Abstract
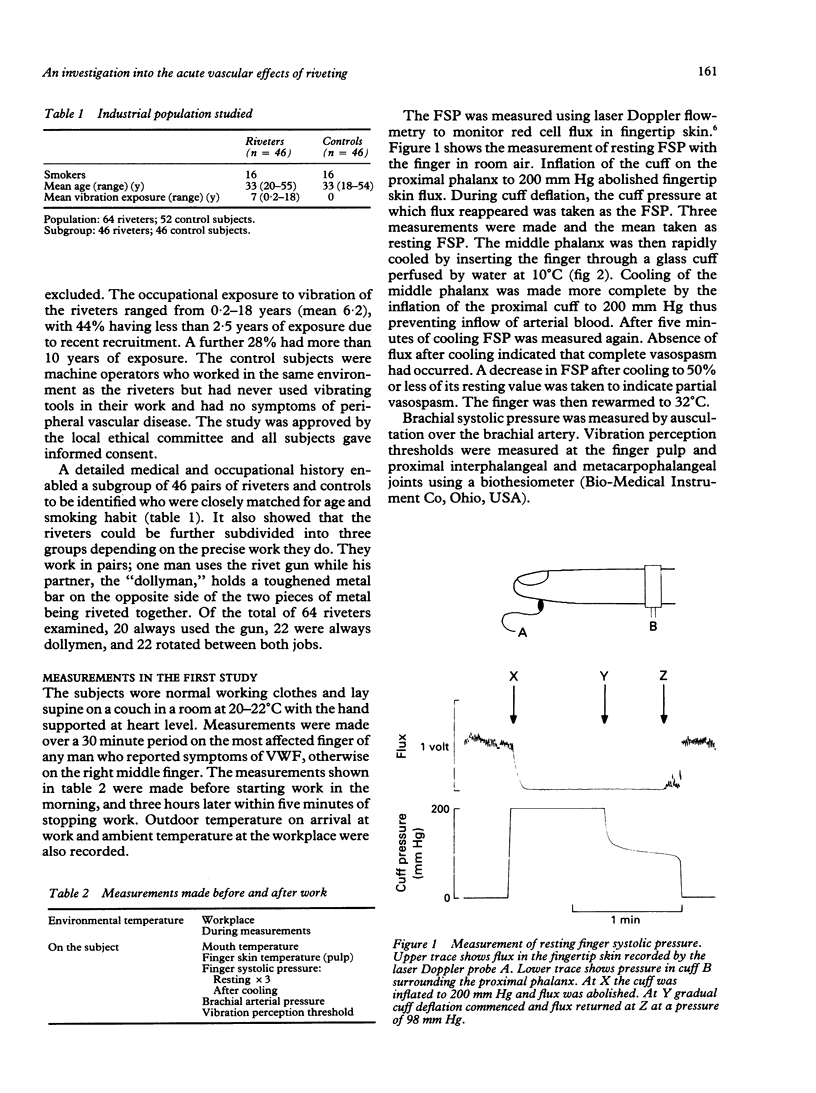
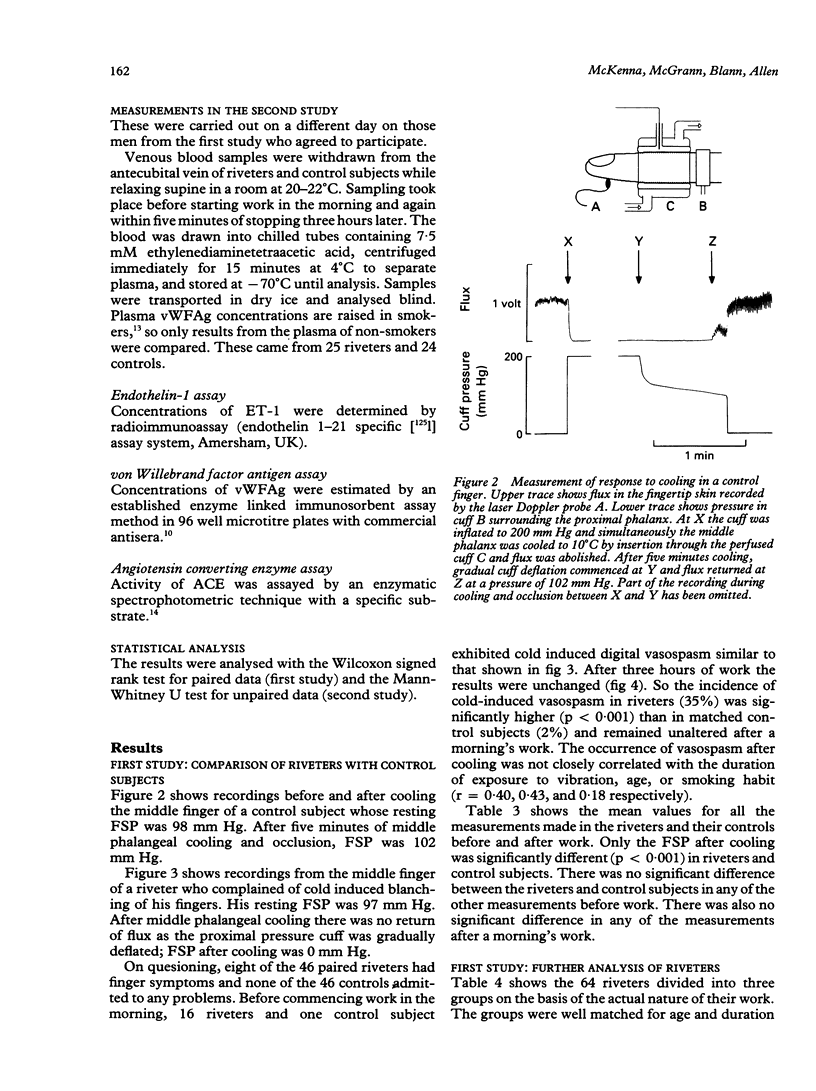
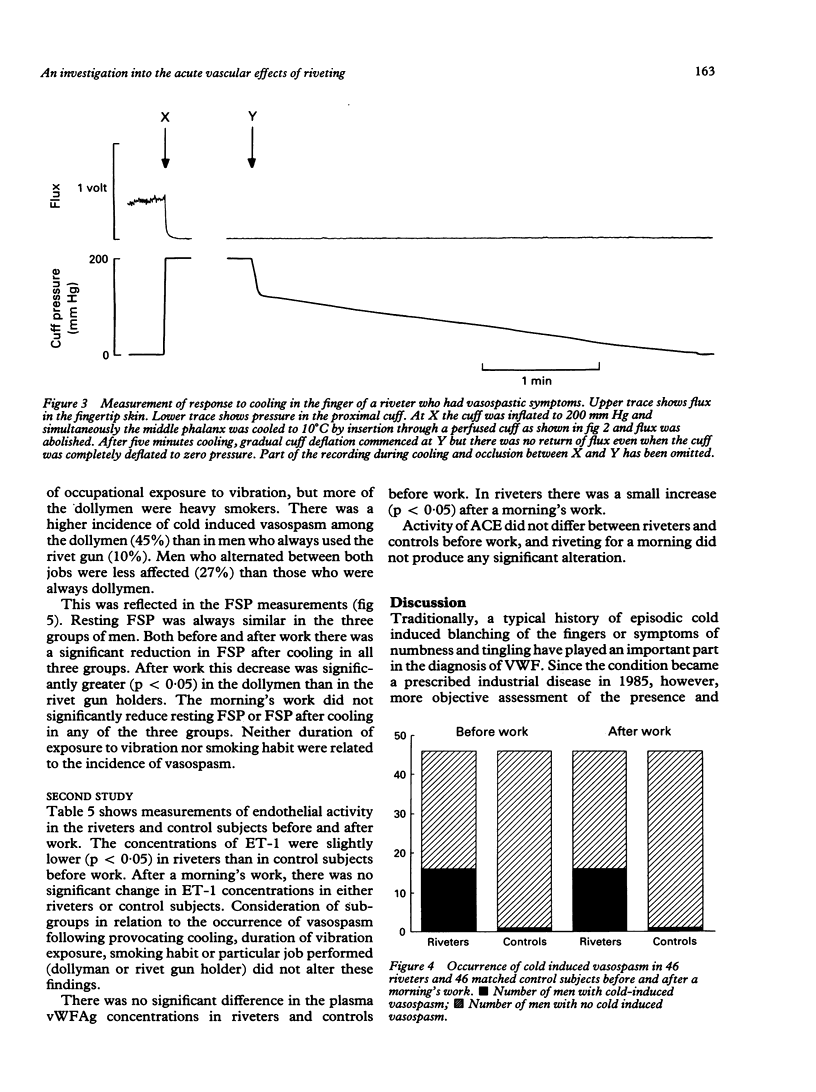
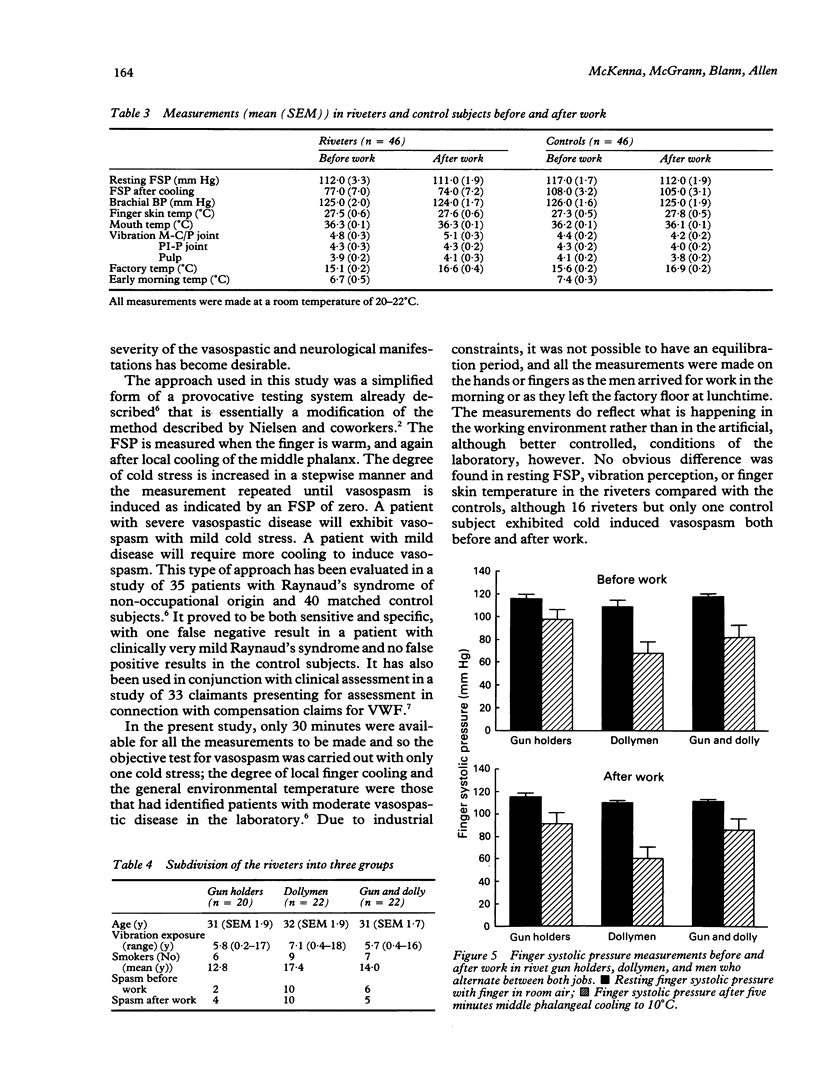
Measurements were made on 46 pairs of riveters and matched control subjects before and after a morning's work. Before starting work, the mean resting finger systolic pressure was 112 (SEM 3.3) mm Hg in the riveters, similar to 117 (1.7) in the control subjects. After cooling the middle phalanx to 10 degrees C for five minutes, 16 riveters but only one control subject exhibited digital vasospasm and these numbers were unaltered after a morning's work. A subgroup of riveters whose role was always to provide counter pressure to the rivet gun showed a higher incidence (45%) of cold induced vasospasm than did riveters who invariably held the gun (10%) or rotated between both roles (27%). Plasma levels of three markers of vascular activity, endothelin-1 (ET-1), von Willebrand factor antigen (vWFAg), and angiotensin converting enzyme (ACE), were measured in non-smoking riveters and control subjects. Before work, ET-1 concentrations were slightly lower (p < 0.05) in the riveters, but vWFAg concentration and ACE activity were similar in riveters and control subjects. Riveting for a morning did not alter ET-1 concentration or ACE activity but did induce a small increase (p < 0.05) in vWFAg concentration, which may indicate damage to the endothelium. This type of vascular assessment may be helpful in assessing vasospastic complications in workers exposed to vibration.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allen J. A., Devlin M. A., McGrann S., Doherty C. C. An objective test for the diagnosis and grading of vasospasm in patients with Raynaud's syndrome. Clin Sci (Lond) 1992 May;82(5):529–534. doi: 10.1042/cs0820529. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Allen J. A., Doherty C. C., McGrann S. Objective testing for vasospasm in the hand-arm vibration syndrome. Br J Ind Med. 1992 Oct;49(10):688–693. doi: 10.1136/oem.49.10.688. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blann A. D., Hopkins J., Winkles J., Wainwright A. C. Plasma and serum von Willebrand factor antigen concentrations in connective tissue disorders. Ann Clin Biochem. 1992 Jan;29(Pt 1):67–71. doi: 10.1177/000456329202900110. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bovenzi M., Petronio L., DiMarino F. Epidemiological survey of shipyard workers exposed to hand-arm vibration. Int Arch Occup Environ Health. 1980;46(3):251–266. doi: 10.1007/BF00380015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caldwell P. R., Seegal B. C., Hsu K. C., Das M., Soffer R. L. Angiotensin-converting enzyme: vascular endothelial localization. Science. 1976 Mar 12;191(4231):1050–1051. doi: 10.1126/science.175444. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ekenvall L., Lindblad L. E. Vibration white finger and digital systolic pressure during cooling. Br J Ind Med. 1986 Apr;43(4):280–283. doi: 10.1136/oem.43.4.280. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engström K., Dandanell R. Exposure conditions and Raynaud's phenomenon among riveters in the aircraft industry. Scand J Work Environ Health. 1986 Aug;12(4 Spec No):293–295. doi: 10.5271/sjweh.2138. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ewenstein B. M., Warhol M. J., Handin R. I., Pober J. S. Composition of the von Willebrand factor storage organelle (Weibel-Palade body) isolated from cultured human umbilical vein endothelial cells. J Cell Biol. 1987 May;104(5):1423–1433. doi: 10.1083/jcb.104.5.1423. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Futatsuka M., Ueno T., Sakurai T. Follow up study of vibration induced white finger in chain saw operators. Br J Ind Med. 1985 Apr;42(4):267–271. doi: 10.1136/oem.42.4.267. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmquist B., Bünning P., Riordan J. F. A continuous spectrophotometric assay for angiotensin converting enzyme. Anal Biochem. 1979 Jun;95(2):540–548. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(79)90769-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ikehata K., Kawauchi S., Kohno F., Nishiyama M., Ide N. Increased platelet function and von Willebrand factor in vibration syndrome. Tokushima J Exp Med. 1980 Jun;27(1-2):23–28. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Juul C., Nielsen S. L. Locally induced digital vasospasm detected by delayed rewarming in Raynaud's phenomenon of occupational origin. Br J Ind Med. 1981 Feb;38(1):87–90. doi: 10.1136/oem.38.1.87. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kahaleh M. B., Osborn I., LeRoy E. C. Increased factor VIII/von Willebrand factor antigen and von Willebrand factor activity in scleroderma and in Raynaud's phenomenon. Ann Intern Med. 1981 Apr;94(4 Pt 1):482–484. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-94-4-482. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nielsen S. L., Lassen N. A. Measurement of digital blood pressure after local cooling. J Appl Physiol Respir Environ Exerc Physiol. 1977 Nov;43(5):907–910. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1977.43.5.907. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nielsen S. L. Raynaud phenomena and finger systolic pressure during cooling. Scand J Clin Lab Invest. 1978 Dec;38(8):765–770. doi: 10.1080/00365517809104885. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olsen N. Diagnostic tests in Raynaud's phenomena in workers exposed to vibration: a comparative study. Br J Ind Med. 1988 Jun;45(6):426–430. doi: 10.1136/oem.45.6.426. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plasma endothelin-1 concentration during cold exposure. Lancet. 1991 May 4;337(8749):1104–1105. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pyykkö I., Färkkilä M., Korhonen O., Starck J., Jäntti V. Cold provocation tests in the evaluation of vibration-induced white finger. Scand J Work Environ Health. 1986 Aug;12(4 Spec No):254–258. doi: 10.5271/sjweh.2142. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pyykkö I., Starck J., Färkkilä M., Hoikkala M., Korhonen O., Nurminen M. Hand-arm vibration in the aetiology of hearing loss in lumberjacks. Br J Ind Med. 1981 Aug;38(3):281–289. doi: 10.1136/oem.38.3.281. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smits P., Hofman H., Rosmalen F., Wollersheim H., Thien T. Endothelin-1 in patients with Raynaud's phenomenon. Lancet. 1991 Jan 26;337(8735):236–236. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(91)92198-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Starck J., Färkkilä M., Aatola S., Pyykkö I., Korhonen O. Vibration syndrome and vibration in pedestal grinding. Br J Ind Med. 1983 Nov;40(4):426–433. doi: 10.1136/oem.40.4.426. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yanagisawa M., Kurihara H., Kimura S., Tomobe Y., Kobayashi M., Mitsui Y., Yazaki Y., Goto K., Masaki T. A novel potent vasoconstrictor peptide produced by vascular endothelial cells. Nature. 1988 Mar 31;332(6163):411–415. doi: 10.1038/332411a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zamora M. R., O'Brien R. F., Rutherford R. B., Weil J. V. Serum endothelin-1 concentrations and cold provocation in primary Raynaud's phenomenon. Lancet. 1990 Nov 10;336(8724):1144–1147. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(90)92766-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


