiana in questing ticks (14), which suggested that birds are reservoirs of B. valaisiana. To our knowledge, the present study is the first study which provides direct evidence that there is an avian reservoir host for B. valaisiana.
The reason for the complete absence of B. afzelii in the present study is unclear, but the lack of B. afzelii may also be related to avian hosts; in the study site used, it is possible that a large and dense pheasant population substantially reduces the basic reproduction number of B. afzelii. Thus, it is possible that this genospecies is taken out of the ecosystem by means of a zooprophylactic role of such birds for B. afzelii, despite the presence of reservoir-competent rodents (mice, voles, and squirrels) in the study site. A lack of reservoir competence and a possible zooprophylactic role of ground-foraging birds in relation to B. burgdorferi sensu stricto and B. afzelii, respectively, would be consistent with results of previous studies on the reservoir incompetence of birds (21, 23).
Besides rodents and pheasants, other tick host species undoubtedly play a role in generating the observed pattern of species diversity of B. burgdorferi sensu lato. For example, the high level of infection (57%), mainly infection with B. garinii and/or B. valaisiana, in nymphs that fed on pheasants was reduced to 16% in questing adult ticks. This was probably the result of dilution by uninfected nymphs that fed on other hosts not competent to transmit these genospecies. Apart from deer, squirrels are likely candidates for this role, because they feed large numbers of nymphs (4) and are competent to transmit B. burgdorferi sensu lato but apparently are not competent to transmit B. garinii (3).
The overall pattern which emerged from the present study is one of differential transmission and maintenance of various genospecies of B. burgdorferi sensu lato depending on the variable interactions between the vertebrate host species and (i) each genospecies or (ii) each developmental stage of the tick. Many hosts may be exposed to multiple tick bites, followed by the possible establishment of mixed infections (7, 26). However, there is increasing evidence that the various host species do not transmit all B. burgdorferi sensu lato strains to ticks with equal efficiency (5, 16, 21–25, 29). Cautions about the transfer of parameter values (e.g., transmission coefficients) from system to system for use in models (31) are supported by these results. The mechanisms underlying the apparent differential transmission of the genospecies of B. burgdorferi sensu lato by the various groups of mammalian and avian hosts remain to be determined.
The genetic diversity of B. burgdorferi sensu lato and the strain-specific interaction with each host species add additional elements to the considerable ecological diversity and thus variation in risk factors for humans of this zoonotic tick-borne disease. For example, in a site dominated by pheasants, such as the site analyzed in the present study, there is potentially a greater risk of neuroborreliosis associated with increased prevalence of B. garinii (38). On the other hand, the finding that many ground-foraging birds (pheasants in this study) primarily feed nymphs which, later as questing adults, are not considered as great a risk to humans as the less easily detected and more numerous nymphs may counterbalance the inflated risk of B. garinii infection for humans.
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
This study was supported by grant GR3/09626 from the Natural Environment Research Council, United Kingdom, by grant 044488/Z/95/A from The Wellcome Trust, London, United Kingdom, and by grant EC Biomed BMHI-CT93-1183 from the Commission of the European Union.
We thank A. P. Van Dam (Amsterdam, The Netherlands) and M. M. Simon (Freiburg, Germany) for providing strains of B. burgdorferi sensu lato.
REFERENCES
- 1.Baranton G, Postic D, Saint Girons I, Boerlin P, Piffaretti J-C, Assous M, Grimont P A D. Delineation of Borrelia burgdorferi sensu stricto, Borrelia garinii sp. nov., and group VS461 associated with Lyme borreliosis. Int J Syst Bacteriol. 1992;42:378–383. doi: 10.1099/00207713-42-3-378. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Cogswell F B, Bantar C E, Hughes T G, Gu Y, Philipp M T. Host DNA can interfere with detection of Borrelia burgdorferi in skin biopsy specimens by PCR. J Clin Microbiol. 1996;34:980–982. doi: 10.1128/jcm.34.4.980-982.1996. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Craine N G, Nuttall P A, Marriott A C, Randolph S E. Rôle of grey squirrels and pheasants in the transmission of Borrelia burgdorferi sensu lato, the Lyme disease spirochaete, in the U.K. Folia Parasitol (Prague) 1997;44:155–160. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Craine N G, Randolph S E, Nuttall P A. Seasonal variation in the rôle of grey squirrels as hosts of Ixodes ricinus, the tick vector of the Lyme disease spirochaete, in a British woodland. Folia Parasitol (Prague) 1995;42:73–80. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Donahue J G, Piesman J, Spielman A. Reservoir competence of white-footed mice for Lyme disease spirochetes. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1987;36:92–96. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1987.36.92. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Dykuizen D E, Polin D S, Dunn J J, Wilske B, Preac-Mursic V, Dattwyler R J, Luft B. Borrelia burgdorferi is clonal: implications for taxonomy and vaccine development. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1993;90:10163–10167. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.21.10163. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Gorelova B N, Korenberg E I, Kovalevskii Y V, Shcherbakov S V. Small mammals as reservoir hosts for borrelia in Russia. Zentralbl Bakteriol. 1995;282:315–322. doi: 10.1016/s0934-8840(11)80132-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Guy E, Stanek G. Detection of Borrelia burgdorferi in Lyme disease patients by PCR. J Clin Pathol. 1991;44:611–614. doi: 10.1136/jcp.44.7.610. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Humair P F, Peter O, Wallich R, Gern L. Strain variation of Lyme disease spirochetes isolated from Ixodes ricinus ticks and rodents collected in two endemic areas in Switzerland. J Med Entomol. 1995;32:433–438. doi: 10.1093/jmedent/32.4.433. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Humair P F, Turrian M N, Aeschlimann A, Gern L. Borrelia burgdorferi in a focus of Lyme borreliosis: epizootiologic contribution of small mammals. Folia Parasitol (Prague) 1993;40:65–70. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Humair P F, Turrian M N, Aeschlimann A, Gern L. Ixodes ricinus immatures on birds in a focus of Lyme borreliosis. Folia Parasitol (Prague) 1993;40:237–242. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Isogai E, Tanaka S, Braga III I S, Itakura C, Isogai H, Kimura K, Fijii N. Experimental Borrelia garinii infection of Japanese quail. Infect Immun. 1994;62:3580–3582. doi: 10.1128/iai.62.8.3580-3582.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Johnson R C, Schmid G P, Hyde F W, Steigerwalt A G, Brenner D J. Borrelia burgdorferi sp. nov.: etiologic agent of Lyme disease. Int J Syst Bacteriol. 1984;34:496–497. [Google Scholar]
- 14.Kirstein F, Rijpkema S G T, Molkenboer M, Gray J. Local variations in the distribution and prevalence of Borrelia burgdorferi sensu lato genomospecies in Ixodes ricinus ticks. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1997;63:1102–1106. doi: 10.1128/aem.63.3.1102-1106.1997. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Kurtenbach K, Carey D, Hoodless A, Nuttall P A, Randolph S E. Competence of pheasants as reservoirs for Lyme disease spirochetes. J Med Entomol. 1998;35:77–81. doi: 10.1093/jmedent/35.1.77. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Kurtenbach K, Dizij A, Seitz H M, Margos G, Moter S E, Kramer M D, Wallich R, Schaible U E, Simon M M. Differential immune responses to Borrelia burgdorferi in European wild rodent species influence spirochete transmission to Ixodes ricinus L. (Acari: Ixodidae) Infect Immun. 1994;62:5344–5352. doi: 10.1128/iai.62.12.5344-5352.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Kurtenbach K, Kampen H, Dizij A, Arndt S, Seitz H M, Schaible U E, Simon M M. Infestation of rodents with larval Ixodes ricinus (Acari: Ixodidae) is an important factor in the transmission cycle of Borrelia burgdorferi s.l. in German woodlands. J Med Entomol. 1995;32:807–817. doi: 10.1093/jmedent/32.6.807. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Le Fleche A, Postic D, Girardet K, Peter O, Baranton G. Characterization of Borrelia lusitaniae sp. nov. by 16S ribosomal DNA sequence analysis. Int J Syst Bacteriol. 1997;47:921–925. doi: 10.1099/00207713-47-4-921. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Liveris D, Gazumyan A, Schwartz I. Molecular typing of Borrelia burgdorferi sensu lato by PCR-restriction fragment length polymorphism analysis. J Clin Microbiol. 1995;33:589–595. doi: 10.1128/jcm.33.3.589-595.1995. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Livesley M A, Carey D, Gern L, Nuttall P A. Problems of isolating Borrelia burgdorferi from ticks collected in United Kingdom foci of Lyme disease. Med Vet Entomol. 1994;8:172–178. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2915.1994.tb00159.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Mather T N, Telford III S R, MacLachlan A B, Spielman A. Incompetence of catbirds as reservoirs for the Lyme disease spirochete (Borrelia burgdorferi) J Parasitol. 1989;75:66–69. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Mather T N, Wilson M L, Moore S I, Ribeiro J M C. Comparing the relative potential of rodents as reservoirs of the Lyme disease spirochete (Borrelia burgdorferi) Am J Epidemiol. 1989;130:143–150. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a115306. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Matuschka F-R, Spielman A. Loss of Lyme disease spirochetes from Ixodes ricinus ticks feeding on European blackbirds. Exp Parasitol. 1992;74:151–158. doi: 10.1016/0014-4894(92)90042-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Nakao M, Miyamoto K, Fukunaga M. Lyme disease spirochetes in Japan: enzootic transmission cycles in birds, rodents, and Ixodes persulcatus ticks. J Infect Dis. 1994;170:878–882. doi: 10.1093/infdis/170.4.878. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Nakao M, Miyamoto K, Fukunaga M. Borrelia japonica in nature: genotypic identification of spirochetes isolated from Japanese small mammals. Microbiol Immunol. 1994;38:805–808. doi: 10.1111/j.1348-0421.1994.tb01861.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Nakao M, Miyamoto K. Mixed infection of different Borrelia species among Apodemus speciosus mice in Hokkaido, Japan. J Clin Microbiol. 1995;33:490–492. doi: 10.1128/jcm.33.2.490-492.1995. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Norris D E, Johnson B J B, Piesman J, Maupin G O, Clark J L, Black W C., IV Culturing selects for specific genotypes of Borrelia burgdorferi in an enzootic cycle in Colorado. J Clin Microbiol. 1997;35:2359–2364. doi: 10.1128/jcm.35.9.2359-2364.1997. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Olsen B, Duffy D C, Jaenson T G T, Gylfe A, Bonnedahl J, Bergström S. Transhemispheric exchange of Lyme disease spirochetes by seabirds. J Clin Microbiol. 1995;33:3270–3274. doi: 10.1128/jcm.33.12.3270-3274.1995. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Olsen B, Jaenson T G T, Noppa L, Bunikis J, Bergström S A. A Lyme borreliosis cycle in seabirds and Ixodes uriae ticks. Nature (London) 1993;362:340–342. doi: 10.1038/362340a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Postic D, Assous M, Grimont P A D, Baranton G. Diversity of Borrelia burgdorferi sensu lato evidenced by restriction fragment length polymorphism of rrf(5S)-rrl(23S) intergenic spacer amplicons. Int J Syst Bacteriol. 1994;44:743–752. doi: 10.1099/00207713-44-4-743. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Randolph S E, Craine N G A. A general framework for comparative quantitative studies on the transmission of tick-borne diseases, using Lyme borreliosis in Europe as an example. J Med Entomol. 1995;32:765–777. doi: 10.1093/jmedent/32.6.765. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Rijpkema S G T, Bruinink H. Detection of Borrelia burgdorferi sensu lato by PCR in questing Ixodes ricinus larvae from the Dutch North Sea island of Ameland. Exp Appl Acarol. 1996;20:381–385. doi: 10.1007/BF00130550. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Rijpkema S G T, Molkenboer M J C H, Schouls L M, Jongejan F, Schellekens J F P. Simultaneous detection and genotyping of three genomic groups of Borrelia burgdorferi sensu lato in Dutch Ixodes ricinus ticks by characterization of the amplified intergenic spacer region between 5S and 23S rRNA genes. J Clin Microbiol. 1995;33:3091–3095. doi: 10.1128/jcm.33.12.3091-3095.1995. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Robertson P A, Woodburn M I A, Neutel W, Bealey C E. Effects of land use on breeding pheasant density. J Appl Ecol. 1993;30:465–577. [Google Scholar]
- 35.Schwartz I, Varde S, Nadelman R B, Wormser G P, Fish D. Inhibition of efficient polymerase chain reaction amplification of Borrelia burgdorferi DNA in blood-fed ticks. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1997;56:339–342. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1997.56.339. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Stafford K C, III, Bladen V C, Magnarelli L A. Ticks (Acari: Ixodidae) infesting wild birds (Aves) and white-footed mice in Lyme, CT. J Med Entomol. 1995;32:453–466. doi: 10.1093/jmedent/32.4.453. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Telford S R, III, Urioste S S, Spielman A. Clustering of host-seeking nymphal deer ticks (Ixodes dammini) infected by Lyme disease spirochetes (Borrelia burgdorferi) Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1992;47:55–60. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1992.47.55. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Van Dam A P, Kuiper H, Vos K, Widjojokusumo A, Spanjaard L, De Jongh B M, Ramselaar A C P, Kramer M D, Dankert J. Different genospecies of Borrelia burgdorferi are associated with distinct clinical manifestations in Lyme borreliosis. Clin Infect Dis. 1993;17:708–717. doi: 10.1093/clinids/17.4.708. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Wang G, Van Dam A P, Le Fleche A, Postic D, Peter O, Baranton G, de Boer R, Spanjaard L. Genetic and phenotypic analysis of Borrelia valaisiana sp. nov. (Borrelia genomic groups VS116 and M19) Int J Syst Bacteriol. 1997;47:926–932. doi: 10.1099/00207713-47-4-926. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Will G, Jauris-Heipke S, Schwab E, Busch U, Rössler D, Soutschek E, Wilske B, Preac-Mursic V. Sequence analysis of ospA genes shows homogeneity within Borrelia burgdorferi sensu stricto and Borrelia afzelii strains but reveals major subgroups within Borrelia garinii species. Med Microbiol Immunol. 1995;184:73–80. doi: 10.1007/BF00221390. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]